Method for determining the concentration of an element in a material
An element and content technology, applied in the direction of material analysis using radiation, analyzing materials, and material analysis using wave/particle radiation, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory results and low mercury content
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 approach
[0038] An advantage over the first embodiment is that the detector need not be energy dispersive and a multi-channel analyzer is not necessary.
[0039] The operation is as follows:
[0040] First, apply the well-known general formula:
[0041] I=I 0 *e -μ*ρ*d (1)
[0042] in
[0043] I 0 = incident energy
[0044] I = measured energy
[0045] μ = absorption coefficient
[0046] so
[0047]
[0048] as well as
[0049]
[0050] And, for measurements using a Cs source,
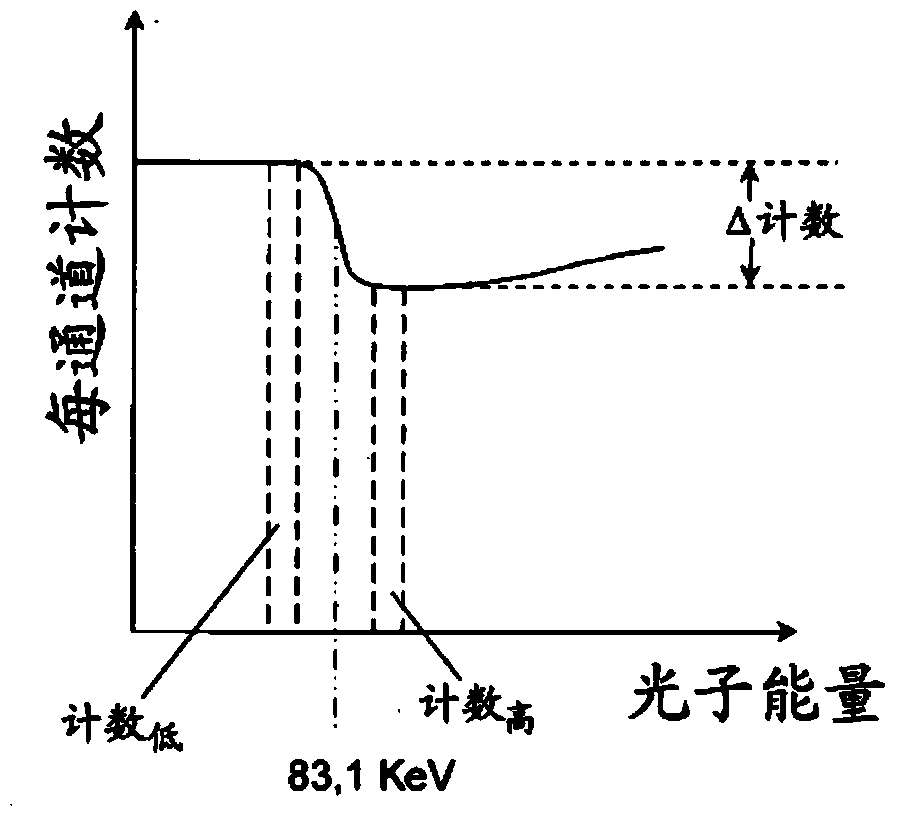
[0051] as from Figure 4 as can be seen
[0052] mu HG =μ 高 -μ 低
[0053] this gets
[0054]
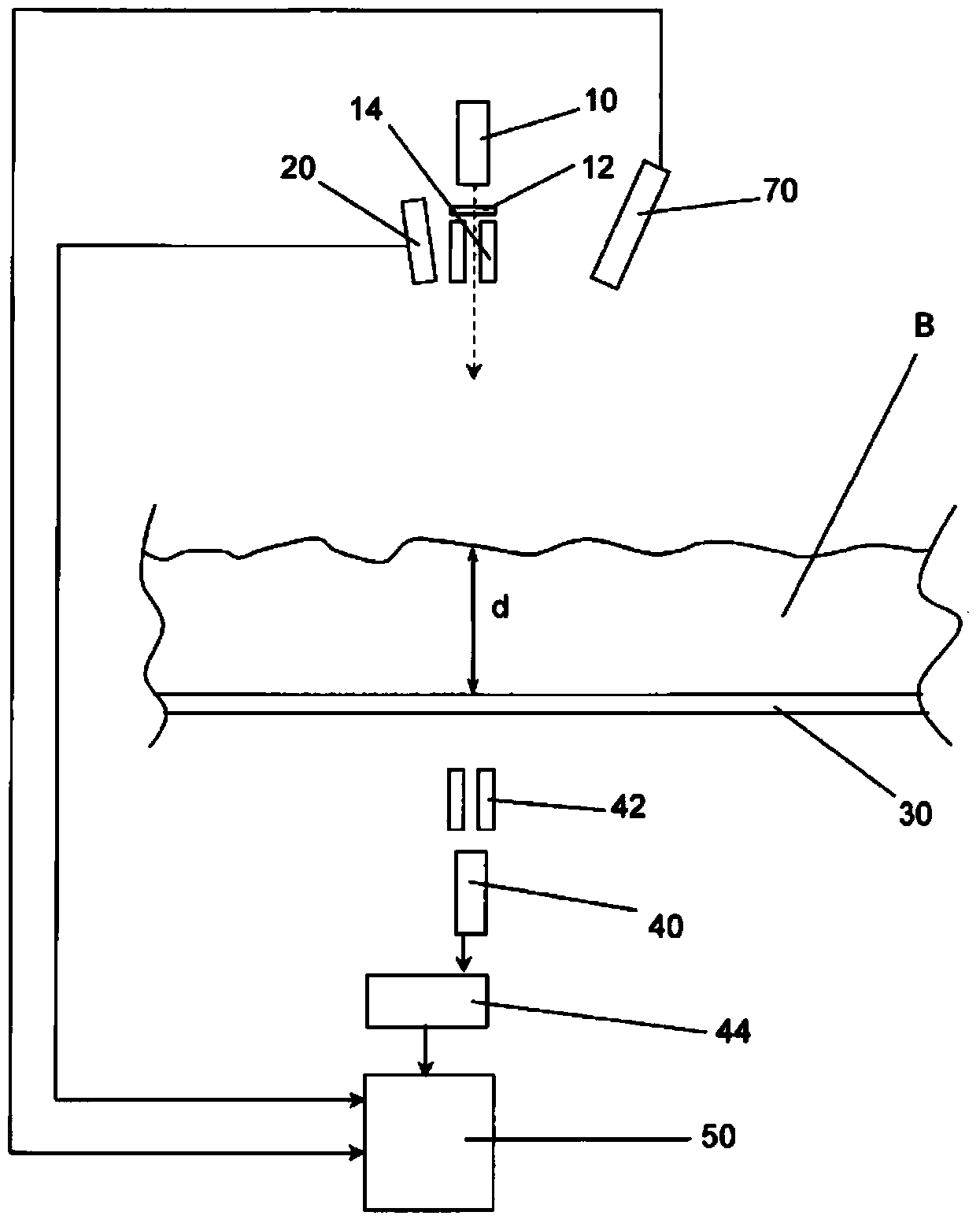
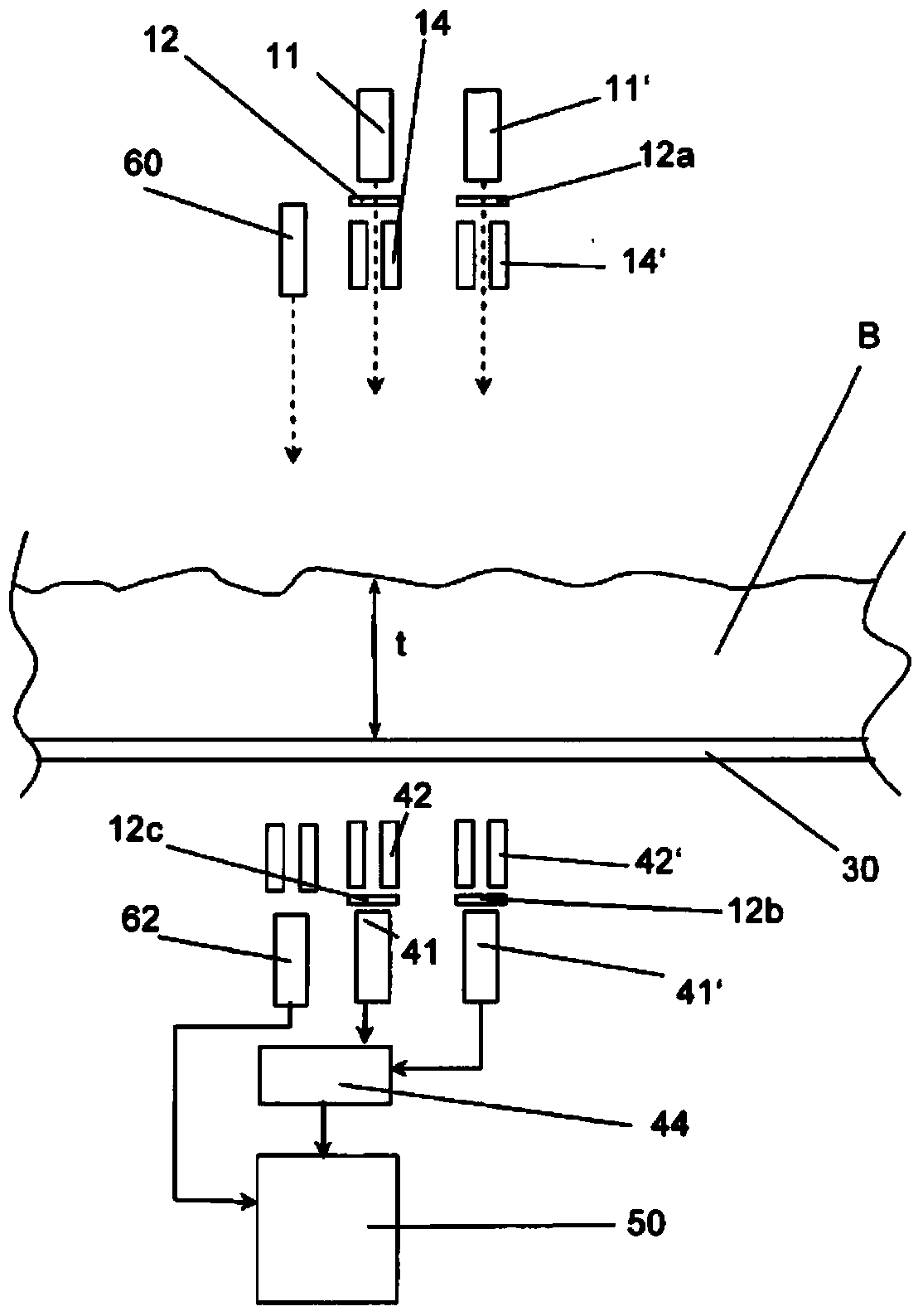
[0055] Figure 5 shown in Figure 4 changes in . Here, a normal detector 45 and a discriminator 65 are used. Am-241 source 11 and Cd-109 source 11 ′ are directed to this common detector 45 and the energy is separated by discriminator 65 .
[0056] Image 6 shown in Figure 5 changes in . Here, the beam of the Cd-109 source 11' is extended through the Am-241 source 11 so that both be...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com