Data card and multi-mode broadband antenna system
An antenna system and broadband antenna technology, applied in the field of data cards, can solve the problems of covering the full frequency band of LTE and the difficulty of data cards
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
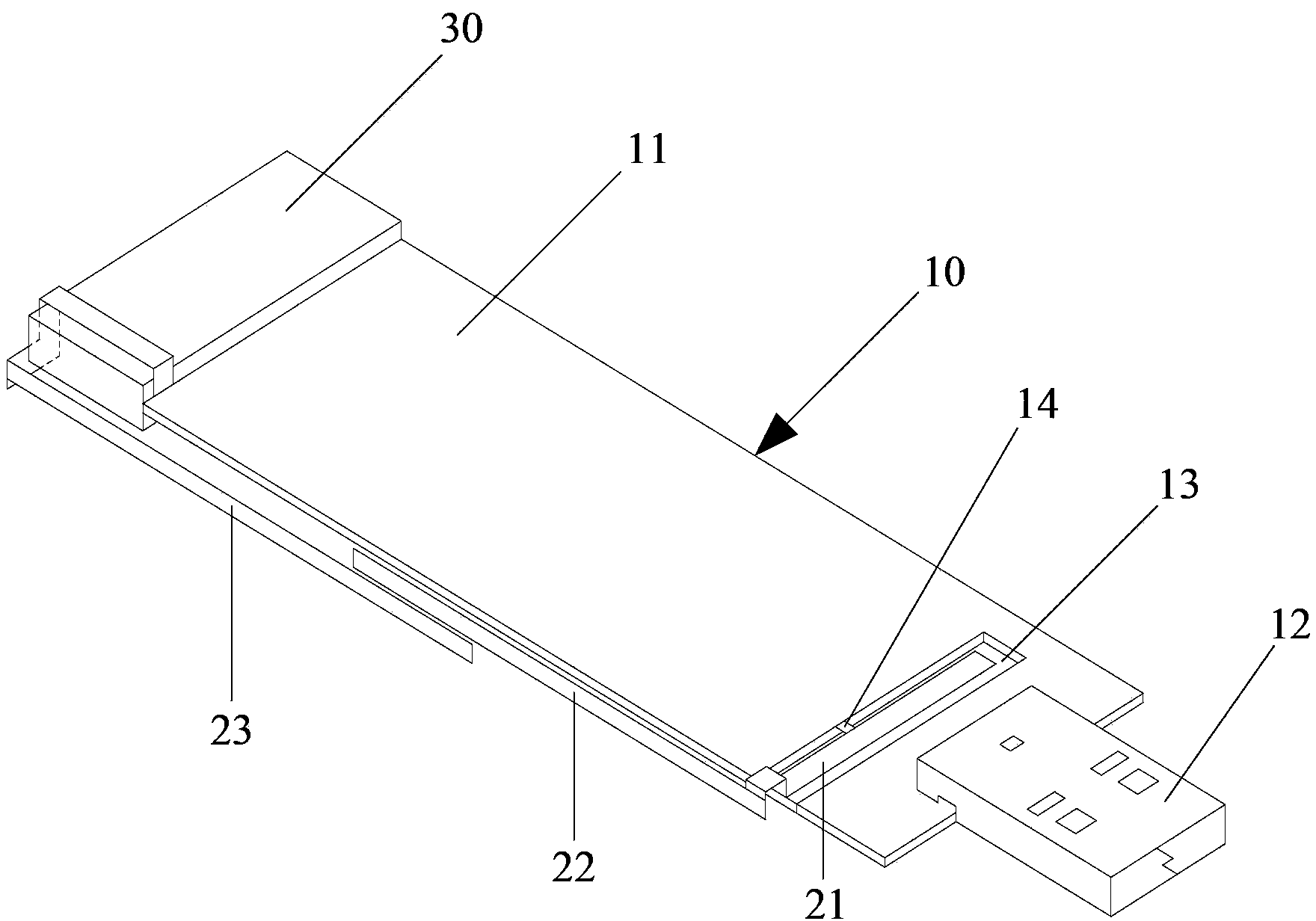
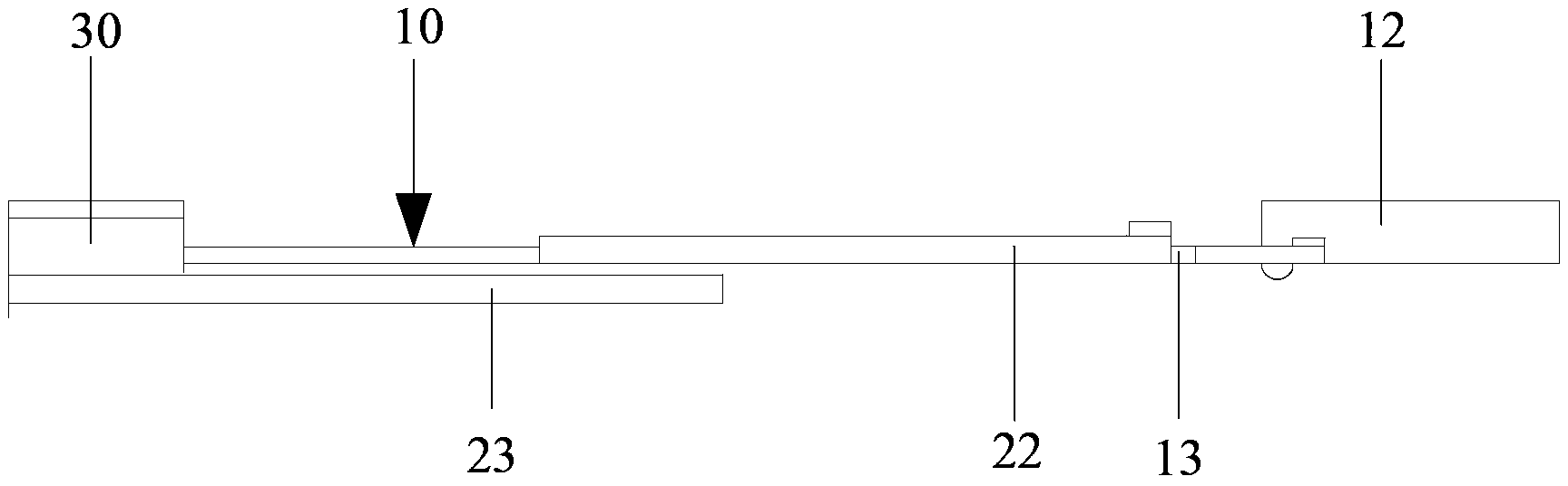
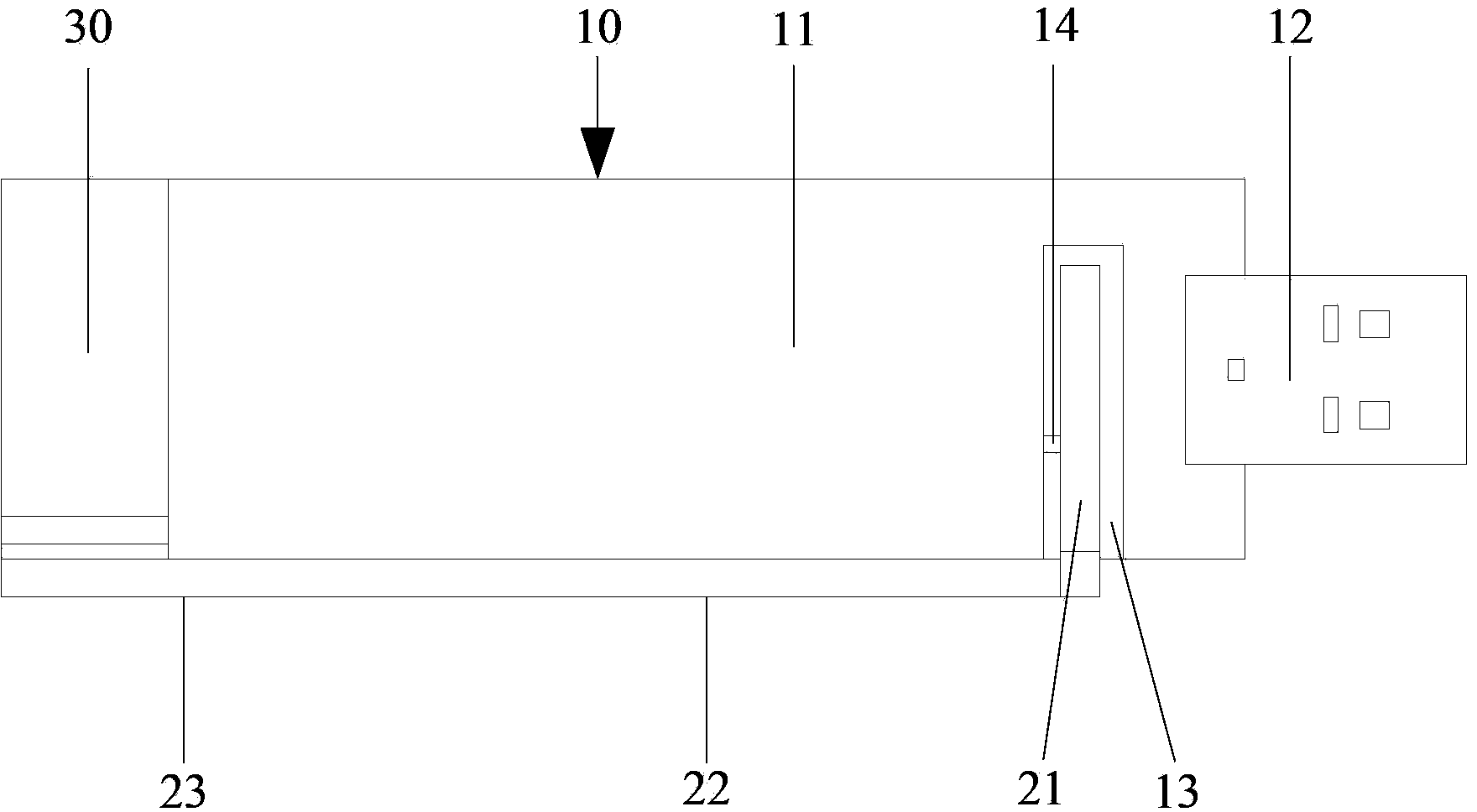
[0038] Such as figure 1 As shown, the multi-mode broadband antenna system for a data card provided by the embodiment of the present invention includes a PCB board 10 , and a first radiator 21 , a second radiator 22 and a third radiator 23 in strip shape.
[0039] One side of the PCB board 10 is covered with a metal ground 11, and the USB plug 12 of the data card is arranged on one short side of the PCB board 10; on one long side of the PCB board 10, there is a place close to the USB plug 12 for accommodating the first radiator 21 grooves 13 . In this embodiment, the first radiator 21 is strip-shaped, and the groove 13 is also strip-shaped, which is compatible with the first radiator 21 .
[0040] The first radiator 21 is located in the groove 13 and is connected to the transceiver module (not shown in the figure) of the data card through the feeder 14 . The first end of the first radiator 21 is located at the bottom of the groove 13 , and the second end of the first radiator...
Embodiment 2
[0055] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, as Figure 5 and Figure 6 As shown, the first radiator 21 is located in the groove 13 of the PCB 10 , and the first end of the second radiator 22 is electrically connected to the second end of the first radiator 21 at the edge of the PCB 10 . The second end of the second radiator 22 is coupled to the first end of the third radiator 23 in the form of a slot. After the second end of the third radiator 23 is bent, it bypasses the plastic bracket 30 in the data card and the One end of the metal ground 11 away from the USB plug 12 is electrically connected.
[0056] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: the second radiator 22 and the third radiator 23 are located on the same horizontal plane, and the second end of the second radiator 22 is connected to the third radiator 23 through a bent part. The first end of the slit forms a gap, which produces a capacitive coupling effect.
[0057] Comp...
Embodiment 3
[0059] This embodiment is basically the same as Embodiment 1, as Figure 7 , Figure 8 and Figure 9 As shown, the first radiator 21 is located in the groove 13 of the PCB 10 , and the first end of the second radiator 22 is electrically connected to the second end of the first radiator 21 at the edge of the PCB 10 . After being bent, the second end of the third radiator 23 bypasses the plastic bracket 30 in the data card and is electrically connected to the end of the metal ground 11 away from the USB plug 12 .
[0060] The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 is that: the second radiator 22 and the third radiator 23 are disposed on the long side where the groove 13 of the PCB 10 is located. The second radiator 22 is located on the front of the PCB 10, the third radiator 23 is located on the back of the PCB 10, and the second end of the second radiator 22 and the first end of the third radiator 23 are respectively on the two sides of the PCB 10. Overlapping p...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com