Train control system
A train control system and technology for trains, applied in electric braking systems, control drives, locomotives, etc., can solve the problems of driver's distracted operation safety, high attention, low continuous and instantaneous force, etc., to reduce the overall Effects of complexity, increased fuel savings, reduced training requirements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
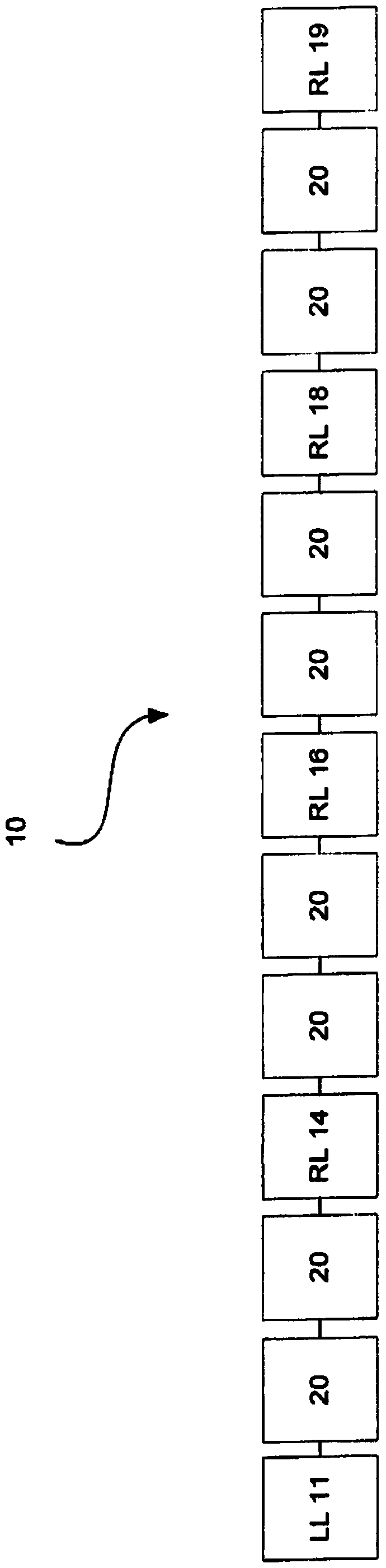
[0016] Conventional DP systems typically include a master locomotive (usually lead locomotive (LL)) that sets throttle / brake values and sends information to slave locomotives (remote locomotives (RL)) to set their throttle / brake values ( See for example an earlier system disclosed in US Patent No. 3,380,399 to Southard et al.). It is generally known that the RL receives throttle commands from the LL and changes this control setting at the RL to save fuel (see US Patent No. 4,344,364 to Nickles et al., the entire contents of which are incorporated herein by reference). Additionally, the ability of the RL to send diagnostic information back to the LL is also known (see US Patent No. 5,570,284 to Roselli et al.).
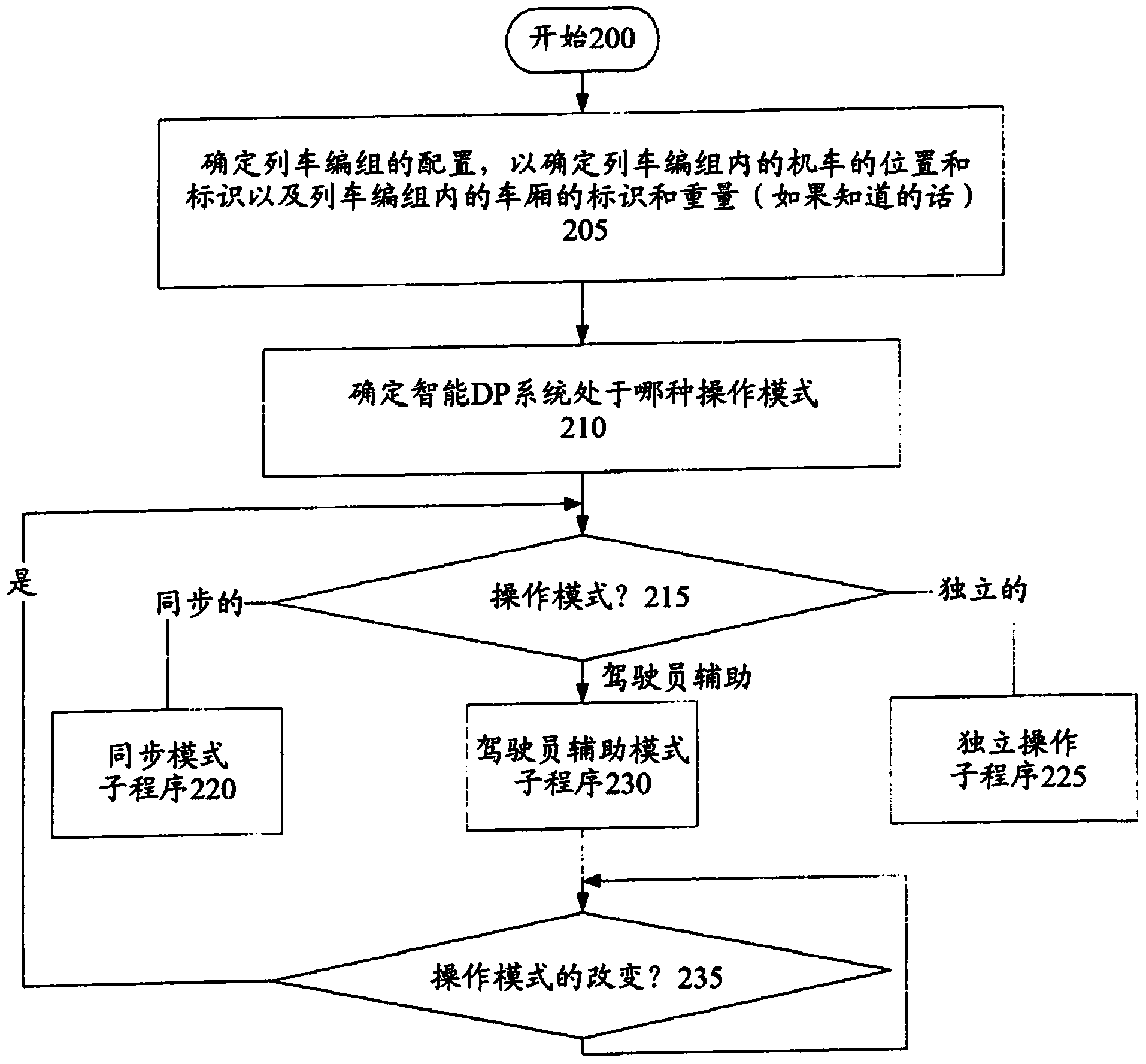
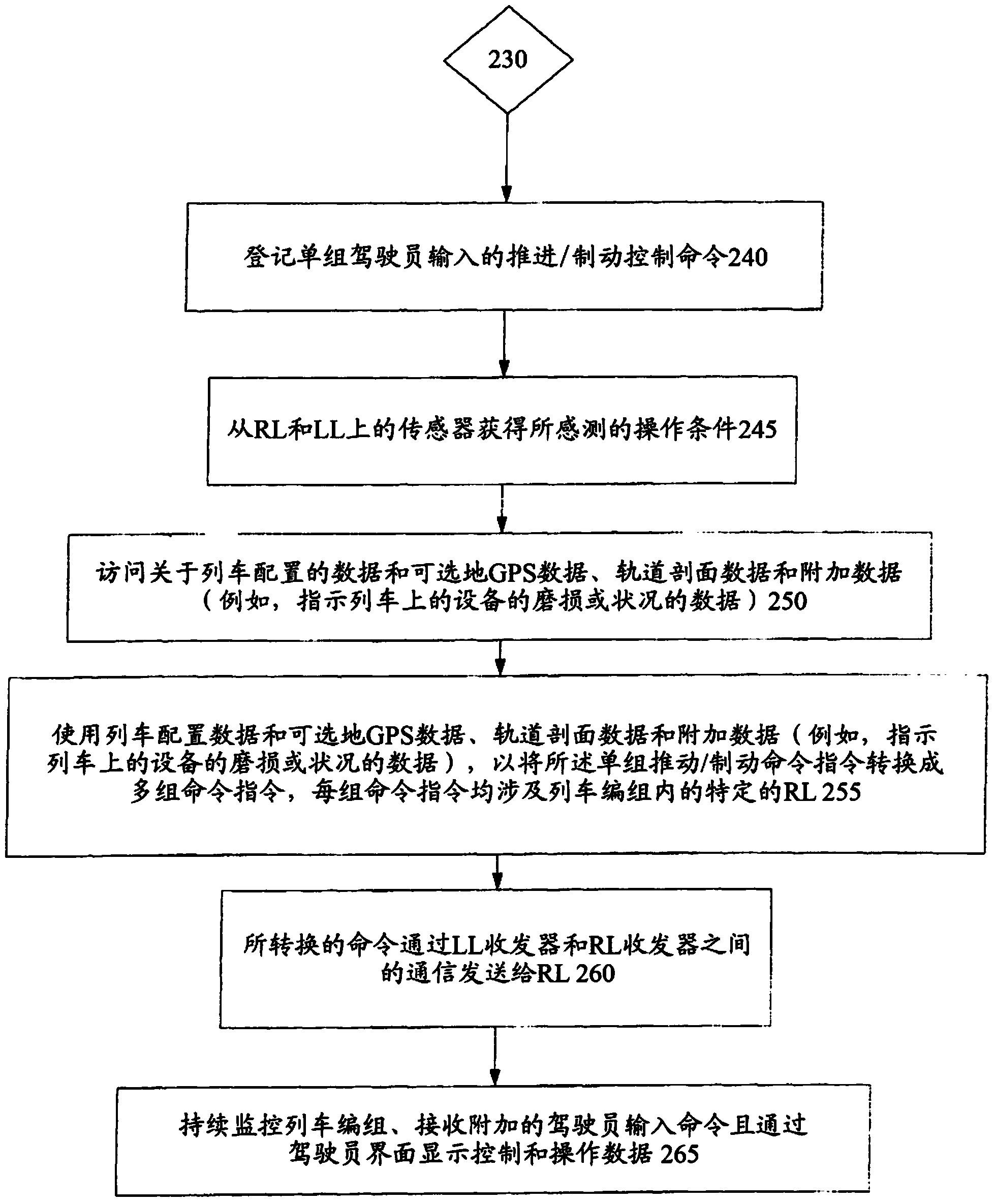
[0017] However, conventional DP systems fail to provide a mode of operation in which the engineer can enter a single set of command inputs which are then converted into RL-specific commands and sent to the corresponding The RL. The disclosed embodiments provide s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com