Imperfection fault diagnosis rule extraction method based on quantitative characteristic relation
A technology for fault diagnosis and quantification of features, applied in general control systems, control/regulation systems, testing/monitoring control systems, etc., can solve problems such as incorrect diagnosis conclusions, changes in original information, and extraction of fault diagnosis rules, achieving low cost, The effect of improving the accuracy and improving the extraction accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
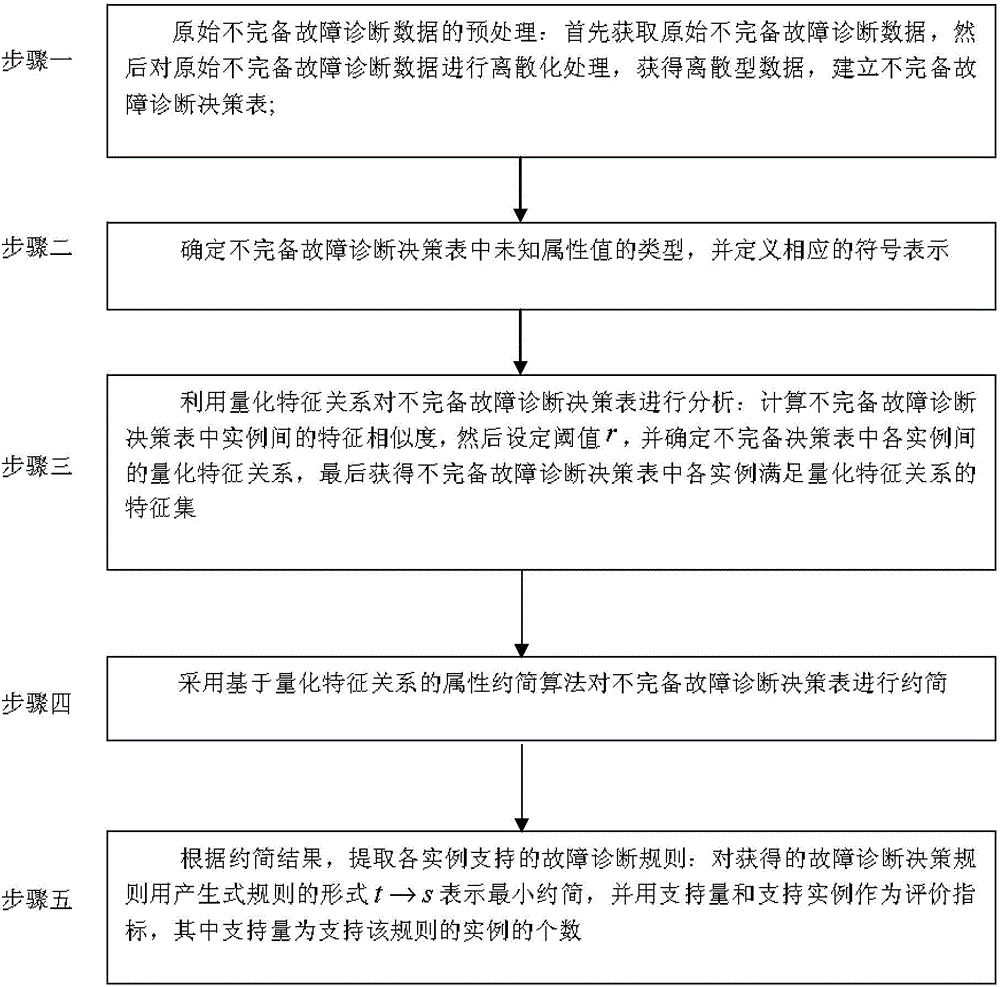
[0022] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 Illustrate this embodiment, a method for extracting incomplete fault diagnosis rules based on quantitative feature relationships, characterized in that the method includes the following steps:
[0023] Step 1. Preprocessing of the original incomplete fault diagnosis data: first obtain the original incomplete fault diagnosis data, then perform discretization processing on the original incomplete fault diagnosis data, obtain discrete data, and establish an incomplete fault diagnosis decision table;
[0024] Step 2. According to the definitions of the three unknown attribute values, determine the types of unknown attribute values in the incomplete fault diagnosis decision table, and define corresponding symbolic representations;
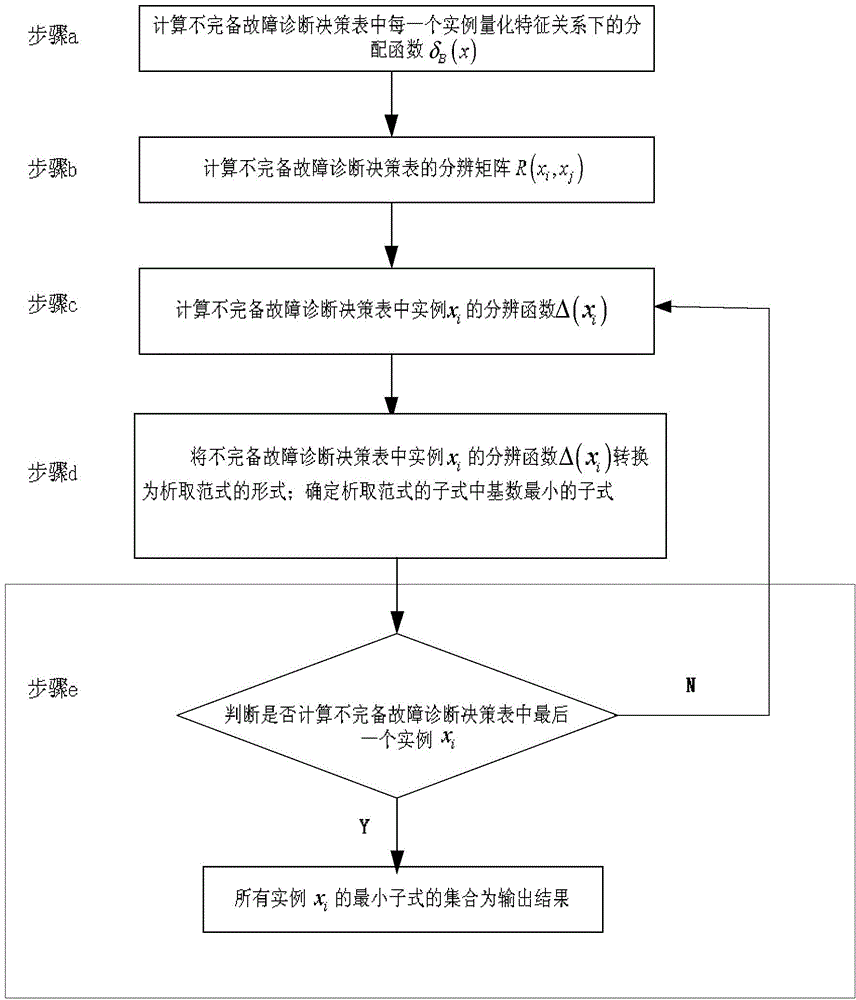
[0025] Step 3: Analyze the incomplete fault diagnosis decision table by using quantitative feature relations: calculate the feature similarity between instances in the incomplete fault diagnosi...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0028] Specific embodiment 2: The difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment 1 is that in said step 2, according to the definition of three unknown attribute values, the type of unknown attribute value in the incomplete fault diagnosis decision table is determined, and the corresponding symbols are defined express:
[0029] The definitions of the three unknown attribute values are as follows:
[0030] Missing type: the attribute value exists but it cannot be obtained for some reason, represented by the symbol "?";
[0031] Missing type: the attribute value can be replaced by any typical value of this attribute, represented by the symbol "*";
[0032] Restricted: The attribute value can be replaced by any typical attribute value of the attribute except the missing attribute value, indicated by the symbol "+".
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0033] Specific embodiment three: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one or two is: the definition of feature similarity in the step three is as follows:
[0034] Feature similarity represents instances xi and x j The feature similarity on the attribute set B is calculated according to formula (1),
[0035] VR B (x i ,x j )=∏ b∈B R b (x i ,x j )·N B (x i ,x j ) (1)
[0036] In formula (1), VR B (x i ,x j ) for instance x i and x j The feature similarity on the attribute set B, B represents the attribute set, b represents an attribute in the attribute set B; R b (x i ,x j ) for instance x i and x j Feature similarity on attribute b; N B (x i ,x j ) for instance x i and x j The proportion of attributes whose value is "?"
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com