Vehicle control based on perception uncertainty
A technology of uncertainty and vehicles, applied in the field of manipulating vehicles and manipulating vehicles, can solve the problems that laser sensors do not directly measure speed, radar sensors do not measure object shape, camera sensors do not directly measure distance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
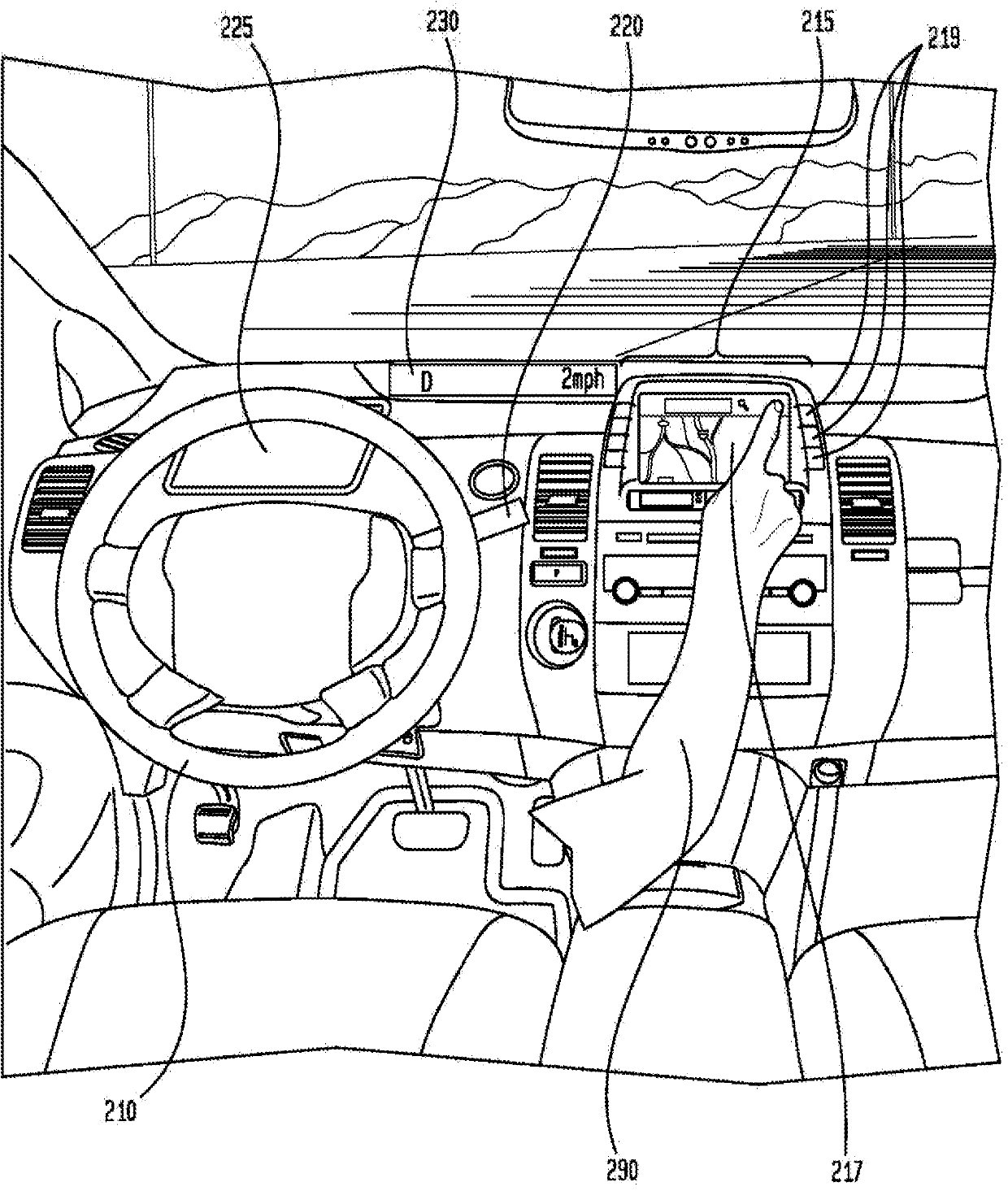
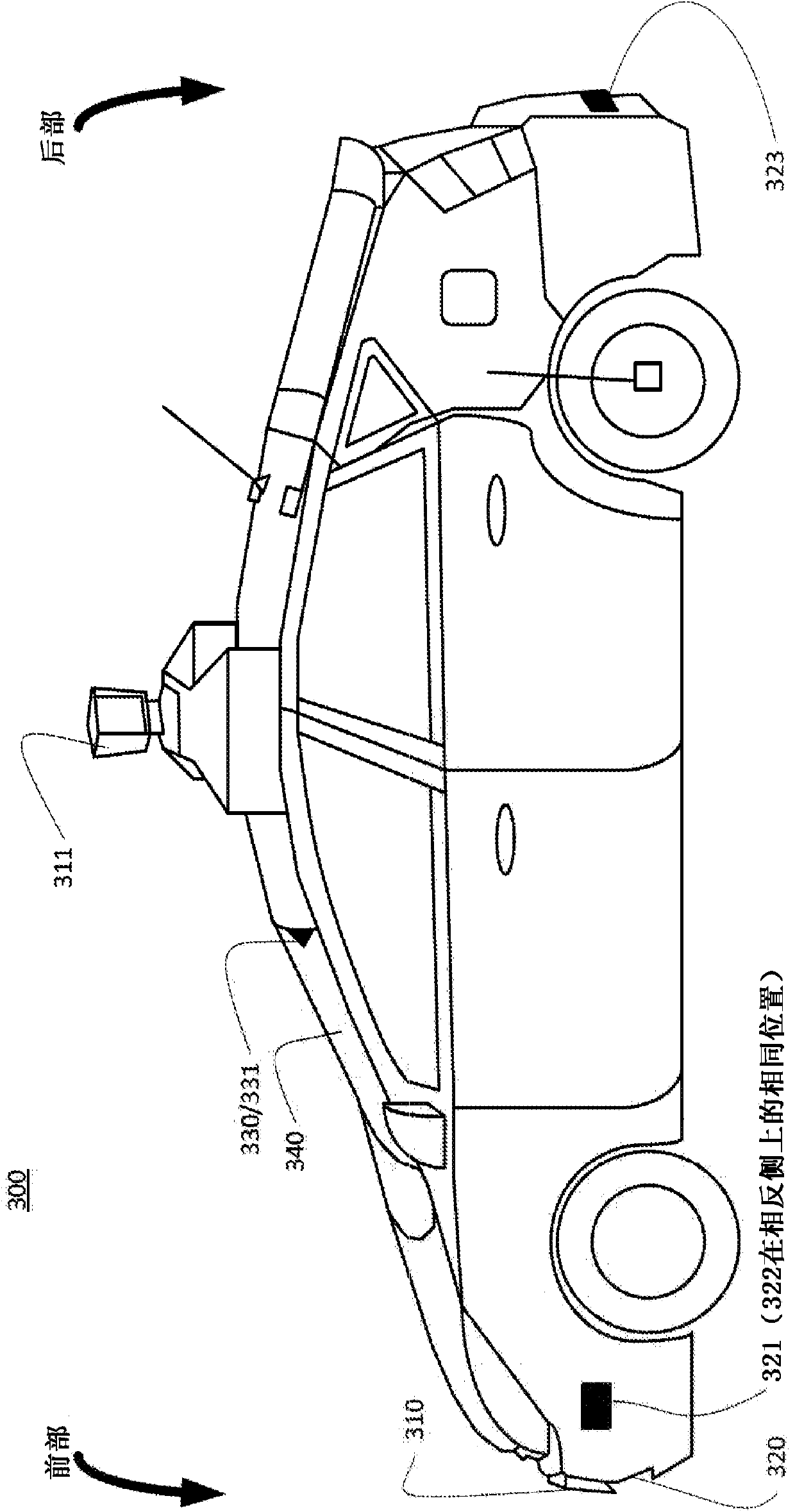
[0028]In one aspect of the present disclosure, a vehicle driving along a roadway may detect objects in the environment surrounding the vehicle. Objects can be detected using sensors with some degree of uncertainty. The type of the object can be identified based on the object type model. Object type models can be associated with object type model uncertainties. Based on the identified object type, a motion model can be identified that predicts the future location of the object. Motion models can also be associated with motion model uncertainties. Uncertainty driving strategies may be identified based on motion model uncertainties, object type model uncertainties, and / or sensor uncertainties. Then, the vehicle can be steered using an uncertain driving strategy.
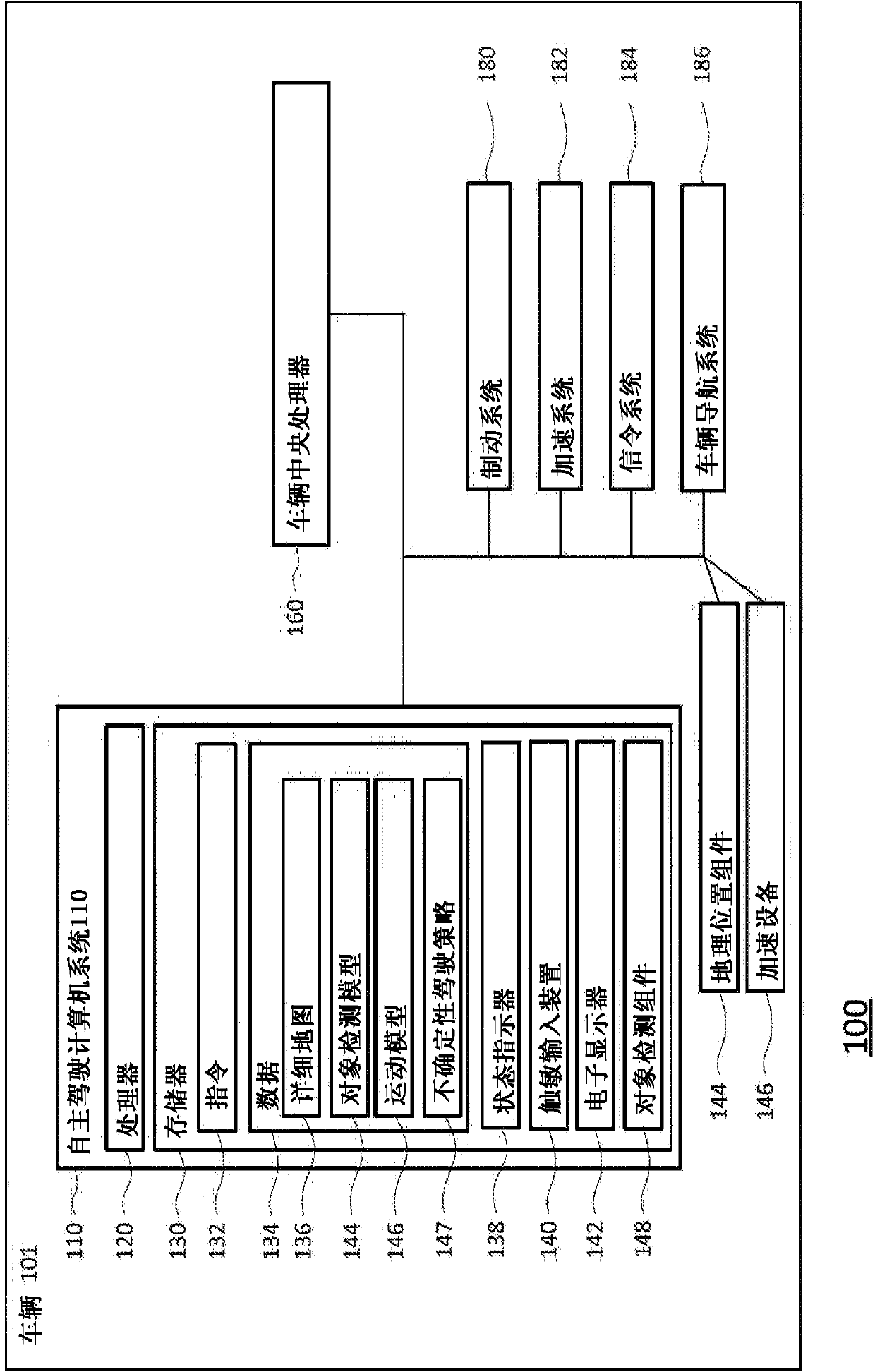
[0029] like figure 1 As shown in , an autonomous driving system 100 according to an aspect of the present disclosure includes a vehicle 101 having various components. Although certain aspects of the present disclo...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com