Distributed stacking data storage method supporting SIMD system structure
A data storage and architecture technology, applied in climate sustainability, memory address/allocation/relocation, energy-saving computing, etc., can solve the problem of occupying scalar memory access ports for a long time, blocking scalar unit memory access, and reducing system performance, etc. problem, to achieve the effect of improving interrupt processing performance, reducing system power consumption, and improving system performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific preferred embodiments, but the protection scope of the present invention is not limited thereby.
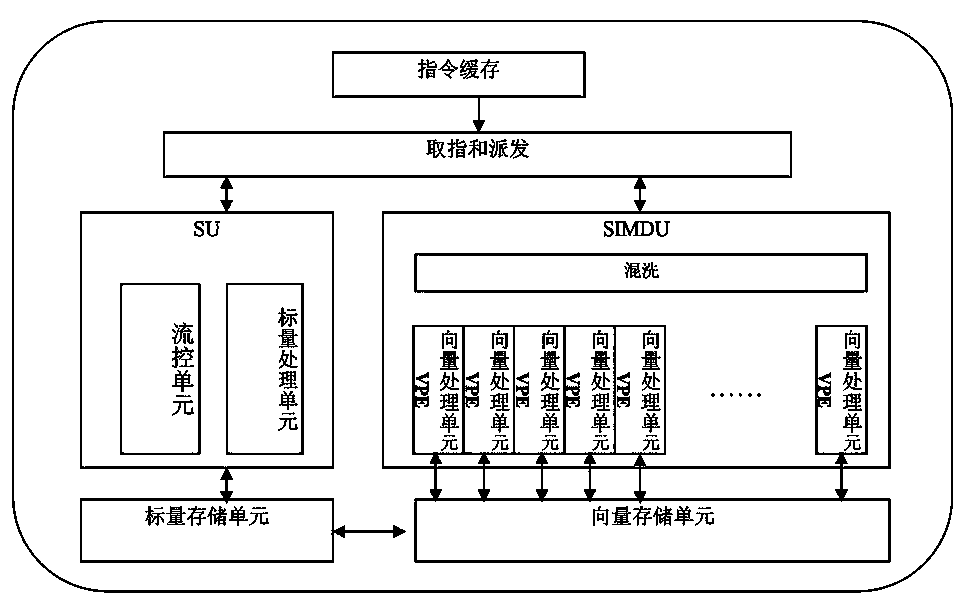
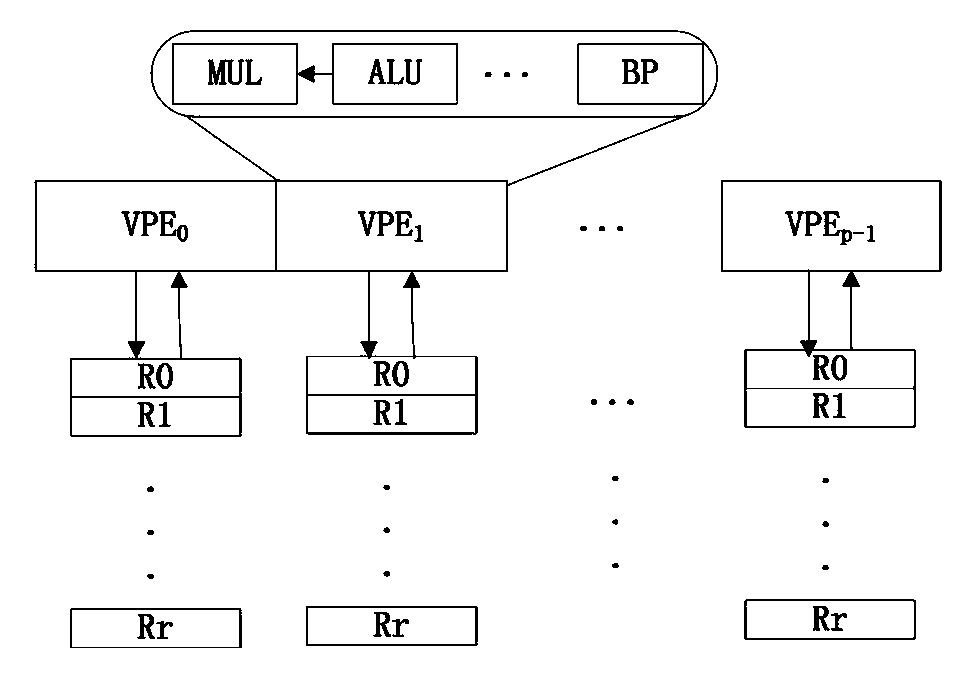
[0032] like figure 1 As shown, the SIMD microprocessor architecture in this embodiment includes a scalar unit (SU) and a SIMD unit (SIMDU), wherein the SU is mainly responsible for program flow control processing, scalar operation and exception handling of the SIMD, and the SIMD is mainly responsible for the vector Operations and support vector-based data shuffling operations, etc. SIMDU is a vector unit and contains p VPE vector processing units. SU and SIMDU share instruction fetching and dispatching components, and SU instructions and SIMDU instructions are executed in parallel during instruction fetching, dispatching, and execution. The SIMD microprocessor also includes a scalar storage unit and a vector storage unit, wherein the scalar storage unit is resp...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com