Method used for catalytic gasoline deep hydrodesulfurization
A technology for catalyzing gasoline and deep hydrogenation, which is applied in hydrotreating process, petroleum industry, processing hydrocarbon oil, etc., can solve the problems of poor adaptability of raw materials and different process flow, so as to reduce the loss of octane number and achieve good technical effect. , the effect of reducing sulfur content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
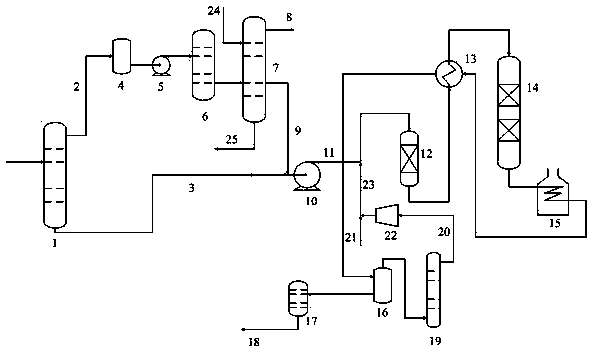
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Catalytic gasoline first goes to the pre-fractionation tower to obtain light and heavy fractions. The separation temperature of the light and heavy fractions is 122°C; the light fraction is deodorized without alkali, and then enters the hydrogenation pre-fractionation tower for separation. The split temperature of mid-gasoline is 66°C. The pre-hydrogenation reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 1.8MPa, volumetric space velocity 3.8 h -1 , Reaction temperature 178℃; Hydrodesulfurization reaction conditions: hydrogen partial pressure 1.6MPa, volumetric space velocity 2.8h -1 The reaction temperature is 285℃; the volume ratio of total hydrogen oil is 360:1. The conditions for alkali-free deodorization are: reactor operating pressure 0.6MPa, reaction temperature 35°C, feed space velocity 0.9h -1 , The air / feed volume ratio is 0.7. The properties and test results of the raw oil are listed in Table 2.
[0037] It can be seen from Table 2 that the use of this techno...
Embodiment 2
[0039] Catalytic gasoline first goes to a pre-fractionation tower to obtain light and heavy fractions. The separation temperature of the light and heavy fractions is 118°C; the light fraction is deodorized without alkali, and then enters the hydrogenation pre-fractionation tower for separation. The split temperature of mid-gasoline is 65°C. The pre-hydrogenation reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 2.0MPa, volumetric space velocity 3.5 h -1 , Reaction temperature 183℃; Hydrodesulfurization reaction conditions: hydrogen partial pressure 1.8MPa, volumetric space velocity 3.0 h -1 The reaction temperature is 288℃; the volume ratio of total hydrogen to oil is 380:1. The conditions for alkali-free deodorization are: reactor operating pressure 0.5MPa, reaction temperature 45°C, feed space velocity 0.8h -1 , The air / feed volume ratio is 0.6. The properties and test results of the raw oil are listed in Table 2.
[0040] It can be seen from Table 2 that the use of this tech...
Embodiment 3
[0042] Catalytic gasoline first goes to the pre-fractionation tower to obtain light and heavy fractions. The separation temperature of the light and heavy fractions is 121°C; the light fraction is deodorized without alkali, and then enters the hydrogenation pre-fractionation tower for separation, resulting in light gasoline and The split temperature of mid-gasoline is 70°C. The pre-hydrogenation reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 1.8MPa, volumetric space velocity 4.2 h -1 , Reaction temperature 180℃; Hydrodesulfurization reaction conditions are: hydrogen partial pressure 1.6MPa, volumetric space velocity 3.2 h -1 The reaction temperature is 279℃; the volume ratio of total hydrogen to oil is 320:1. ; The conditions for alkali-free deodorization are: reactor operating pressure 0.5MPa, reaction temperature 40°C, feed space velocity 1.1h -1 , The air / feed volume ratio is 0.6. The properties and test results of the raw oil are listed in Table 2.
[0043] It can be see...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com