Device and method for utilizing sand launder seepage to simulate coastal zone salt-fresh water abrupt interface
A technology of brackish and fresh water interface and abrupt interface, applied in the field of groundwater dynamics in coastal zone, can solve problems such as lack of substantial progress and direct observation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
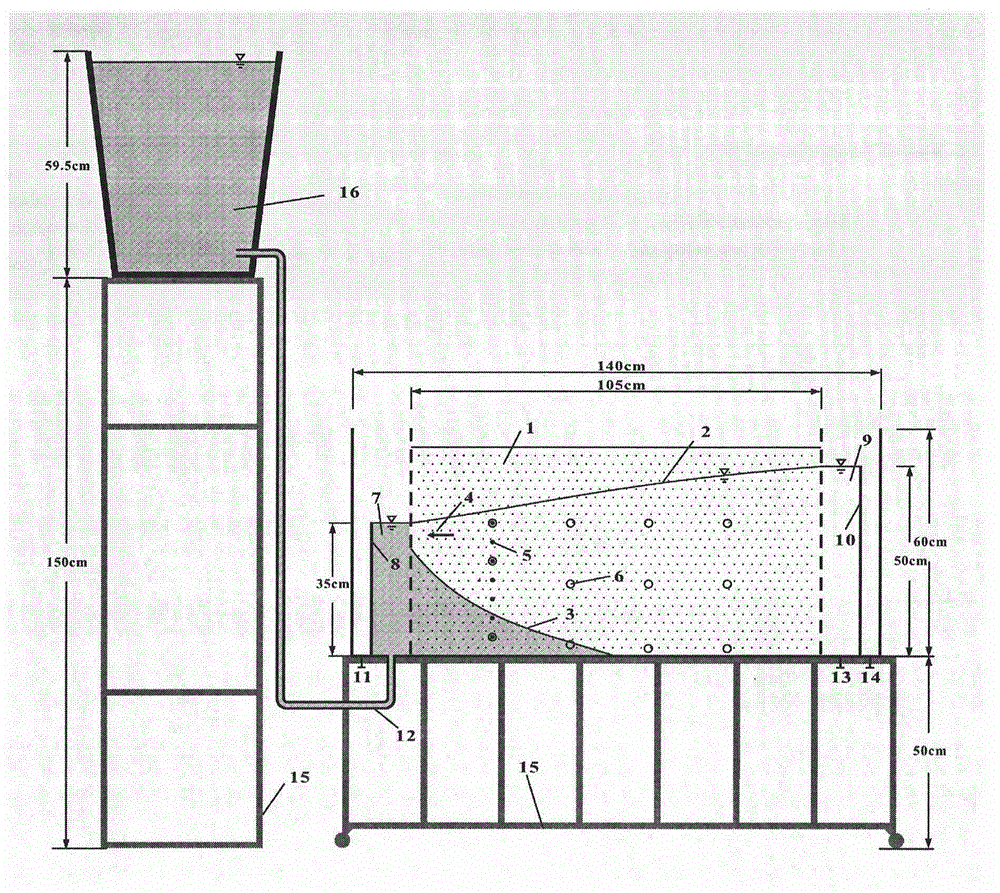
[0015] When the medium in the seepage tank is the same kind of sand and the density of fresh water is 1g / cm 3 When changing the density of salt water and changing the head difference between salt water and fresh water, observe the inclination of the salt water interface to the fresh water end and the extension distance from the front of the salt water interface to the fresh water end. Changes in head and density at piezometric holes.
[0016] (1) The density of salt water is 1.025g / cm 3 Simulation experiment of salty and fresh water interface in coastal zone
[0017] (a) When the height of the movable baffle at the left end is 45cm, observe the pressure at each observation point of the phreatic steady flow in the sand tank and the water head and density of each pressure measuring hole, and observe the position of the stable salty-fresh water interface, including the first vertical line The height from the interface to the bottom plate of the seepage tank or the depth from th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com