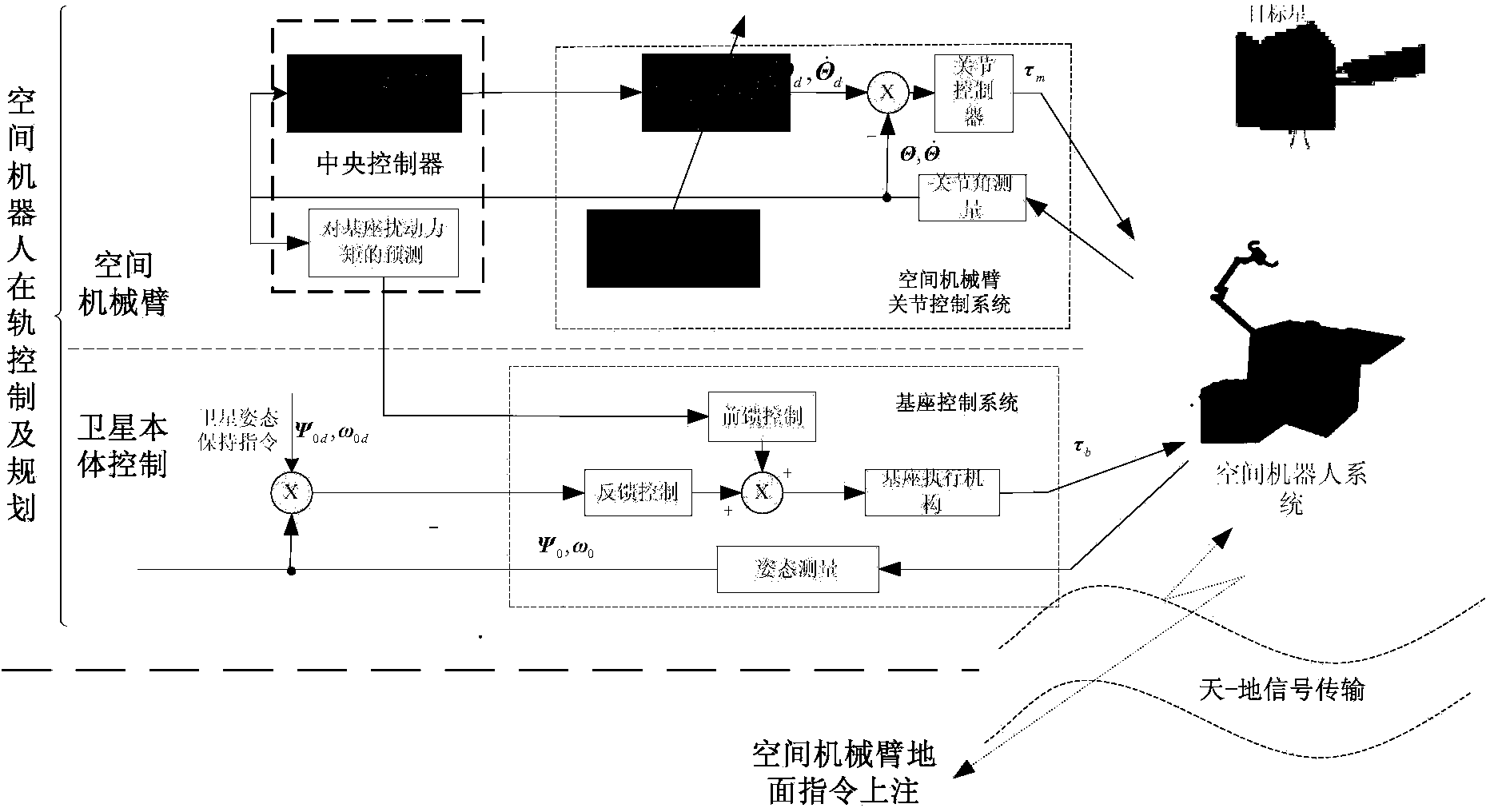
Accelerated speed optimal space robot online track planning method based on control period self-adaptive clock synchronization
A space robot and trajectory planning technology, applied in attitude control and other directions, can solve the problems of unstable robot and drastic changes in acceleration, achieve the effect of small calculation amount, reduce flexible jitter, and improve tracking accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
[0024] Specific implementation mode 1: An online trajectory planning method for an acceleration-optimized space robot based on control cycle adaptive clock synchronization in this implementation mode includes the following steps:
[0025] Step 1. Establish a mathematical model of the space robot joint trajectory curve position, velocity and acceleration with optimal acceleration within a trajectory segment planning period, and obtain the joint trajectory equation;
[0026] Step 2. According to the continuity condition of the joint trajectory interpolation, obtain the parameters in the joint trajectory equation in the step 1, and carry out the continuous planning of the joint space trajectory;
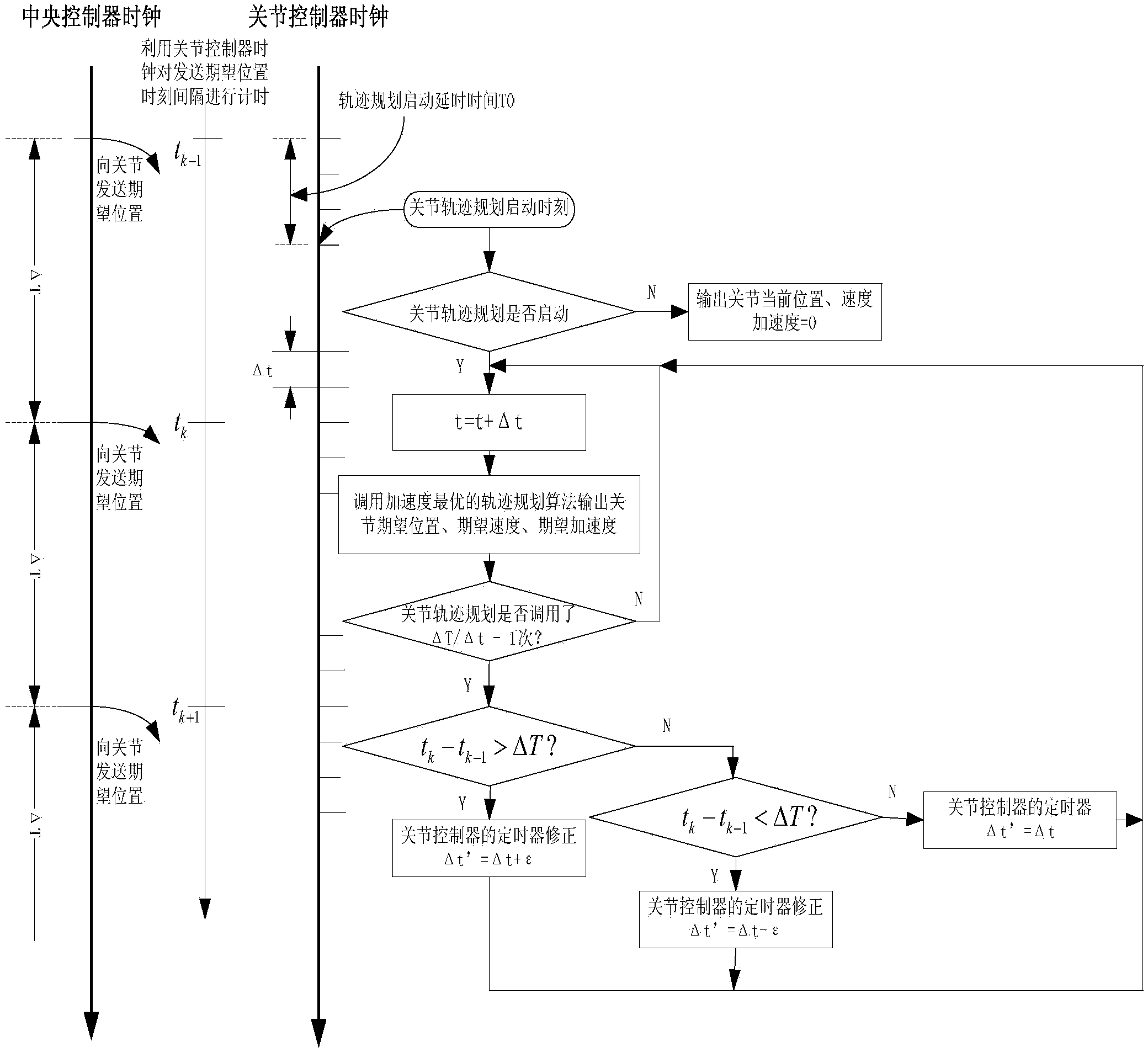
[0027] Step 3: Perform synchronous control on the basis of continuous planning of the joint space trajectory, that is, complete an online trajectory planning method for an acceleration-optimized space robot based on control period adaptive clock synchronization.
[0028] The effect of t...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0034] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: said step one establishes the mathematical model of the robot trajectory curve position, velocity and acceleration with optimal acceleration in a trajectory segment planning period, specifically:
[0035] In a joint trajectory planning cycle t p In , if the acceleration is optimal, the acceleration is selected as a constant value, the velocity trajectory is a linear function of time, and the highest degree of position trajectory is a quadratic function of time, namely:
[0036] y(t)=a 0 +a 1 t+a 2 t 2 (1)
[0037] v ( t ) = y · ( t ) = a 1 + 2 a 2 t - - - ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0041] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: said step two is based on the continuity condition of joint trajectory interpolation, and obtains the parameters in the joint trajectory equation in step one:
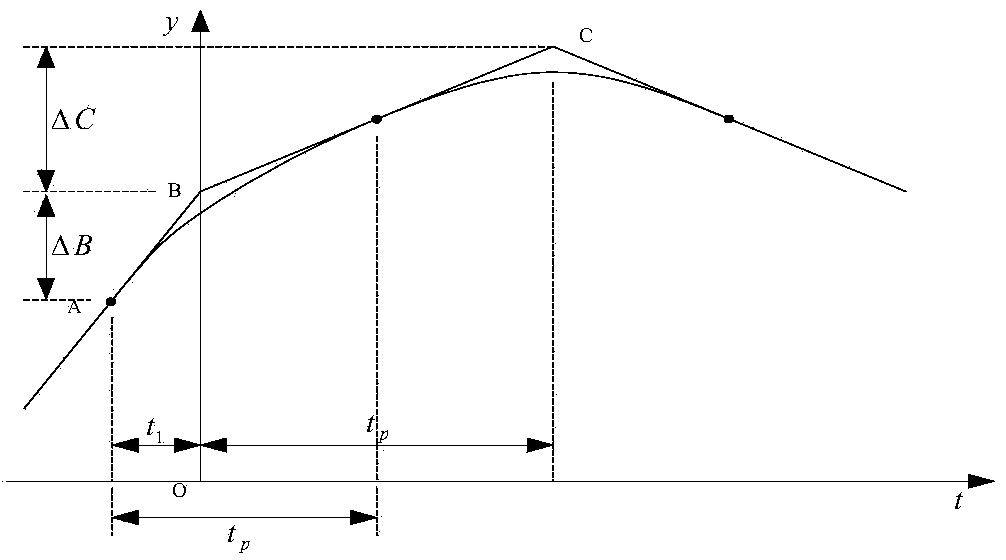
[0042]Assume that at the current moment, the trajectory just passes through point A and moves to point B, which happens to be the beginning of the transition trajectory segment from point B to point C, where point A is the initial position of the joint at the initial moment of joint trajectory planning, B and C is the expected position point at the adjacent moment of the joint, defined, △B=A-B, △C=C-B, then it can be obtained from the continuity of the position and velocity trajectory:
[0043] y ( - t 1 ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com