Screening module and screening method based on FPGA (Field Programmable Gate Array)
A screening module and screening code technology, applied in key distribution, can solve the problems of large storage pressure, large amount of data interaction, poor real-time performance, etc., and achieve the effect of alleviating storage pressure, reducing the amount of transmitted data, and reducing the amount of interactive data.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
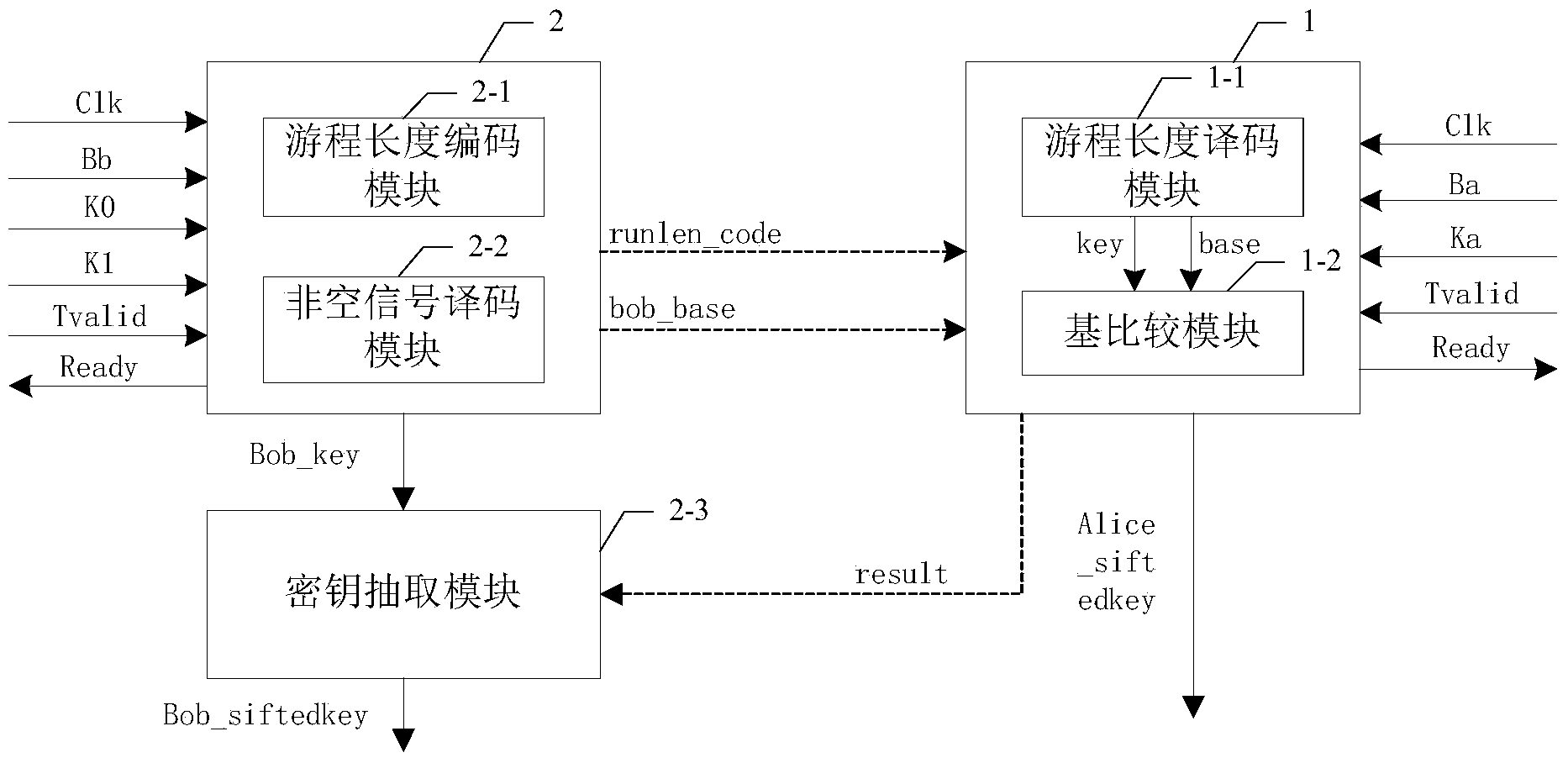
[0035] Specific implementation mode one: see figure 1 Describe this embodiment, the screening module based on FPGA described in this embodiment, it comprises Alice module 1 and Bob module 2, described Alice module 1 and Bob module 2 all adopt FPGA to realize,
[0036] Alice module 1, used to filter out the screening code from the received bare code,
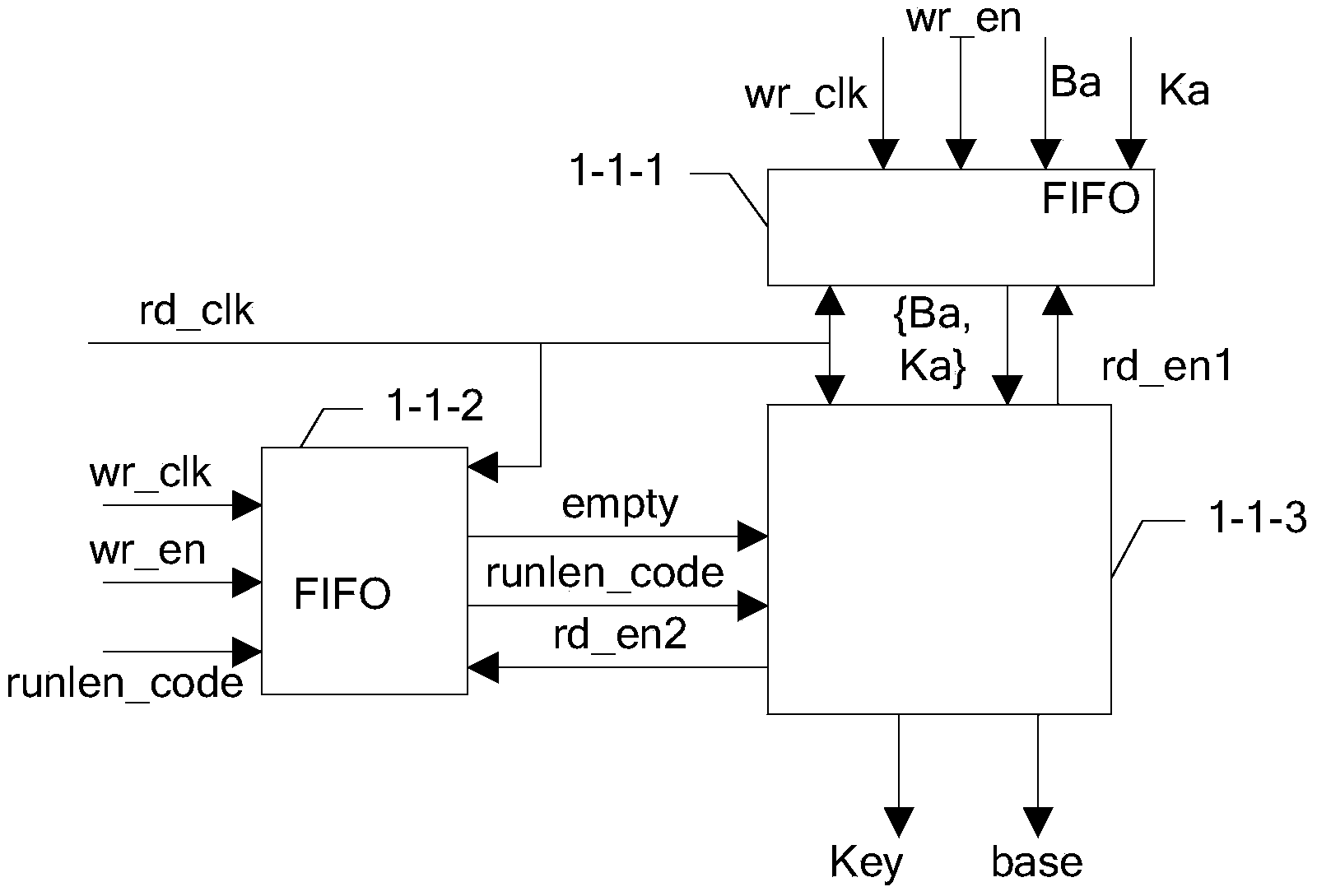
[0037] Bob module 2, is used for filtering out screening code from the naked code that receives, Alice module 1 comprises run-length decoding module 1-1 and base comparison module 1-2; Bob module 2 comprises run-length encoding module 2-1, Non-empty signal decoding module 2-2 and key extraction module 2-3,
[0038] The run-length encoding module 2-1 is used to calculate the number of occurrences of events that meet the condition "K0==0&&K1==0" between two adjacent events received, and obtain the count result run_len, the adjacent Two events refer to two adjacent events in time sequence that both satisfy the condition "K0!=0||K1...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0046] Specific embodiment two: this embodiment is a further limitation to the non-empty signal decoding module 2-2 in the FPGA-based screening module described in specific embodiment one, in this embodiment, the non-empty signal decoding module 2-2 The conversion principle used to convert the detection results corresponding to the input non-null signal positions, nempty_k0 and nempty_k1, into valid naked codes is: when the value of nempty_k0 is '0' and the value of nempty_k1 is '0', it is valid The bare code Bob_key is '1'; when the value of nempty_k0 is '1' and the value of nempty_k1 is '0', the effective bare code Bob_key is '0'; when the value of nempty_k0 is '1', the value of nempty_k1 When the value is '1', the effective bare-code Bob_key is '1' or '0'.
specific Embodiment approach 3
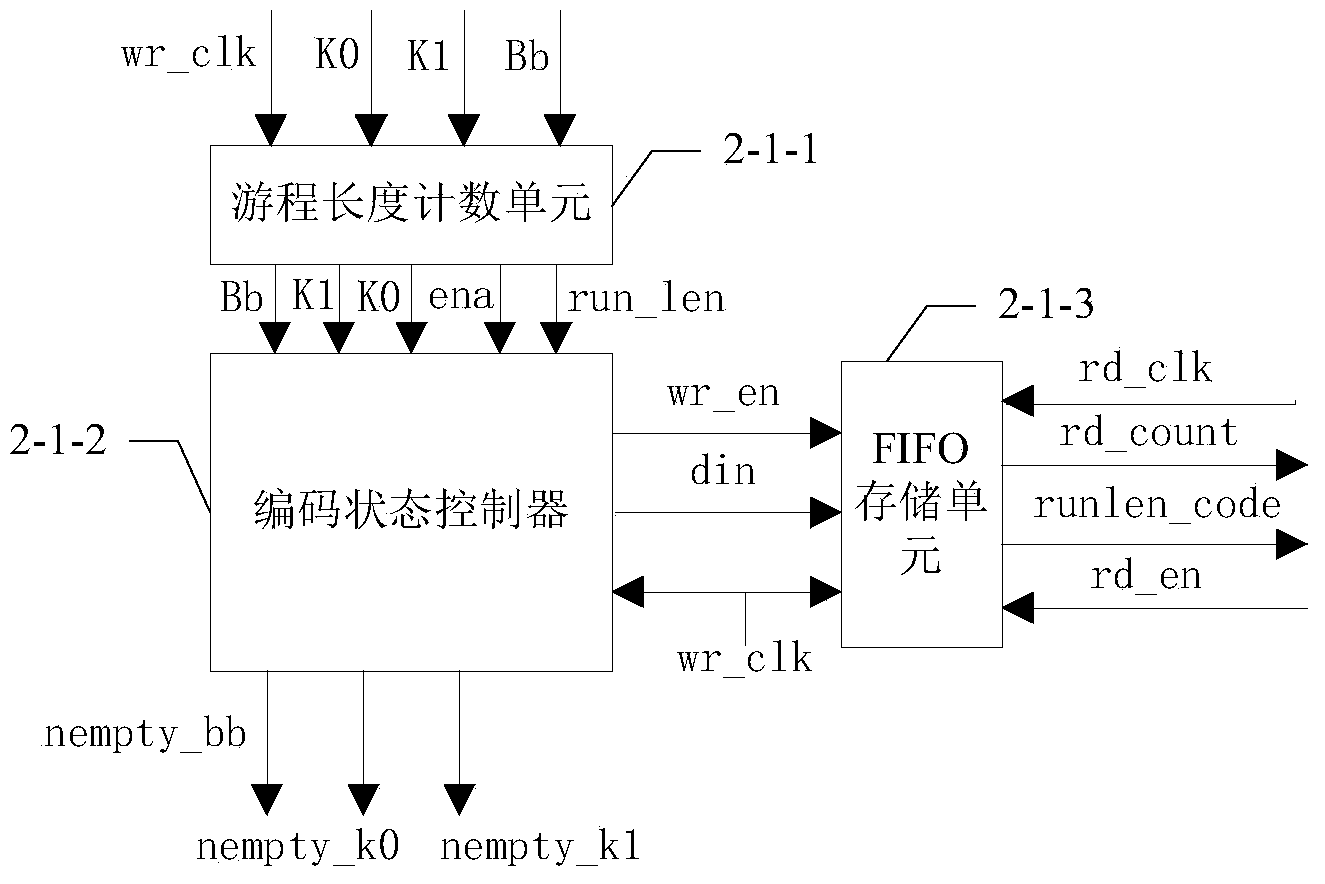
[0047] Specific implementation mode three: see figure 2 Describe this embodiment, the difference between this embodiment and the FPGA-based screening module described in the specific embodiment one or two is that the run length encoding module 2-1 includes a run length counting unit 2-1-1, an encoding state Controller 2-1-2 and FIFO storage unit 2-1-3;
[0048] The run length counting unit 2-1-1 is used to calculate the number of occurrences of events that meet the condition "K0==0&&K1==0" between two adjacent events received, obtain the counting result run_len, and count the counting result run_len Send to the encoding state controller 2-1-2;
[0049] The encoding state controller 2-1-2 is used to control the write enable signal wr_en, write the counting result run_len into the FIFO storage unit 2-1-3, and write the detection results nempty_k0, nempty_k1 and non-empty The measurement base empty_bb corresponding to the signal position is output to the non-empty signal decod...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com