X-ray CT device and control method
An X-ray and X-ray tube technology, applied in the field of X-ray CT devices, can solve the problems of undercounting characteristics and inability to separate photons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 1 Embodiment approach
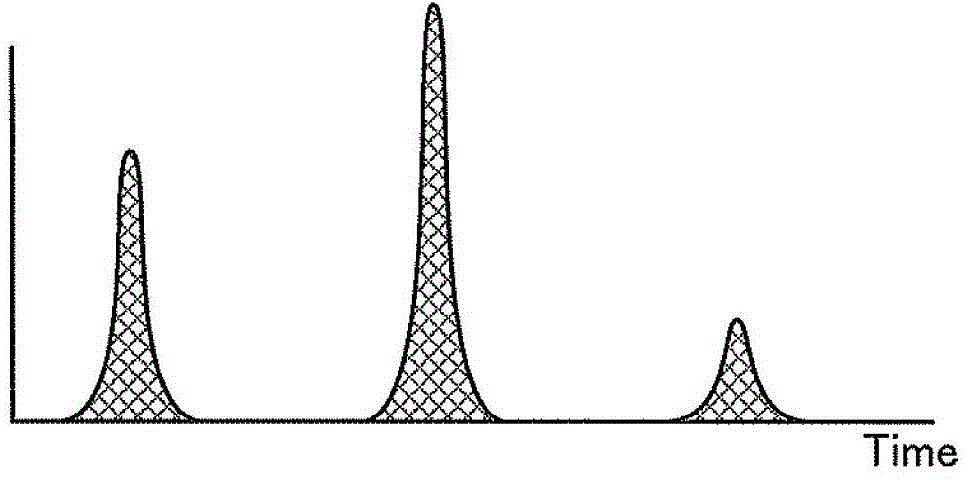
[0027] First, photon counting CT will be described before describing the X-ray CT apparatus according to the first embodiment.
[0028] In photon counting CT, the amount of light (X-rays) is measured by counting the number of photons. The greater the number of photons per unit time, the stronger the light (X-rays). In addition, although individual photons have different energies, in photon counting CT, information on the energy components of X-rays can be obtained by measuring the energy of photons. That is, in photon counting CT, data collected by irradiating X-rays with one tube voltage can be divided into a plurality of energy components and imaged. For example, in photon counting CT, it is possible to obtain image data for identifying substances by utilizing the difference in K absorption limit.
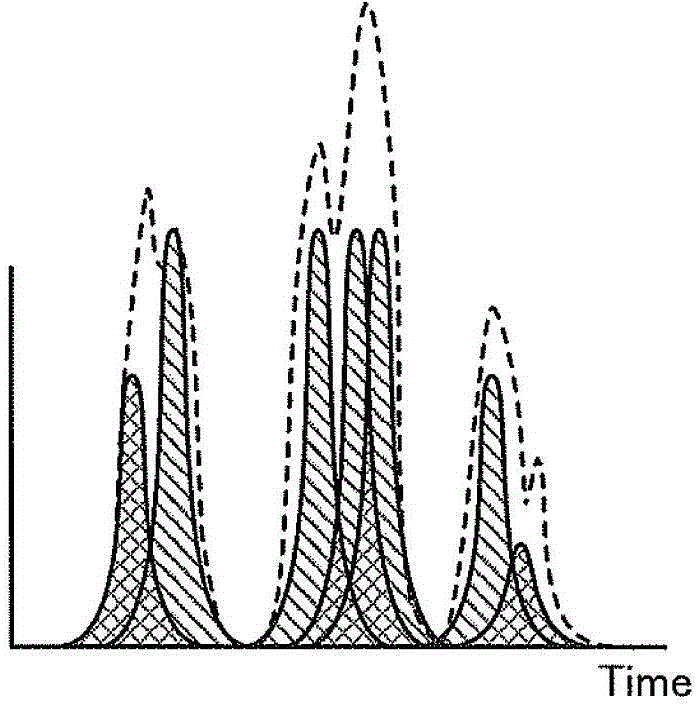
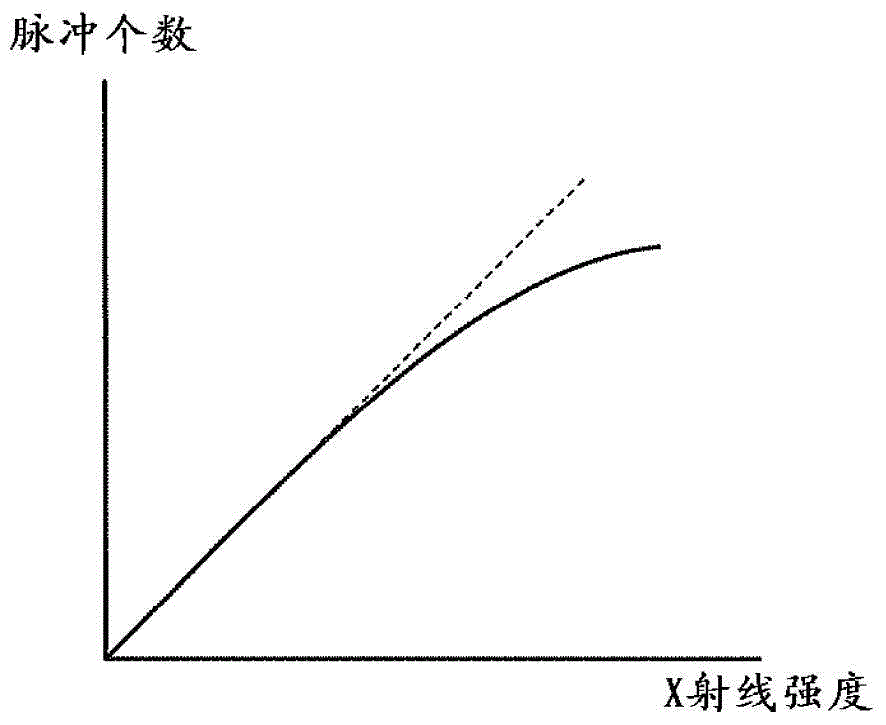
[0029] However, in photon counting CT, when the amount of incident radiation is large, "pile up" in which data counted by individual photons is accumulated occurs. When stacki...
no. 2 Embodiment approach
[0082] In the second embodiment, a case where the detector 13 is configured differently from the first embodiment will be described. In addition, the X-ray CT apparatus according to the second embodiment has the same configuration as the X-ray CT apparatus according to the first embodiment described using FIG. 1 except for the detector 13 .
[0083] In the detector 13 according to the second embodiment, the plurality of first elements 131 constituting the first element group and the plurality of second elements 132 constituting the second element group are two-dimensionally dispersed and arranged. Figure 8A as well as Figure 8B It is a figure for demonstrating an example of the detector concerning 2nd Embodiment. For example, if Figure 8A As shown, the first element 131 and the second element 132 are respectively arranged in an element row along the body axis direction in the detector 13 . and, if Figure 8A As shown, the element rows of the first element 131 and the el...
no. 3 Embodiment approach
[0089] In the third embodiment, for the case of performing the control process for reducing the radiation caused by the first scan, use Figure 9 Be explained. Figure 9 It is a figure for demonstrating the 1st scan concerning 3rd Embodiment.
[0090] In addition, the X-ray CT apparatus according to the third embodiment has the same configuration as the X-ray CT apparatus according to the first embodiment described with reference to FIG. The implementation is different. Hereinafter, the first scan performed in the third embodiment will be described.
[0091] The scan control unit 33 according to the third embodiment performs the first scan by irradiating the half circumference of the subject P with X-rays. That is, if Figure 9 As shown, the scan control unit 33 performs only X-ray irradiation in the range "from 0 degrees to 180 degrees". In other words, the first scan performed in the third embodiment is a half scan.
[0092] In addition, the scan control unit 33 accord...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com