A kind of cobalt base alloy and its thermal processing, heat treatment method and application
A heat treatment method and technology of cobalt-based alloys, which are applied in the field of medical materials, can solve problems such as inability to effectively inhibit restenosis in stents, achieve the effects of solving restenosis in stents, reducing or inhibiting restenosis in stents, and reducing the formation of thrombus
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
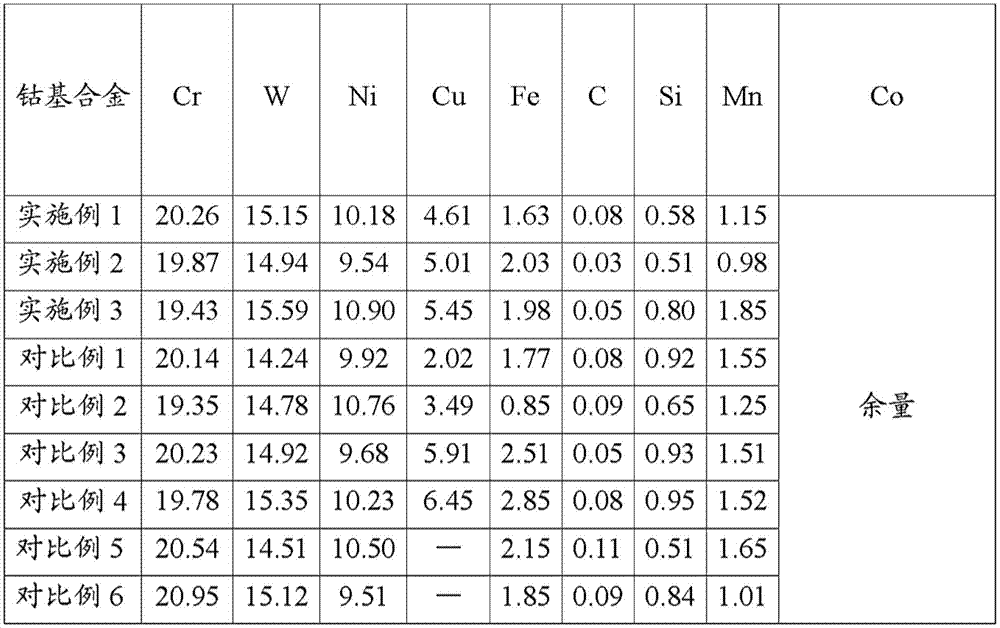
[0059] The content is 20.26 (weight) % of Cr, W: 15.15 (weight) %; Ni: 10.18 (weight) %; Fe: 1.63 %; C: 0.08 (weight) %; Si: 0.58 (weight) %; Mn: 1.15(weight)%; Cu: 4.61(weight)%; the rest is cobalt-based alloy of Co and unavoidable impurities after hot working, specifically:
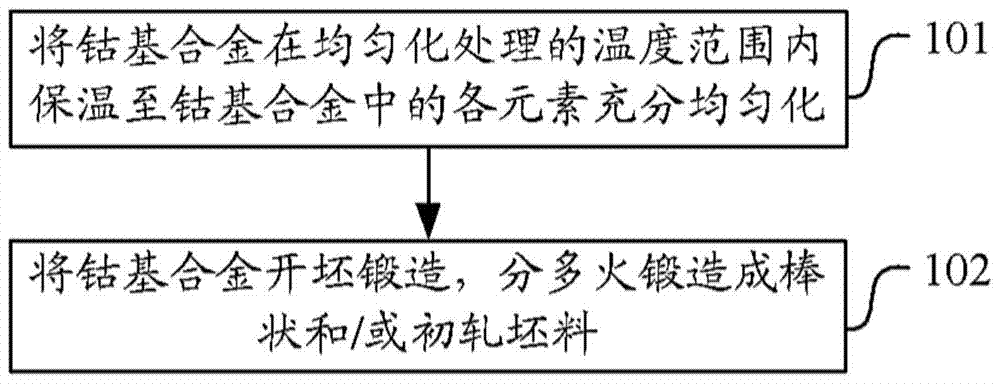
[0060] Homogenize the cobalt-based alloy at 1200-1250°C for 2-4 hours until the elements in the cobalt-based alloy are fully homogenized;
[0061] The cobalt-based alloy is billet-forged and multi-fired forged into rods and / or blooms, and the final forging temperature is not lower than 1000°C.
[0062] After thermal processing and then heat treatment, specifically:
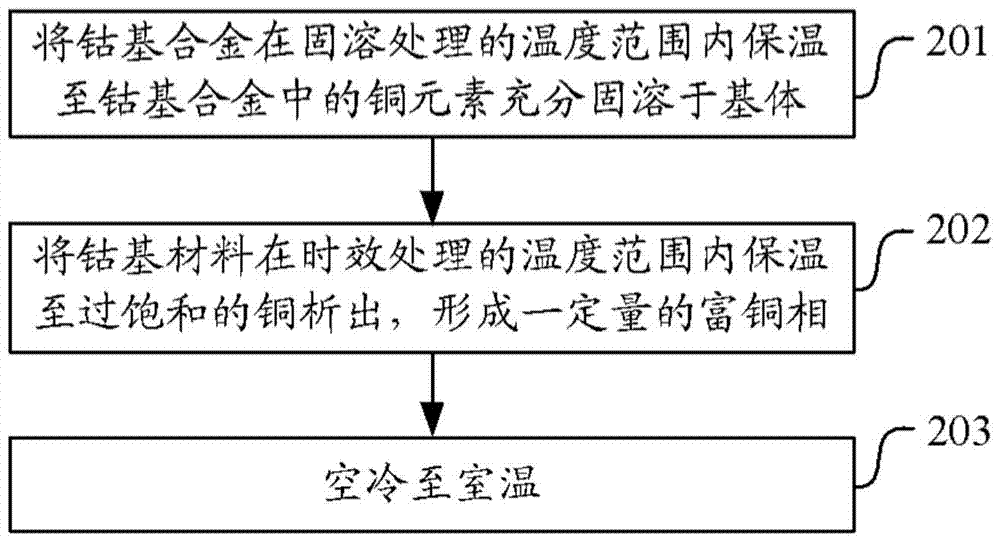
[0063] Solid solution treatment of the cobalt-based alloy at 1100-1200°C for 1-2 hours until the copper element in the cobalt-based alloy is fully dissolved in the matrix;
[0064] Heat the cobalt-based alloy at 700°C for 2-6 hours until the supersaturated copper is precipitated and a certain amount of copper-rich phase is formed;
[006...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Repeat embodiment 1, following difference is arranged: content is that Cr is 19.87 (weight) %, W: 14.94 (weight) %; Ni: 9.54 (weight) %; Fe: 2.03 (weight) %; C: 0.03 (weight) % ) %; Si: 0.51 (weight) %; Mn: 0.98 (weight) %; Cu: 5.01 (weight) %; the rest is Co and unavoidable impurities Cobalt-based alloy after hot working and heat treatment. See Table 1 for the composition content data of the cobalt-based alloy in Example 2 above, and see Table 2 for the cobalt-based alloy after thermal processing and heat treatment.
Embodiment 3
[0070] Repeat embodiment 1, following difference is arranged: content is that Cr is 19.43 (weight) %, W: 15.59 (weight) %; Ni: 10.90 (weight) %; Fe: 1.98 (weight) %; C: 0.05 (weight) % ) %; Si: 0.80 (weight) %; Mn: 1.85 (weight) %; Cu: 5.45 (weight) %; the rest is Co and unavoidable impurities of cobalt-based alloy after hot working and heat treatment. See Table 1 for the composition content data of the cobalt-based alloy in Example 3, and see Table 2 for the cobalt-based alloy after thermal processing and heat treatment.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| tensile strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com