Flexible optimization of the signal-to-noise ratio for ultra dense coherent WDM systems
An optical signal and multiplexing technology, applied in the field of optical communication systems, can solve the problems of low sensitivity to optical noise, reduced transmission range, weak tolerance, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
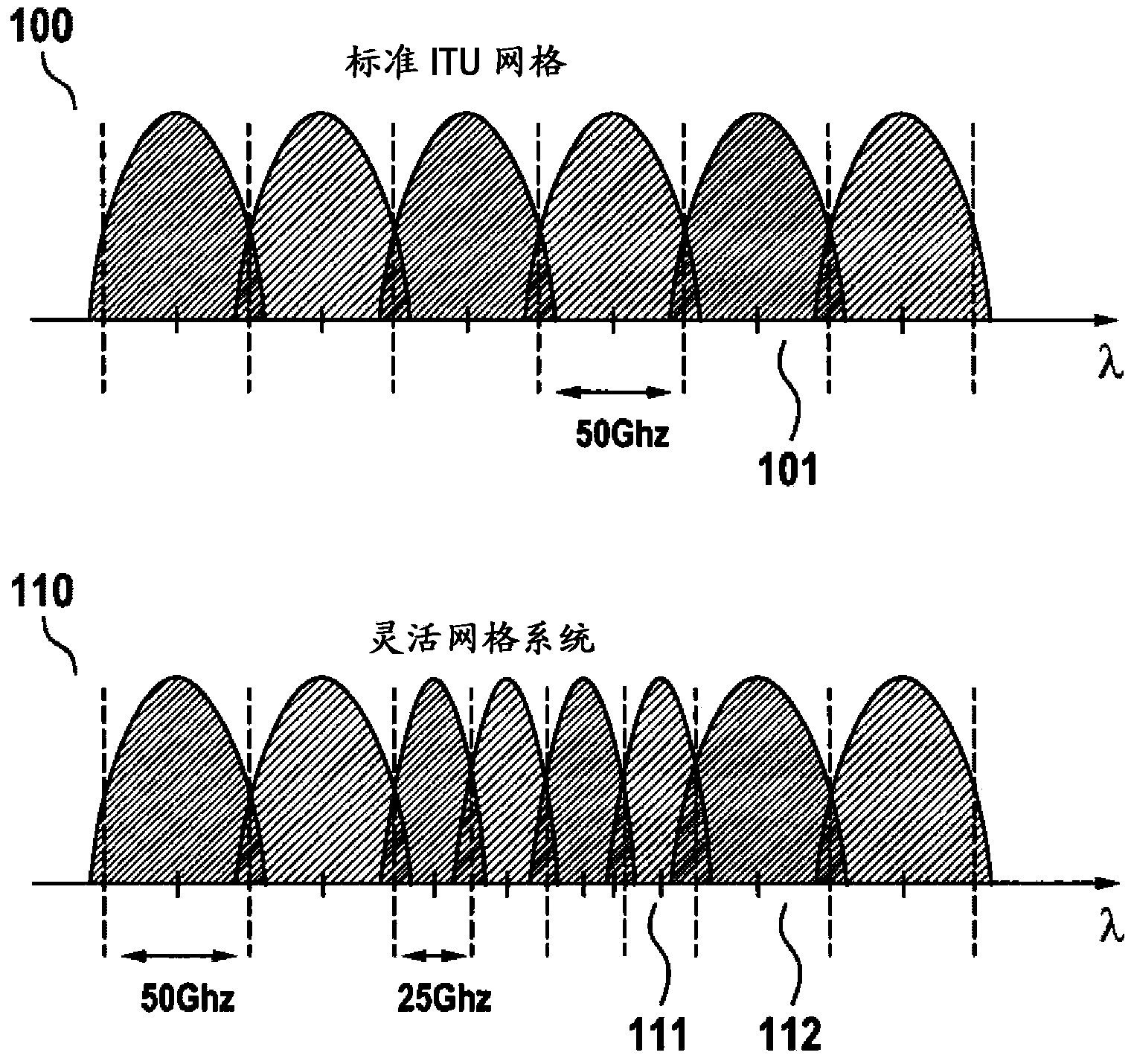
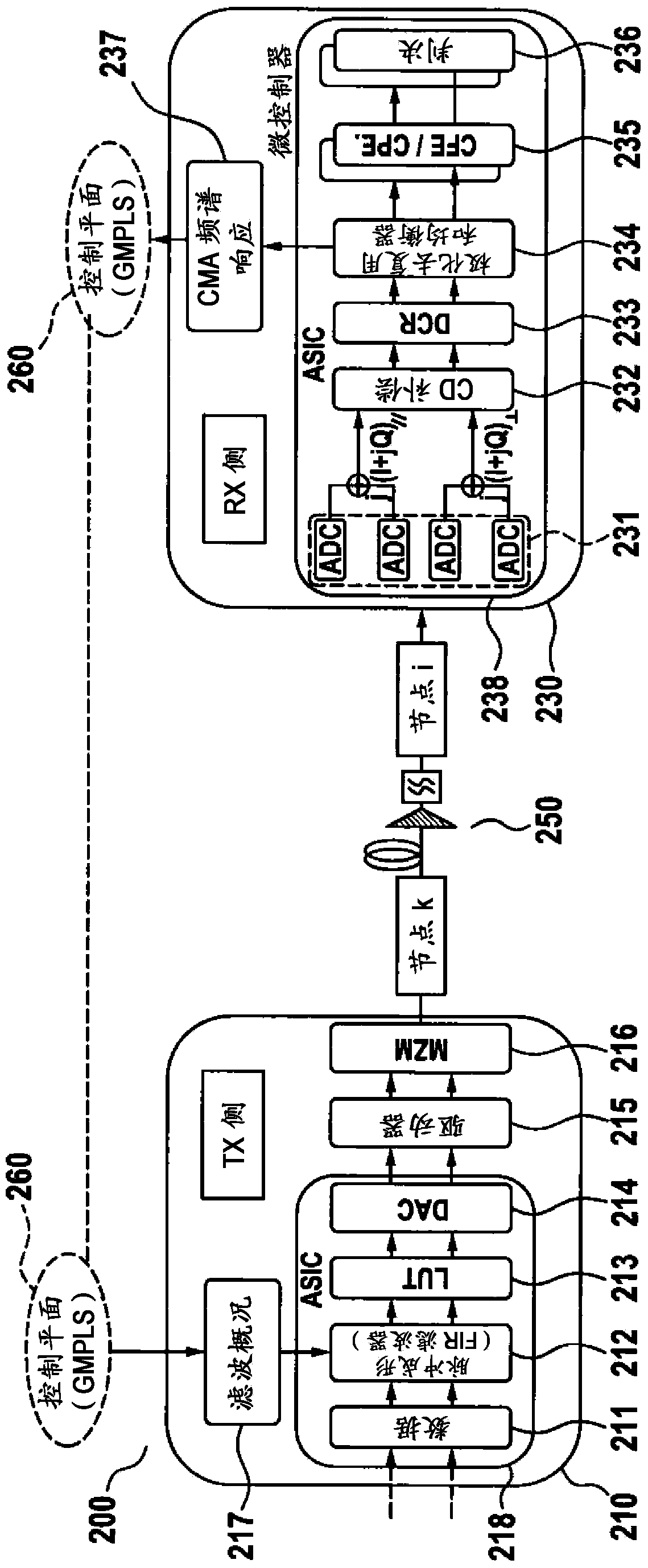
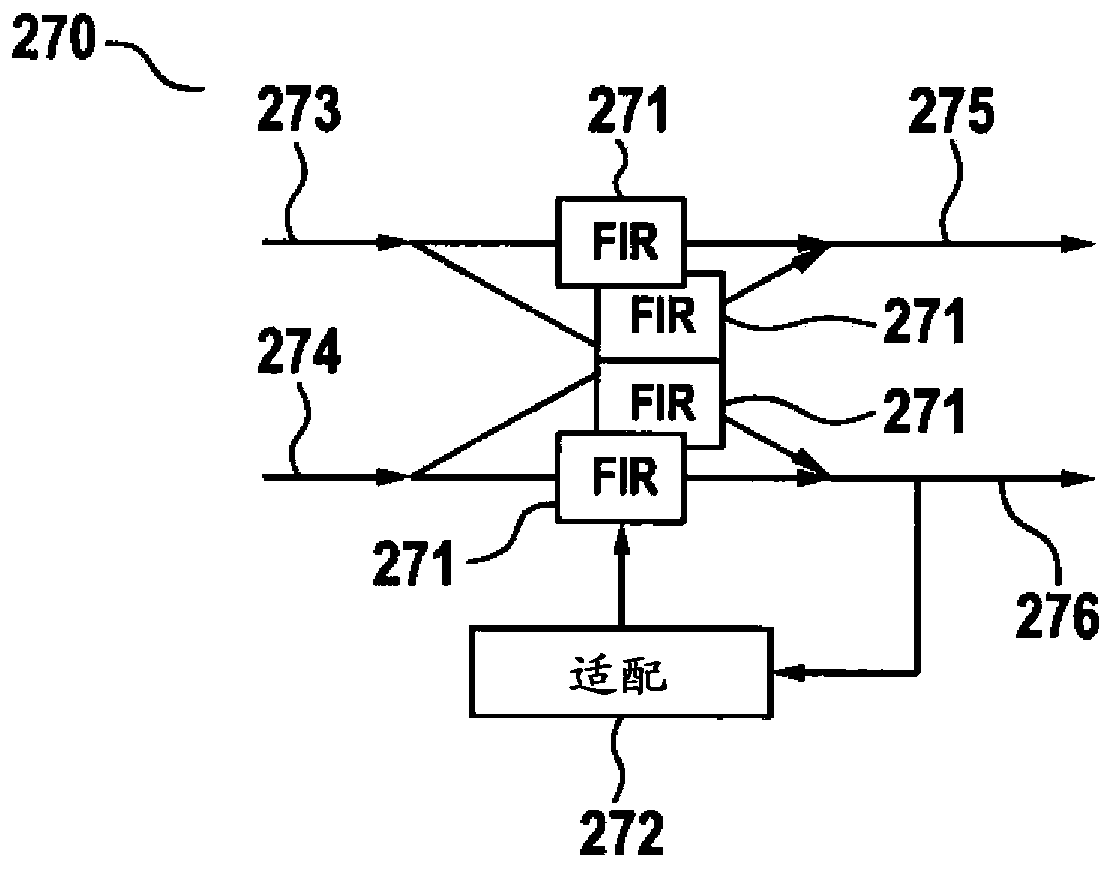
[0032] As outlined in the introductory chapter, WDM channels of different widths can be used to adapt the capacity of the optical transmission system to accommodate impairments in the optical transmission path. exist figure 1 WDM channels 111 , 112 with different channel widths (channel spacing) are illustrated in the WDM channel diagram 110 . When adapting to the width of the WDM channel 111 , the transmitter filter used at the transmitter of the WDM channel 111 has to be adapted to the reduced or increased bandwidth of the WDM channel 111 . Such transmitter filters are mainly used for pulse shaping in order to reduce cross-talk between adjacent WDM channels 111,112. Thus, the transmitter filter may also be referred to as a pulse-shaping filter. The frequency response of a transmitter filter can be designed to optimize (ie to increase) the electrical signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) at the corresponding receiver. In order to adapt the transmitter filter to the modified width of...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com