Channel distribution and user correlation strategy based on AMAB model
A channel allocation and strategy technology, applied in wireless communication, electrical components, network topology, etc., can solve problems such as time-consuming, unfavorable implementation, and complex association process
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
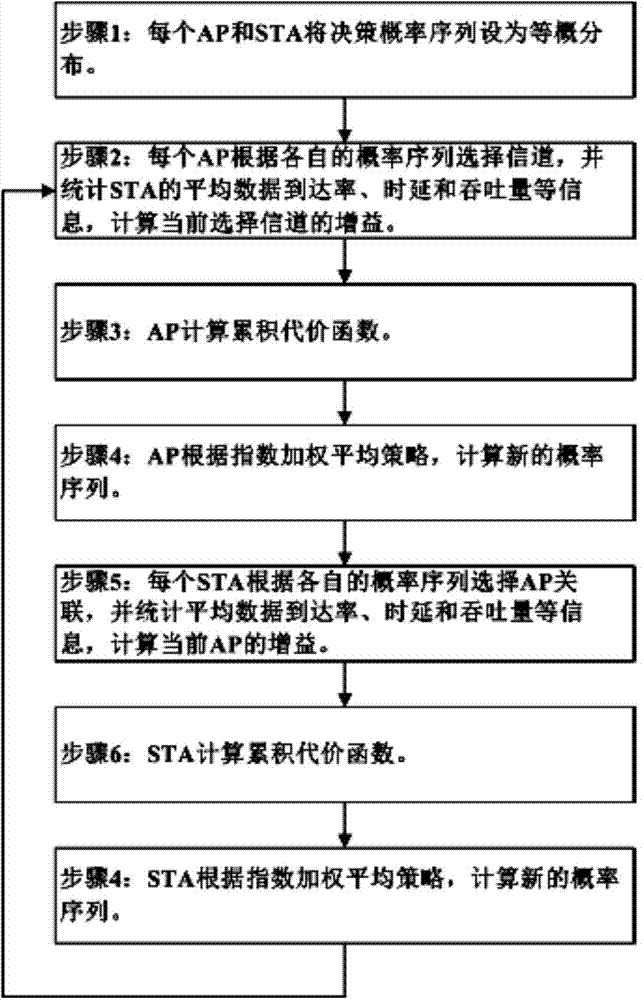
[0087] A channel allocation and user association strategy based on the AMAB model. The steps are: when APs and STAs are distributed in a highly dense network, and a new AP accesses the network, the following channel allocation and user association strategy is adopted.
[0088] Step 1: For any AP in the current scene, the number of channels that can be allocated is M. Each AP saves a probability distribution sequence for channel selection, and the channel probability sequence selected by the AP in the t-th round of decision-making is recorded as:
[0089] P t =(p 1,t ,p 2,t ,...,p M,t )
[0090] (1) where p j,t is the probability of selecting a channel in the t-th round of decision-making;
[0091] (2) The initial values of the AP's channel selection probability sequence are all equally probable distributions.
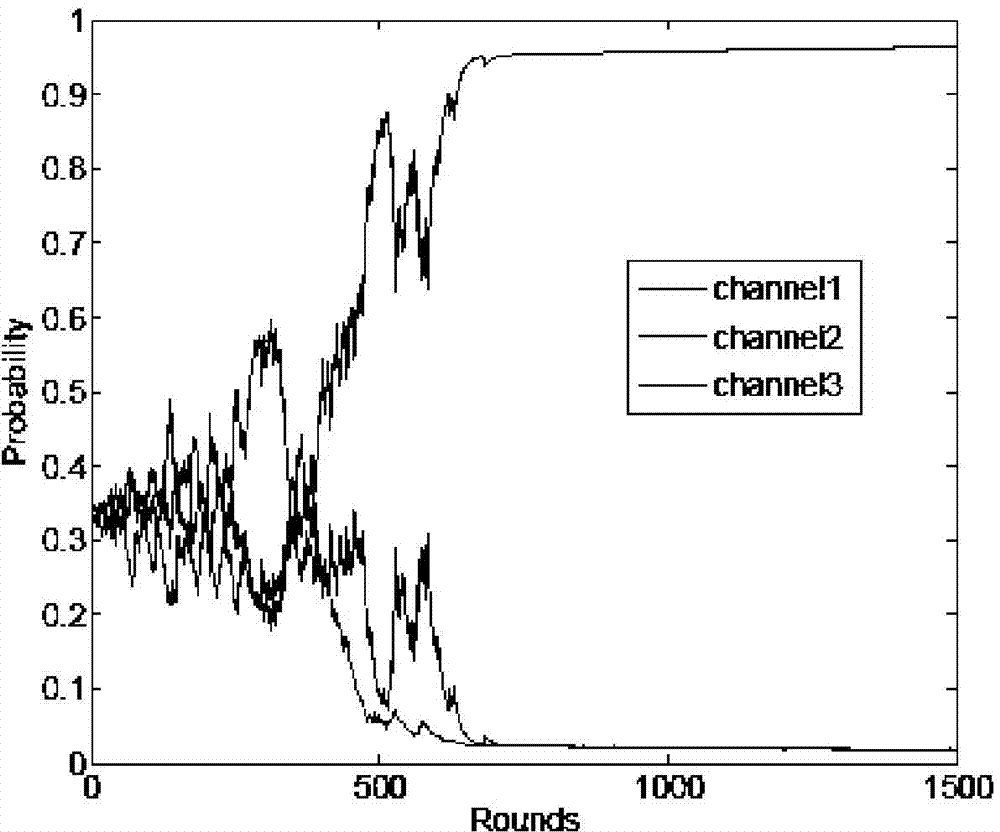
[0092] Step 2: each AP according to the probability sequence P of the current round t t =(p 1,t ,p 2,t ,...,p M,t ) to select a channel, and count informat...
Embodiment 2
[0108] When APs and STAs are distributed in a high-density network, and a new STA accesses the network, the following channel allocation and user association strategies are adopted.
[0109] Step 1: For any STA in the current scene, the number of APs that can be associated is M. The STAs respectively store a probability distribution sequence associated with the AP, and the probability sequence selected by the STA in the t-th round of decision-making is recorded as:
[0110] P t =(p 1,t ,p 2,t ,...,p M,t )
[0111] (1) where p j,t is the probability of choosing AP in the t-th round of decision-making;
[0112] (2) The initial value of the probability sequence of each STA is an equal probability distribution.
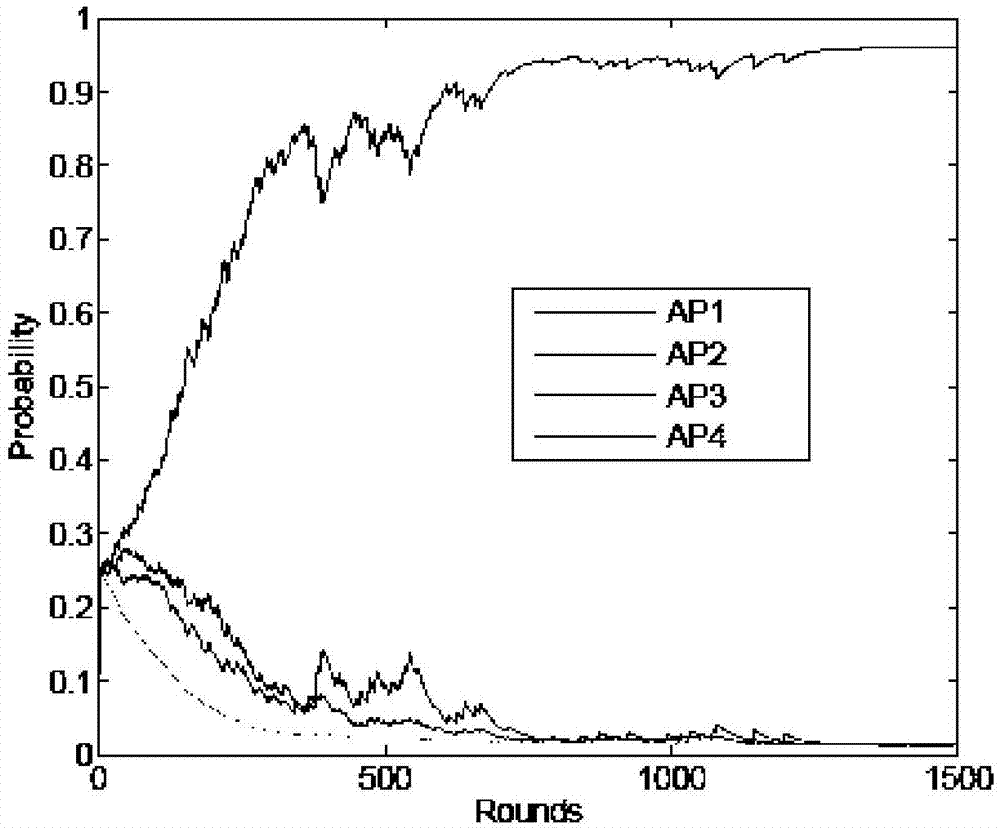
[0113] Step 2: each STA a according to the probability sequence P of the current round t t =(p 1,t ,p 2,t ,...,p M,t ) to select the AP to associate with, and count the respective average data arrival rate, delay, and throughput information, and then obtain the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com