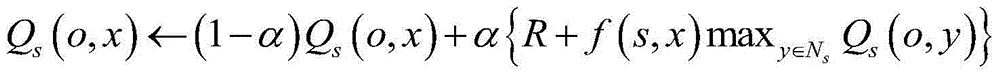Method for establishing a routing path through Q learning on-board network based on fuzzy reasoning
A fuzzy reasoning and in-vehicle network technology, applied in the field of communication, can solve problems such as changes, slow algorithm convergence speed, inability to accurately reflect the status of in-vehicle network links, etc., and achieve the effect of improving accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
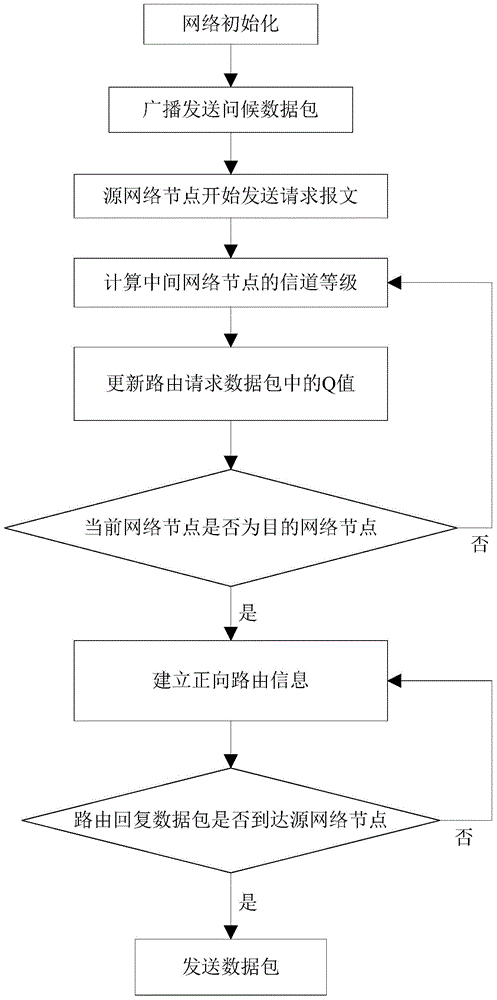
[0033] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
[0034] refer to figure 1 , the specific implementation steps of the present invention are as follows:
[0035] Step 1, network initialization.
[0036] Set the Q value table of each network node in the network to be initially empty, the learning rate is set to 0.8, and the routing table is set to
[0037] Leave blank.
[0038] Step 2, broadcast and send the greeting data packet.
[0039] All network nodes in the network periodically broadcast and send greeting HELLO data packets. After the receiving network node receives the HELLO packet sent by the adjacent network node, it queries whether the adjacent network node exists in the adjacent network node table, and if so, continues to receive Greeting HELLO packets from other network nodes, otherwise, add the adjacent network node into the adjacent network node table.
[0040] Step 3, the source network node starts t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com