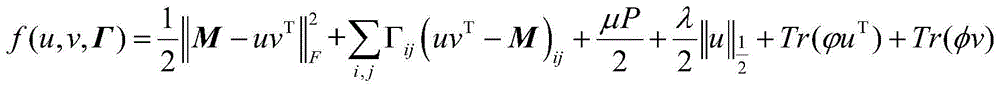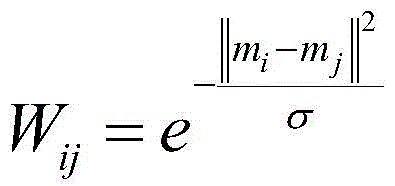A Raman Spectral Image Unmixing Method Based on Non-negative Matrix Adjacency
A Raman spectroscopy, non-negative matrix technology, applied in the field of image processing, can solve problems such as unsatisfactory assumptions, and achieve the effect of improving noise resistance and stability
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Based on the rank 1-NMU algorithm, the invention proposes a non-negative matrix proximity algorithm for sparse graph relations.
[0033] The basic rank 1-NMU algorithm can be formulated as an optimization problem as shown in the following formula:
[0034]
[0035] in: is the F norm. matrix is the image data matrix, matrix u and matrix v are row vectors with length m and length n respectively.
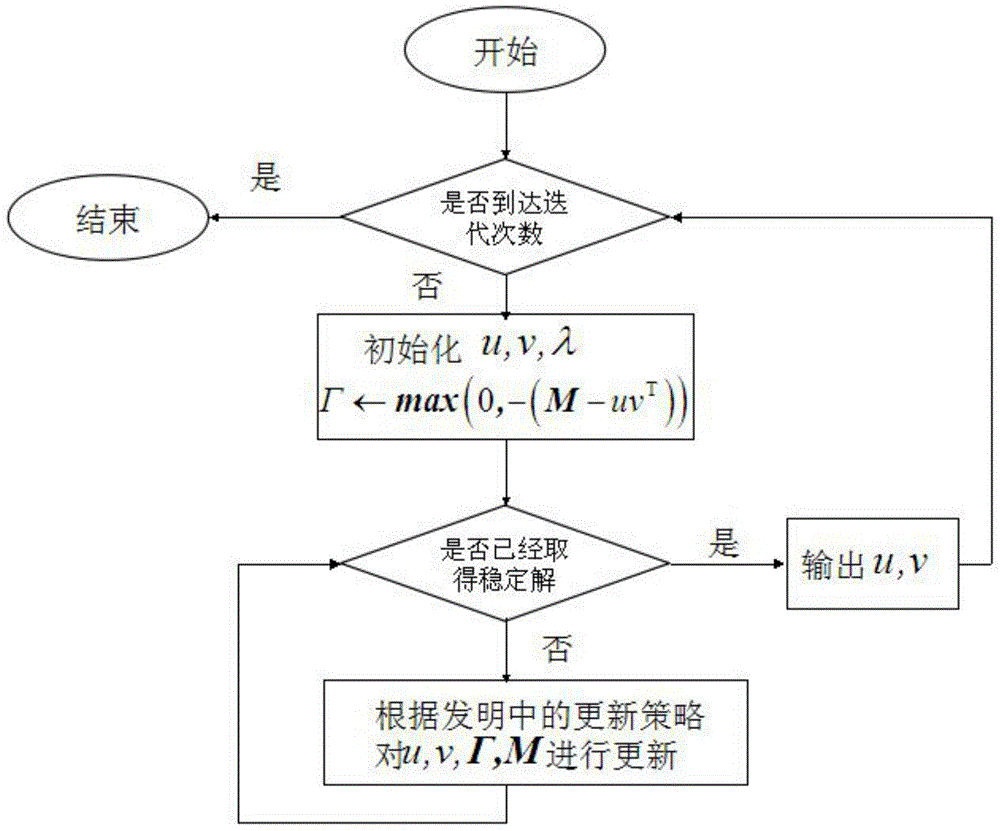
[0036] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention is based on the Raman spectral image unmixing method that the non-negative matrix is adjacent, comprises the following steps:
[0037] (1) Perform noise reduction and defluorescence processing on the Raman image to obtain processed image data.
[0038] (2) For the pixels in the image data, calculate the weight between the pixels according to the following formula:
[0039]
[0040] where: m i and m j are any two pixels in the image data, and σ is the kernel width of the thermal kernel function.
[0041] (...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Below we take the structural components of the tea plant cell wall as an example to describe the specific implementation of the method proposed by the present invention.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com