A kind of bacillus megaterium and its application
A technology of Bacillus megaterium and plant growth-promoting bacteria, applied to Bacillus megaterium and its application field, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory effect, the ability of the strain to produce indole acetic acid or the ability of dephosphorizing the growth-promoting bacteria, etc., and achieve good results. The effect of promoting growth, improving the cultivation environment of red soil, and improving the utilization rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0041] 1. Medium preparation, including the following four types of medium:
[0042] LB medium: peptone 10g, yeast extract 5g, sodium chloride 10g, agar 20g, distilled water 1000ml, pH7.0-7.2, sterilized at 121°C for 20min.
[0043] LB liquid medium: without agar, other conditions are the same as above.
[0044] Inorganic phosphorus bacteria medium (PKO medium): 5g tricalcium phosphate, 10g glucose, 0.5g ammonium sulfate, 0.3g sodium chloride, 0.3g magnesium sulfate heptahydrate, 0.3g potassium chloride, 0.03g manganese sulfate, heptahydrate Ferrous sulfate 0.03g, pH7.0 agar 20g, distilled water 1000ml, pH7.0~7.2. Sterilize at 121°C for 20min.
[0045] Inorganic salt medium: ammonium sulfate 2.0g; sodium dihydrogen phosphate 0.5g; dipotassium hydrogen phosphate 0.5g; magnesium sulfate heptahydrate 0.2g; calcium chloride dihydrate 0.1g, distilled water 1000mL, pH7.0, sterilized at 121℃ , 20min.
[0046] 2. Isolation of growth-promoting bacteria
[0047] Weigh 10g of the red...
Embodiment 2
[0055] Aerobic test
[0056] Pour the sterilized LB culture medium into 3 sterilized test tubes, at about 2 / 3, on the aseptic operating table, use an inoculation needle to pick up the bacteria cultured on the slant, puncture and inoculate into the above culture base (must pierce to the bottom of the tube). Cultivate at 30°C, and observe the results in 3 days to 7 days respectively. Those that grow on the surface of the agar column are aerobic bacteria, and those that grow along the puncture line are anaerobic or facultative anaerobic bacteria. The test results show that ZH5 (CGMCCNo.8802) colonies grow along the surface of the agar column, and no colonies grow in the puncture line, which is strictly aerobic.
[0057] Determination of catalase
[0058] Drop 1 drop of 3% H2O2 on a clean glass slide, take 1 ring of 18-24h LB slant culture, and smear it in H2O2. If there are bubbles, it is positive, otherwise it is negative. The test results showed that ZH5 (CGMCCNo.8802) was ...
Embodiment 3
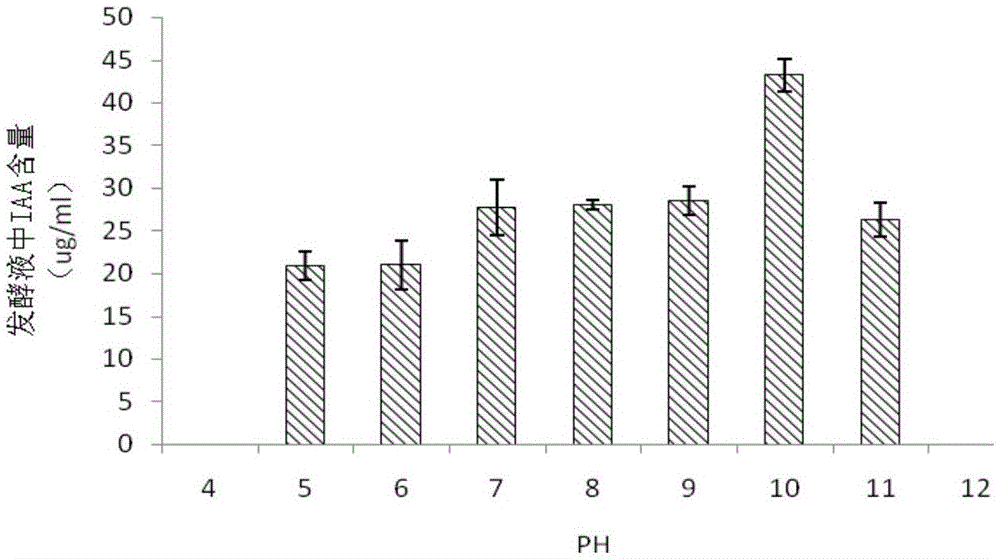
[0076] In order to further verify the ability and optimal conditions of the plant growth-promoting bacterium ZH5 obtained in Example 1 to produce indoleacetic acid, the following explores the influence of different liquid volumes, pH, different carbon sources, and different nitrogen sources on the production of indoleacetic acid.
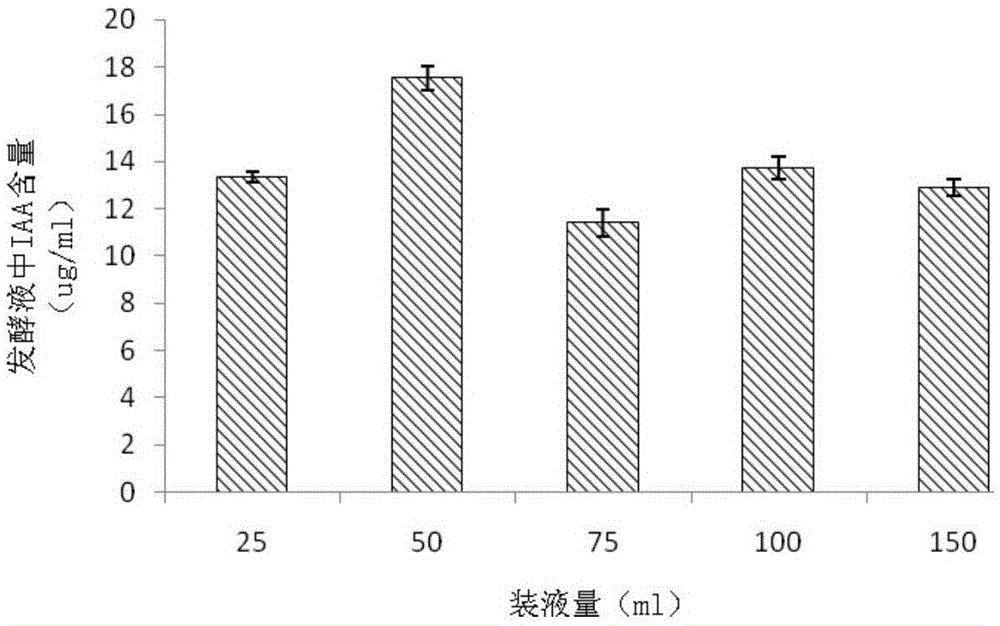
[0077] Put the LB liquid medium containing L-tryptophan (100mg / L) in 25ml, 50ml, 75ml, 100ml, 150ml in a 250mL Erlenmeyer flask, and inoculate it in the logarithmic growth phase by 1% (v / v) inoculum After the ZH5, put it at 30°C, 180r·min -1 Cultivate on a shaking table for 24 hours, and measure the amount of IAA produced by a quantitative method. The result is as figure 2As shown, because the strain ZH5 (CGMCCNo.8802) is a good metabolism, the aeration rate affects the efficiency of the strain producing IAA. When the liquid volume is 50mL, the strain produces the most IAA, and then as the liquid volume increases, the yield decreases.
[0078] Ad...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com