Variable-step photovoltaic MPPT (Maximum Power Point Tracking) control method based on angle of contingence
A control method and variable step size technology, which is applied in photovoltaic power generation, control/regulation systems, and electrical variable adjustment. It can solve problems such as dead zone, tracking non-convergence, and difficulty in selecting the maximum step size, achieving simple design and solution selection. difficult effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
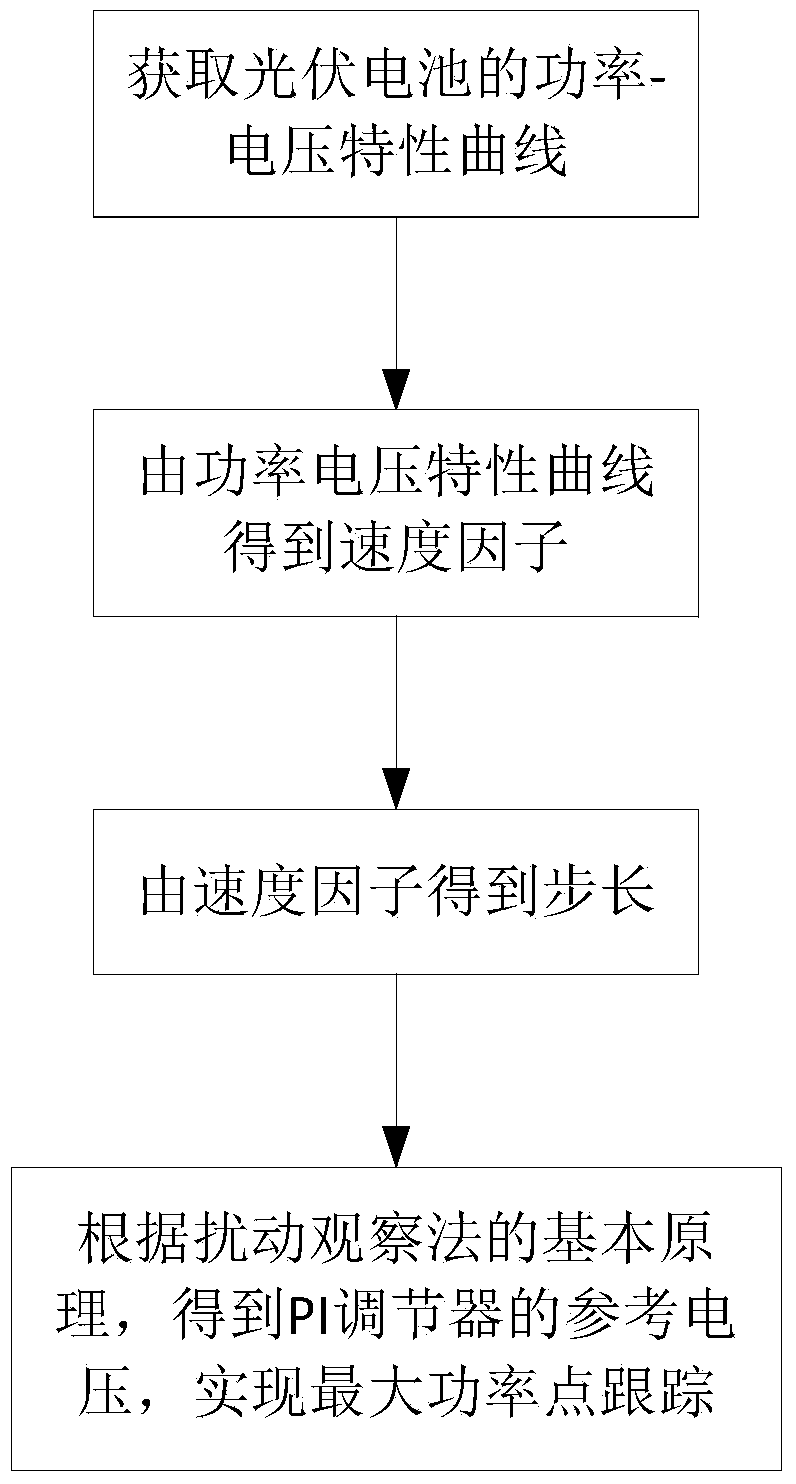
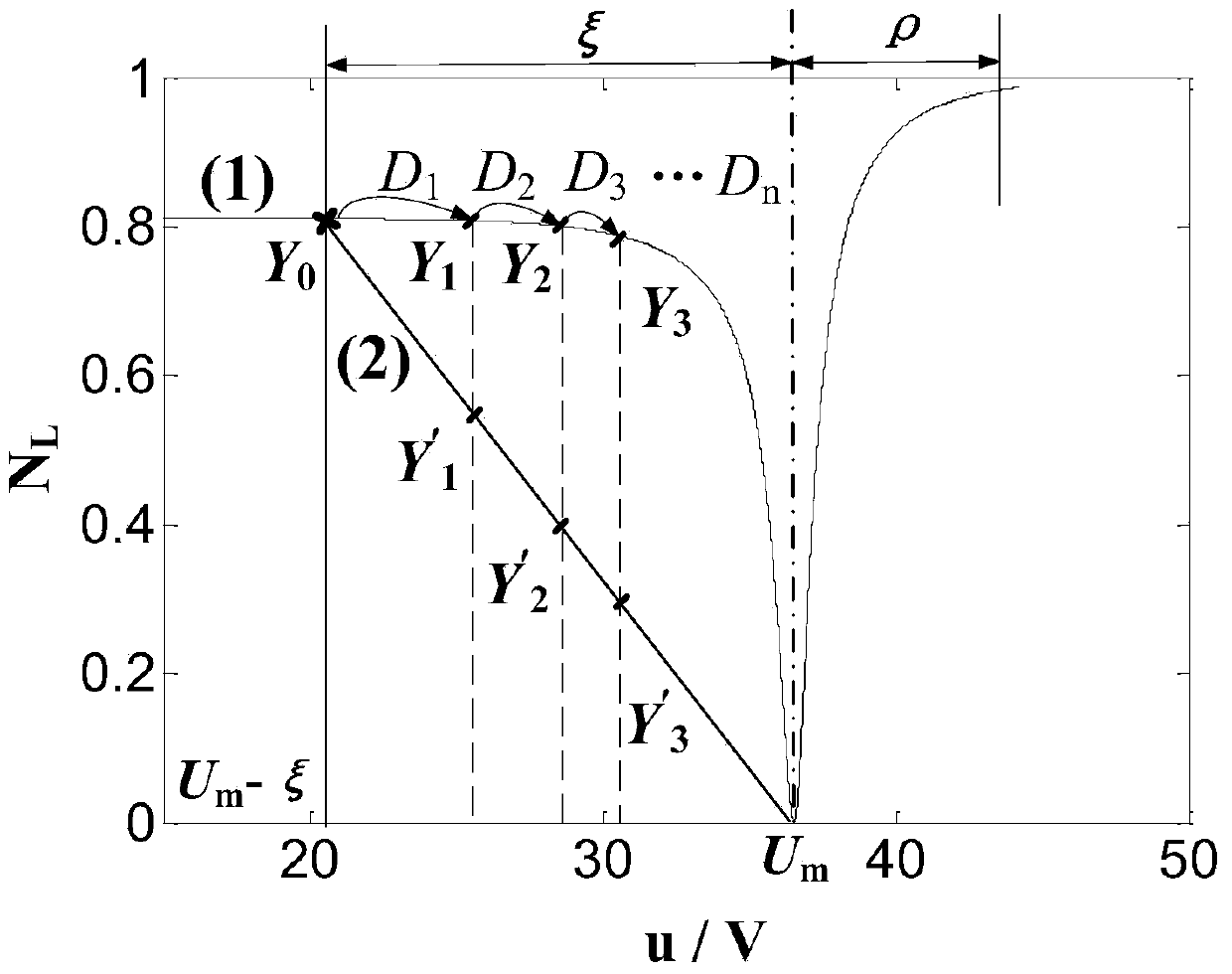
[0026] In order to make the object, technical solution and advantages of the present invention clearer, the present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments. It should be understood that the specific embodiments described here are only used to explain the present invention, not to limit the present invention. In addition, the technical features involved in the various embodiments of the present invention described below can be combined with each other as long as they do not constitute a conflict with each other.
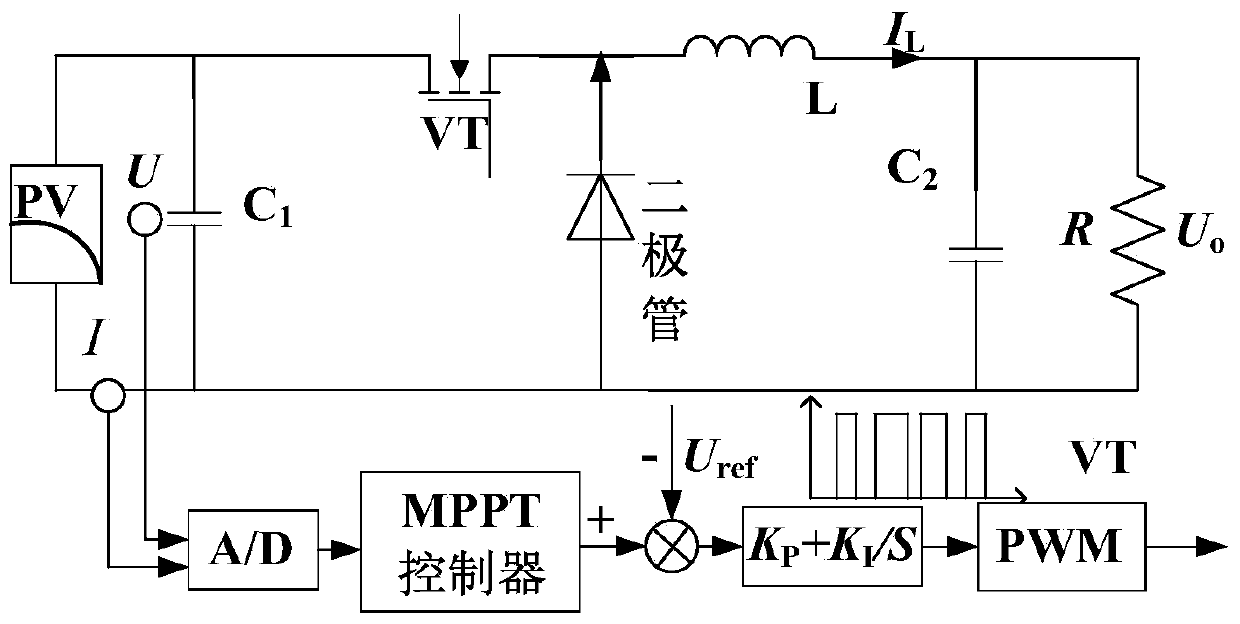
[0027] Such as figure 1 As shown, the variable step size photovoltaic maximum power point tracking system is mainly composed of photovoltaic cells, Buck circuit and control circuit. The control circuit includes A / D converter, MPPT controller, proportional integral (PI) regulator and pulse width modulator (PWM). First, the voltage and current are sampled through the sensor, and then the data is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com