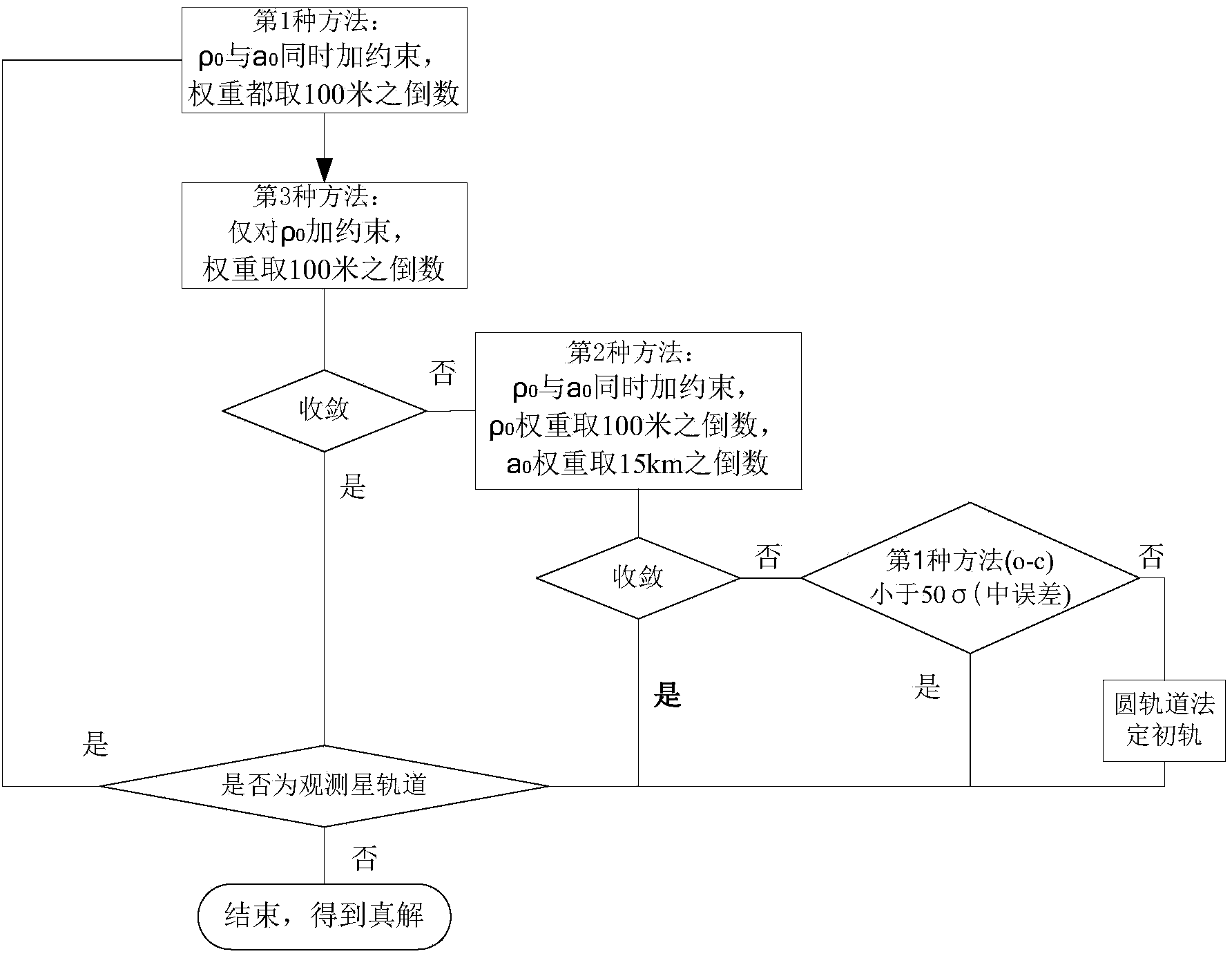
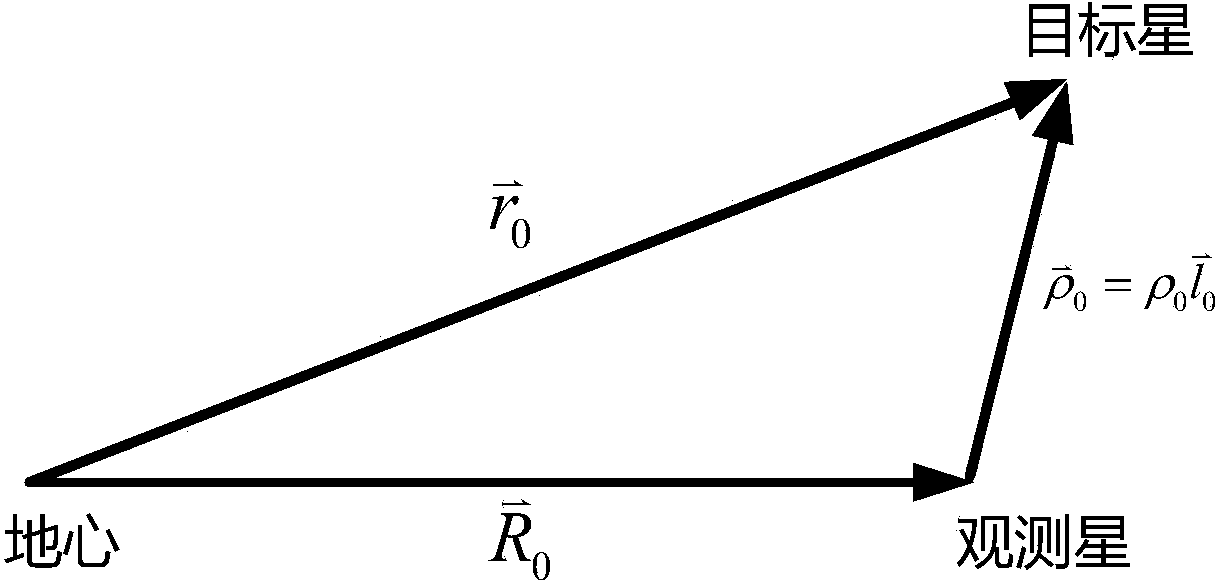Method for determining preliminary orbit of low-orbit target satellite according to space-based satellite angle measurement data
A technology for target stars and satellites, which is applied in the field of low-orbit target satellite angle measurement data to determine its initial orbit, and can solve problems that affect the accuracy of orbit determination
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0127] The orbital elements of the satellites are as follows:
[0128] a=7203.709km
[0129] i=80°
[0130] Ω=130.14°
[0131] e=0.00187
[0132] λ=M+ω=272.59°
[0133] ρ 0 =1526.9km
[0134] ρ min =635.4km
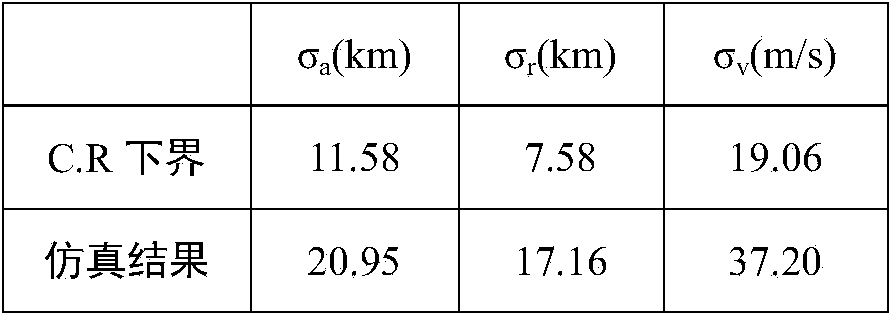
[0135] The angle measurement accuracy is 19 arc seconds, the data is 479 seconds, 240 points, one point every 2 seconds, the simulation results of the initial orbit accuracy and the relationship with the lower bound of C.R see image 3 .
Embodiment 2
[0137] The orbital elements of the target star are as follows:
[0138] a=7311.066km
[0139] i=70°
[0140] Ω=143.93°
[0141] e=0.0016
[0142] λ=M+ω=272.95°
[0143] ρ 0 =1840.2km
[0144] ρ min =1187.3km
[0145] The angle measurement accuracy is 19 arc seconds, the data is 258 seconds, 129 points, one point every 2 seconds, the simulation results of the initial orbit accuracy and the relationship with the lower bound of C.R see Figure 4 .
Embodiment 3
[0147] The orbital elements of the satellites are as follows:
[0148] a=7405.907km
[0149] i=70°
[0150] Ω=146.75°
[0151] e=0.00133
[0152] λ=M+ω=275.11°
[0153] ρ 0 =2241.6km
[0154] ρ min =1523.4km
[0155] The angle measurement accuracy is 19 arc seconds, the data is 281 seconds, 141 points, one point every 2 seconds, the simulation results of the initial orbit accuracy and the relationship with the lower bound of C.R see Figure 5 .
[0156] It can be seen from the simulation results that the solution provided by the present invention can converge the results of the calculation program near the true solution, and there is little difference from the theoretical optimal solution C.R lower bound, which fully proves the correctness and feasibility of this method.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com