Method to prevent pitting of LED chip electrodes when evaporating aluminum
A LED chip and evaporation technology, which is applied in the direction of circuits, electrical components, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of pitting caused by the growth of aluminum film, and achieve the effect of high reliability and strong operability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] The principle of the present invention is: the aluminum film is divided into small parts, the thickness of each small part of aluminum is relatively thin, the time used for vapor deposition of this small part of aluminum is short, and the aluminum particles have no time to form larger particles. When the next part of aluminum is vapor-deposited again after a certain time interval, the aluminum particles need to re-nucleate, re-grow and re-form a film, and cannot directly grow on the previous layer of aluminum film.
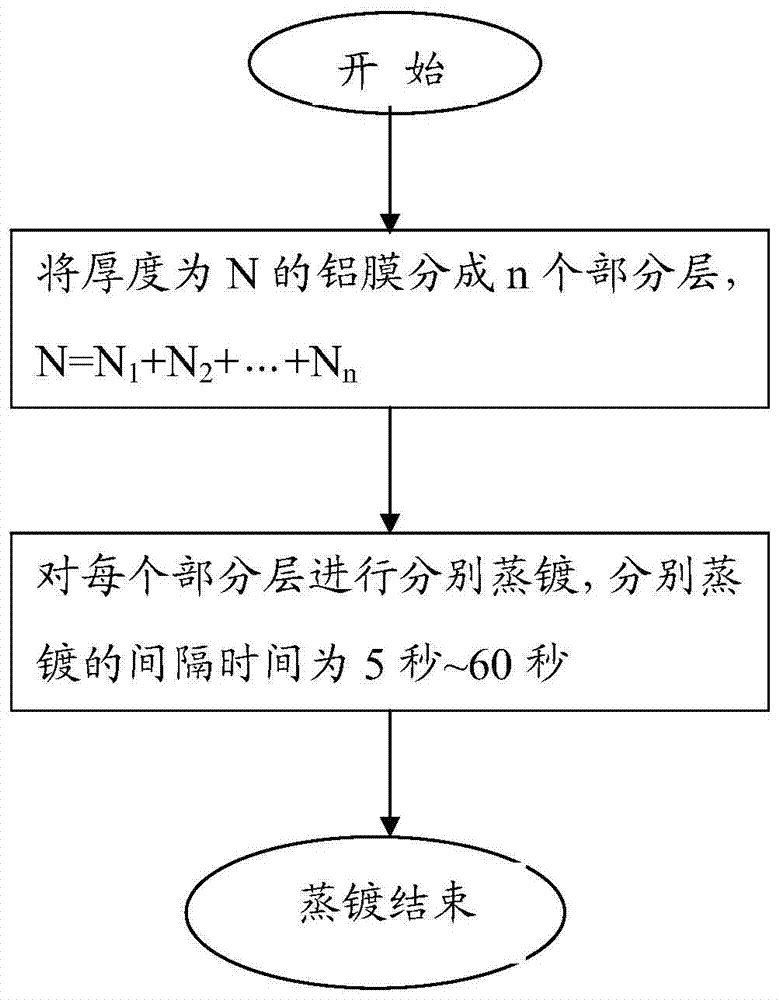
[0032] Please refer to image 3 , the method for preventing the LED chip electrode from producing pits when evaporating aluminum in this embodiment includes: dividing the aluminum film with a thickness of N into n partial layers and evaporating them separately, N=N 1 +N 2 +…+N n , the interval time for vapor deposition of each partial layer is 5 seconds to 60 seconds, until the entire aluminum film is evaporated.
[0033] Preferably, the N 1 =N 2 =…=N ...
Embodiment 2
[0039] In this embodiment, the method for preventing pitting of LED chip electrodes during vapor deposition of aluminum includes: dividing the aluminum film with a thickness of N into n partial layers for respective vapor deposition, N=N 1 +N 2 +…+N n , the interval time for vapor deposition of each partial layer is 5 seconds to 60 seconds, until the entire aluminum film is evaporated.
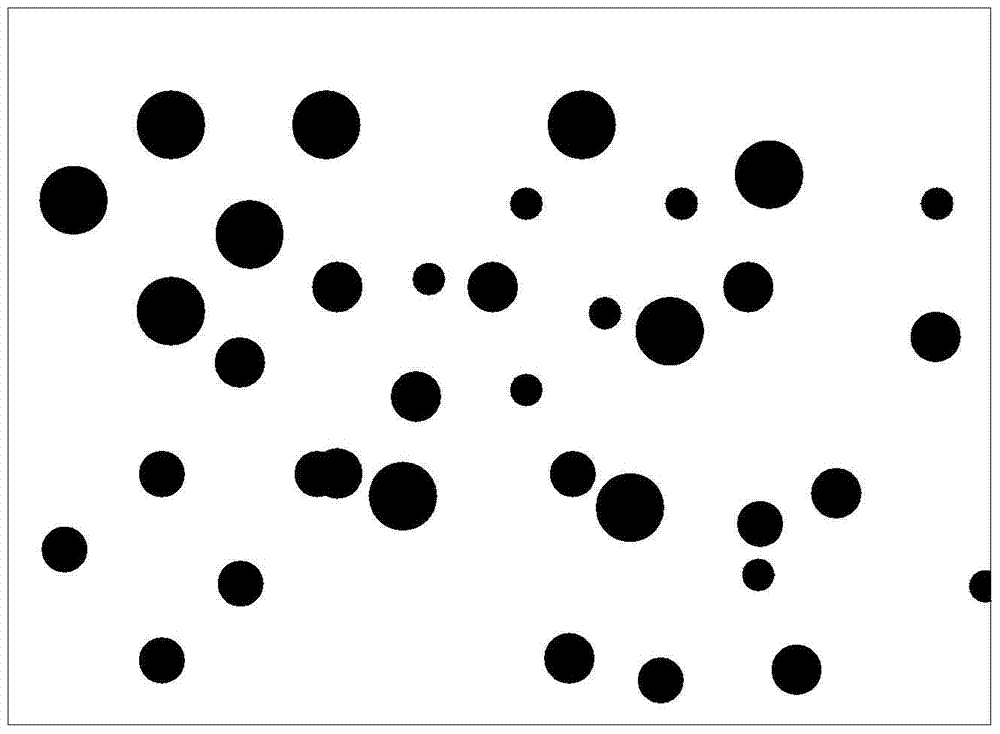
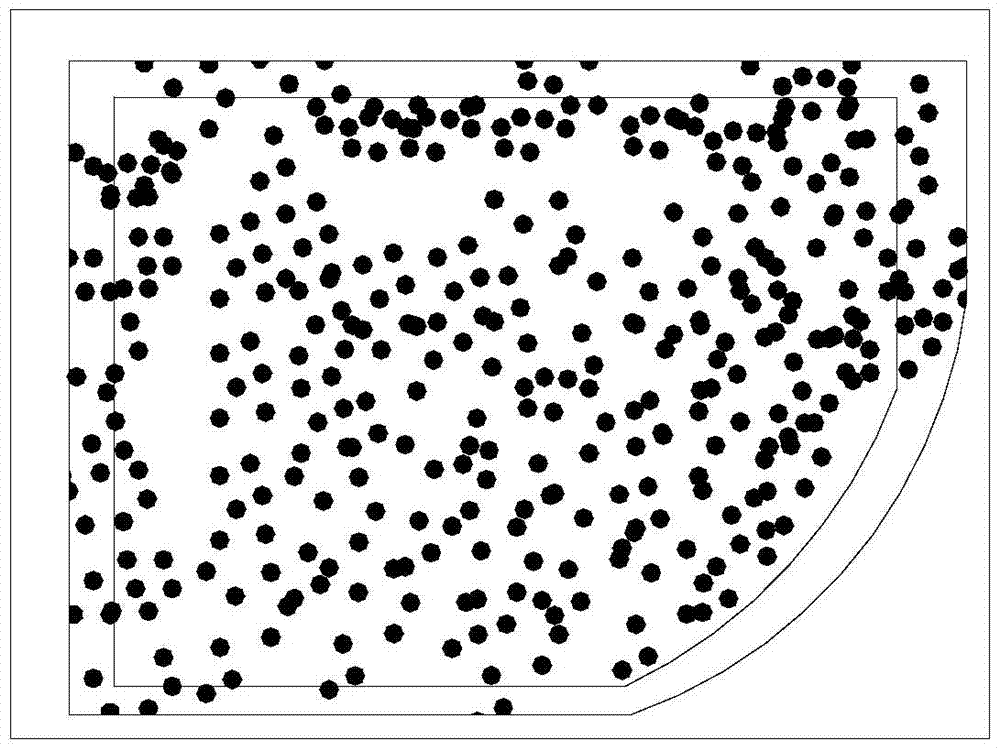
[0040] When this method is used to vapor-deposit metal aluminum in this embodiment, although the total thickness of the aluminum is relatively thick, every small part of the aluminum is relatively thin. In this way, no matter how thick the total thickness of the final aluminum film is, the aluminum particles cannot grow into larger particles. There are no larger aluminum particles which means no pitting. Because the problem of pitting caused by the growth of the aluminum film is successfully solved by layered evaporation of aluminum.
[0041] In a specific embodiment, taking an aluminum-th...
Embodiment 3
[0045] In this embodiment, the method for preventing pitting of LED chip electrodes during vapor deposition of aluminum includes: dividing the aluminum film with a thickness of N into n partial layers for respective vapor deposition, N=N 1 +N 2 +…+N n , the interval time for vapor deposition of each partial layer is 5 seconds to 60 seconds, until the entire aluminum film is evaporated.
[0046] When this method is used to vapor-deposit metal aluminum in this embodiment, although the total thickness of the aluminum is relatively thick, every small part of the aluminum is relatively thin. In this way, no matter how thick the total thickness of the final aluminum film is, the aluminum particles cannot grow into larger particles. There are no larger aluminum particles which means no pitting. Because the problem of pitting caused by the growth of the aluminum film is successfully solved by layered evaporation of aluminum.
[0047] In a specific embodiment, taking an aluminum-th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com