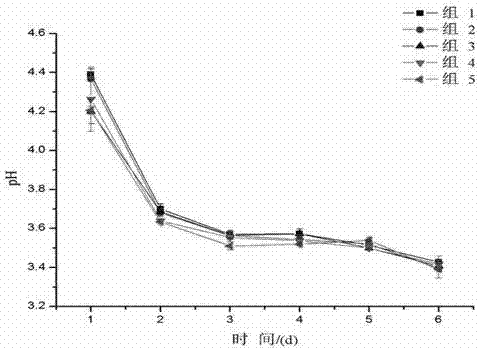
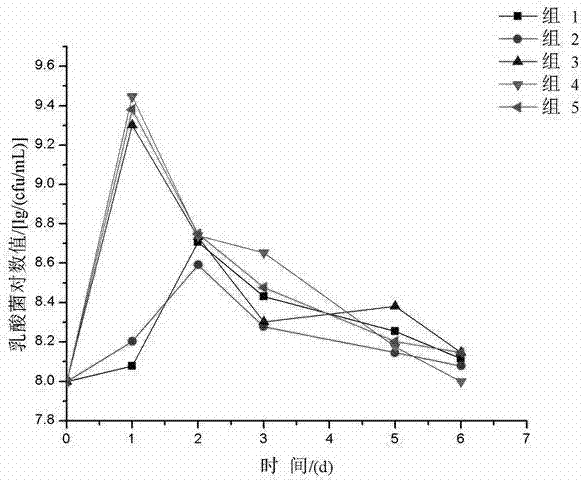
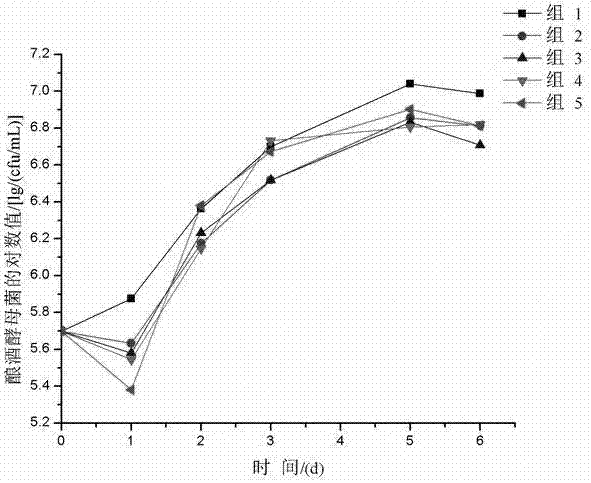
Indigenous lactic acid bacteria and its method and product for mixed fermentation of edible and medicinal bacteria with Saccharomyces cerevisiae
A technology of indigenous lactic acid bacteria and Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is applied in the field of bioprocessing of edible and medicinal fungi, can solve the problems of poor variety of processed products, easy spoilage, easy browning and other problems, so as to optimize bioprocessing methods, ensure nutritional value and sensory Quality, the effect of broadening the processing field
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0047] Example 1 Cultivation of indigenous lactic acid bacteria and preparation of bacterial liquid
[0048] The applicant isolated and screened the strain obtained from Flammulina velutipes fruiting bodies, which was indigenous lactic acid bacteria 4J1, and was classified as Leuconostoc pseudoentericola ( Leuconostoc pseudomesenteroides ), which was deposited in the General Microbiology Center of China Microbial Culture Collection and Management Committee on December 2, 2014, with the deposit number CGMCC No. 10129.
[0049] Table 1 Results of lowering cholesterol by indigenous lactic acid bacteria of the present invention
[0050]
[0051] The strains were inoculated into fermentation medium 1 with an inoculum of 1% to 4%, cultured at a constant temperature of 25°C to 37°C for 16 to 24 hours, with a shaker rotating speed of 50 to 200 rpm, and collected by centrifugation with 0.8% to 2 %(G / mL) NaCl suspends the bacteria to obtain the indigenous lactic acid bacteria liquid for use....
Embodiment 2
[0053] Example 2 Preparation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae liquid
[0054] Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains (purchased from Angel Yeast Co., Ltd.) were cultured in fermentation medium 2 at a constant temperature of 25℃~37℃ for 14~24h, collected by centrifugation, and used 0.8%~2% (g / mL) NaCl Suspend the bacteria in the solution to obtain the yeast liquid of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is reserved for use.
[0055] Fermentation medium 2:
[0056] YPD medium (1L): yeast extract 10.0g, peptone 20.0g, glucose 20.0g, distilled water 1L, pH 6.5, 121℃, 20min sterilization.
Embodiment 3
[0057] Example 3 Preparation of edible and medicinal fungus products by mixed fermentation
[0058] S1 uses fresh enoki mushrooms (including discarded mushrooms) that are not infected by other microorganisms as raw materials, remove impurities, dry or dry the surface moisture before use.
[0059] S2 Put the Flammulina velutipes prepared in step S1 into the container according to the ratio of 50~150g Flammulina velutipes to 100~300mL container volume, add salt with 2.0% salt content of Flammulina velutipes quality, and add 0.5% calcium chloride at the same time, and cover cover.
[0060] S3 Put the container with Flammulina velutipes in steam sterilization at 80-121°C for 5 to 35 minutes, and cool for use. This can ensure that the shape of the enoki mushroom is complete, and it has good elasticity, and it can be cooled for later use.
[0061] S4 Mix the indigenous lactic acid bacteria liquid obtained in Example 1 and the Saccharomyces cerevisiae liquid in a volume ratio of 2:1 to obta...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com