Method for rapidly identifying adulterated meat
A fast and identification model technology, applied in the field of rapid identification of adulterated meat, can solve the problems of complex sample pretreatment by chromatographic technology, difficulty in adapting to batch rapid detection, and ordinary people's inability to use it, so as to realize online analysis, facilitate popularization and use, Strong selectivity and anti-interference ability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
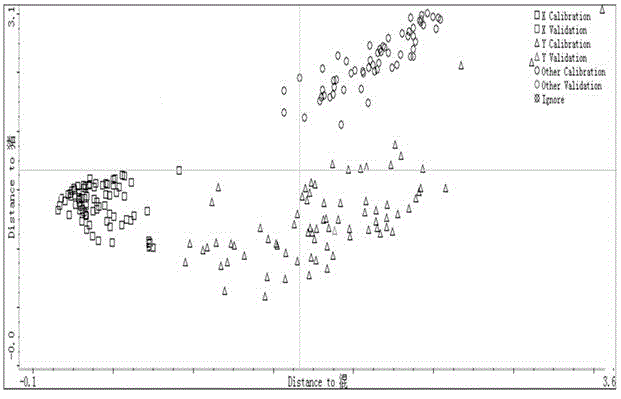
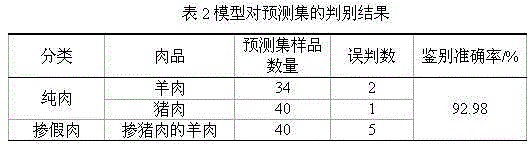
[0031] like figure 1 and figure 2 As shown, the pure meat is mutton and pork, and the adulterated meat is mutton mixed with pork.
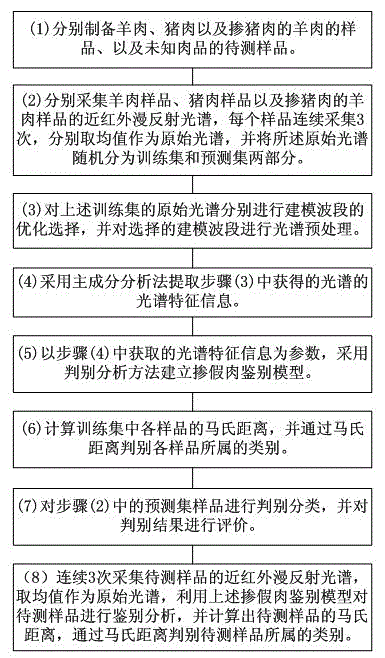
[0032] (1) Samples of mutton, pork, and mutton mixed with pork, and samples of unknown meat to be tested were prepared respectively.
[0033] The unknown meat, as well as pure mutton and pork, were crushed into mince, respectively, to make samples to be tested, mutton samples, pork samples and mutton samples mixed with pork. Wherein, when preparing the adulterated meat, it is only necessary to mix the two kinds of minced meat evenly. Sample preparation is simple and easy to operate.
[0034] (2) Collect the near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra of mutton samples, pork samples, and pork-mixed mutton samples respectively. Each sample is collected 3 times continuously, and the average value is taken as the original spectrum, and the original spectrum is randomly divided into training set and The prediction set has two parts.
[0035] The ne...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com