Method for measuring thermal conductivity
A technology of thermal conductivity and thermal pulse, which is applied in the field of measuring the thermal conductivity of materials, can solve the problems of long measurement time and achieve the effect of low effort
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The following description is merely exemplary in nature and is not intended to limit the present invention, application, or use. It should be understood that throughout the drawings, corresponding reference numbers indicate similar or corresponding components and features.
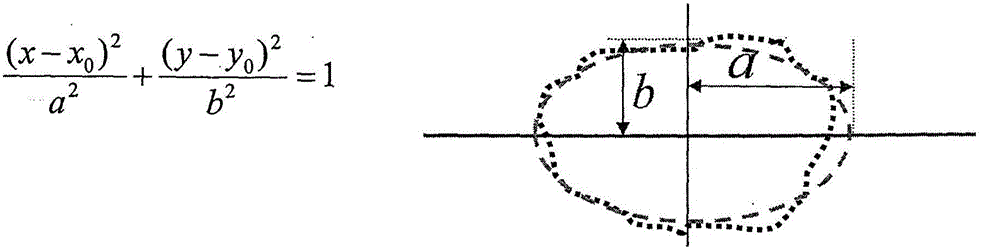
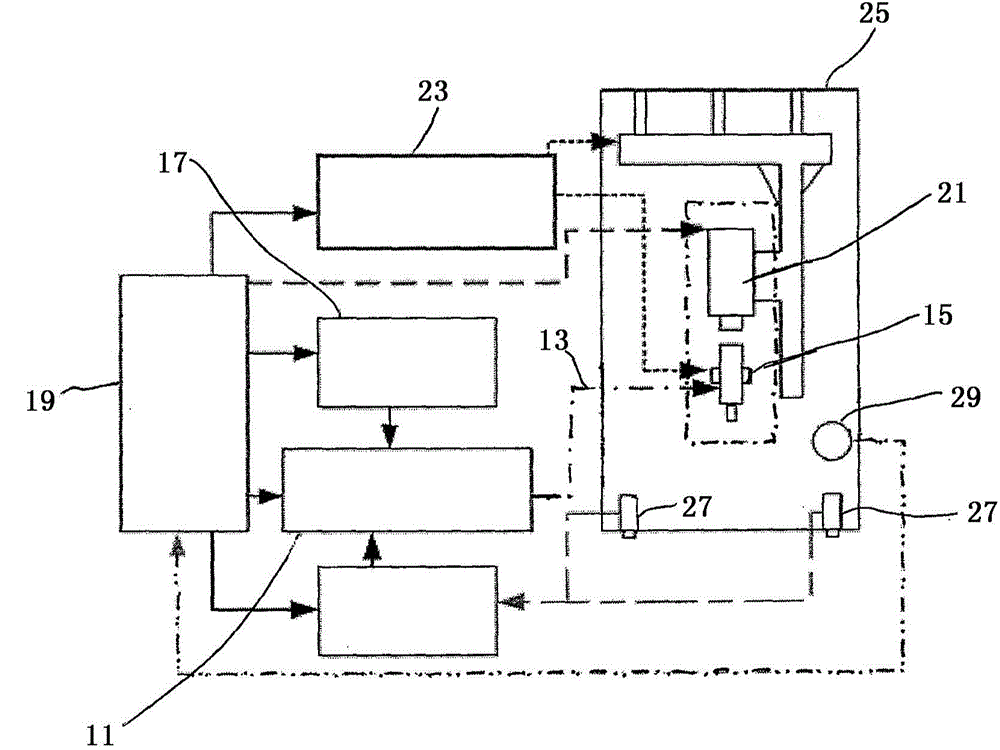
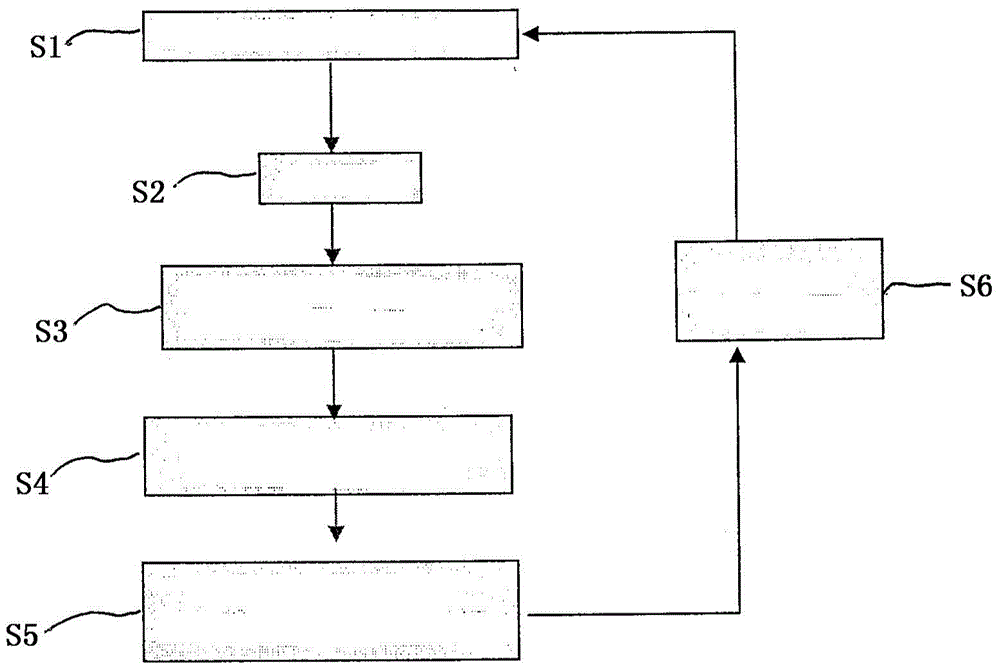
[0033] In order to measure the thermal conductivity of an isotropic or anisotropic medium or material, a heat source, especially a laser, is used to apply a heat pulse to the flat front side of the material to generate a temporarily preferred spot or hot spot on the material. The front side is the side of the material on which the heat pulse is applied, especially the side facing the heat source. Generally, each side of the material is qualified as a front side. The inventors of the present invention have found that it is assumed that a semi-infinite medium or material has an insulating surface that is temporarily heated at a point-like position and that the material (especially an orthotropic materia...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com