Wireless sensor network modeling method based on nonvolatile two-dimensional cellular automata
A two-dimensional cell, non-volatile technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, climate sustainability, etc., can solve problems such as long interval periods and impractical batteries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
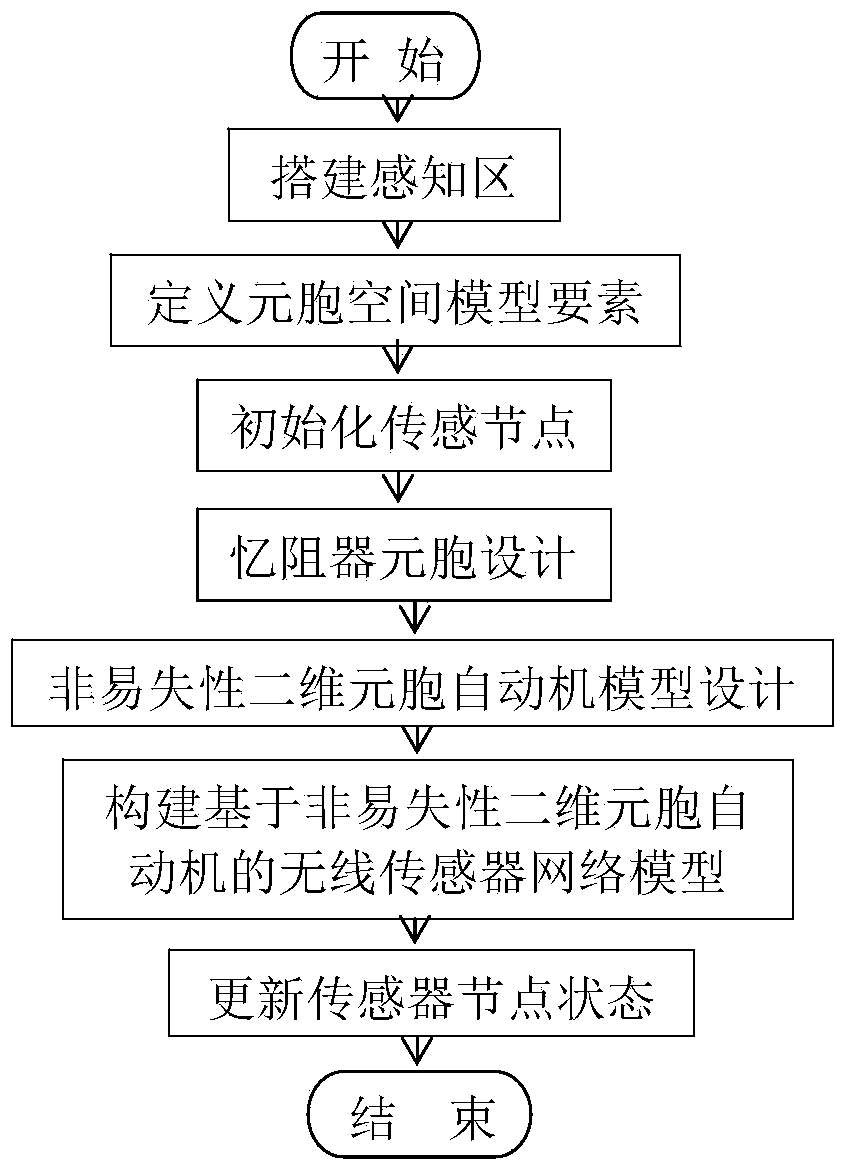
[0040] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and specific embodiments.
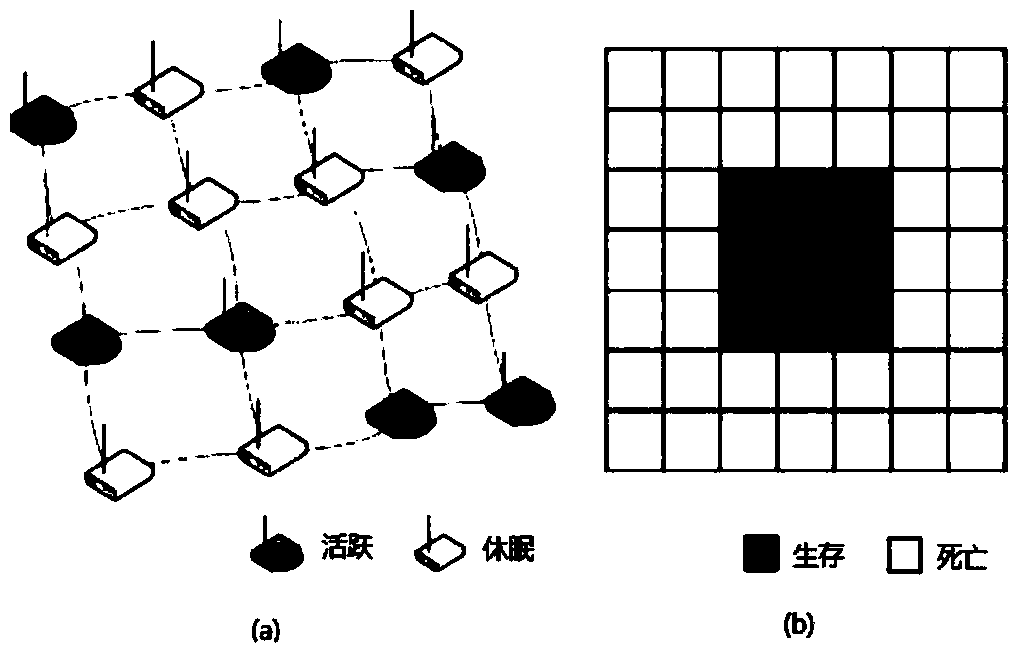
[0041] Memristor is a non-linear resistor with memory function proposed by Professor Leon Chua of the University of California, Berkeley in 1971 and confirmed by HP scientists in 2008. As the fourth basic element after resistors, capacitors, and inductors, memristors are used to describe magnetic flux And the relationship between charge q(t): M(q)=dφ(q) / dq, where: Obviously, the current i(t) flowing through the memristor and the voltage v(t) across the memristor satisfy the relationship: v(t)=M(q)i(t), it can be known that the memristor at a certain moment t 0 The memristor value M(q(t 0 )) depends on the current passing through it from t=-∞ to t=t 0 The time integral of , thus showing the characteristic of time memory.
[0042] Considering the unique characteristics of memristors, as well as the excellent characteristics of memristors s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com