Hash ciphertext re-encryption method based on noise and decryption method after re-encryption
A re-encryption and noise technology, applied in the direction of public keys, instruments, and digital transmission systems for secure communication, can solve the problem of increased encryption and decryption overhead, and achieve the effect of small encryption and decryption overhead, enhanced encryption strength, and fast decryption.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
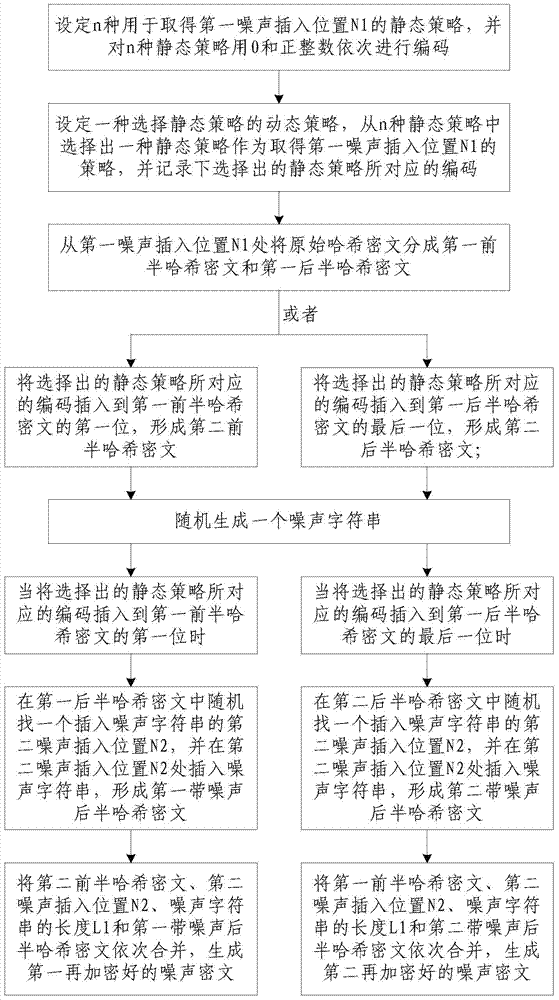
[0033] Such as figure 1 As shown, the noise-based hash ciphertext re-encryption method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0034] Step 1. Set n kinds of static strategies for obtaining the first noise insertion position N1, and encode the n kinds of static strategies with 0 and positive integers sequentially; wherein, n is a natural number and 2≤n≤10; N1 is a natural number and N1<L3, L3 is the length of the original hash ciphertext and is a natural number;
[0035] In this embodiment, the original hash ciphertext is: af1460a7f2732e78165c5bcfce66769c, the length L3 of the original hash ciphertext is 32, the user password string corresponding to the original hash ciphertext is: myNewPassword, the user The length of the password string is 13;
[0036] In this embodiment, the value of n in step 1 is 3, and the three static strategies for obtaining the first noise insertion position N1 are: Type 1: the first noise insertion position N1 is the original hash ...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Such as figure 1As shown, the noise-based hash ciphertext re-encryption method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0069] Step 1. Set n kinds of static strategies for obtaining the first noise insertion position N1, and encode the n kinds of static strategies with 0 and positive integers sequentially; wherein, n is a natural number and 2≤n≤10; N1 is a natural number and N1<L3, L3 is the length of the original hash ciphertext and is a natural number;
[0070] In this embodiment, the original hash ciphertext is: 26fa61d8e9a212eb79b87fa22983d18d, the length L3 of the original hash ciphertext is 32, and the user password string corresponding to the original hash ciphertext is: MYnEwPassword, the user The length of the password string is 13;
[0071] In this embodiment, the value of n in step 1 is 3, and the three static strategies for obtaining the first noise insertion position N1 are: Type 1: the first noise insertion position N1 is the original ha...
Embodiment 3
[0103] Such as figure 1 As shown, the noise-based hash ciphertext re-encryption method of the present invention comprises the following steps:
[0104] Step 1. Set n kinds of static strategies for obtaining the first noise insertion position N1, and encode the n kinds of static strategies with 0 and positive integers sequentially; wherein, n is a natural number and 2≤n≤10; N1 is a natural number and N1<L3, L3 is the length of the original hash ciphertext and is a natural number;
[0105] In this embodiment, the original hash ciphertext is: 13DD9A82F226513CA7A50DCDCAB36BD2, the length L3 of the original hash ciphertext is 32, the user password string corresponding to the original hash ciphertext is: MYNewPassword, the user The length of the password string is 13;
[0106] In this embodiment, the value of n in step 1 is 3, and the three static strategies for obtaining the first noise insertion position N1 are: Type 1: the first noise insertion position N1 is the original hash ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com