A space-borne auxiliary GPS method and system based on dynamic orbit extrapolation
A technology of orbit extrapolation and dynamics, which is applied in the field of satellite navigation and positioning, can solve problems such as loss of positioning, achieve the effects of reducing positioning time, shortening cold start time, and improving positioning accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0025] The spaceborne assisted GPS method and system based on dynamic orbit extrapolation provided by the present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings.
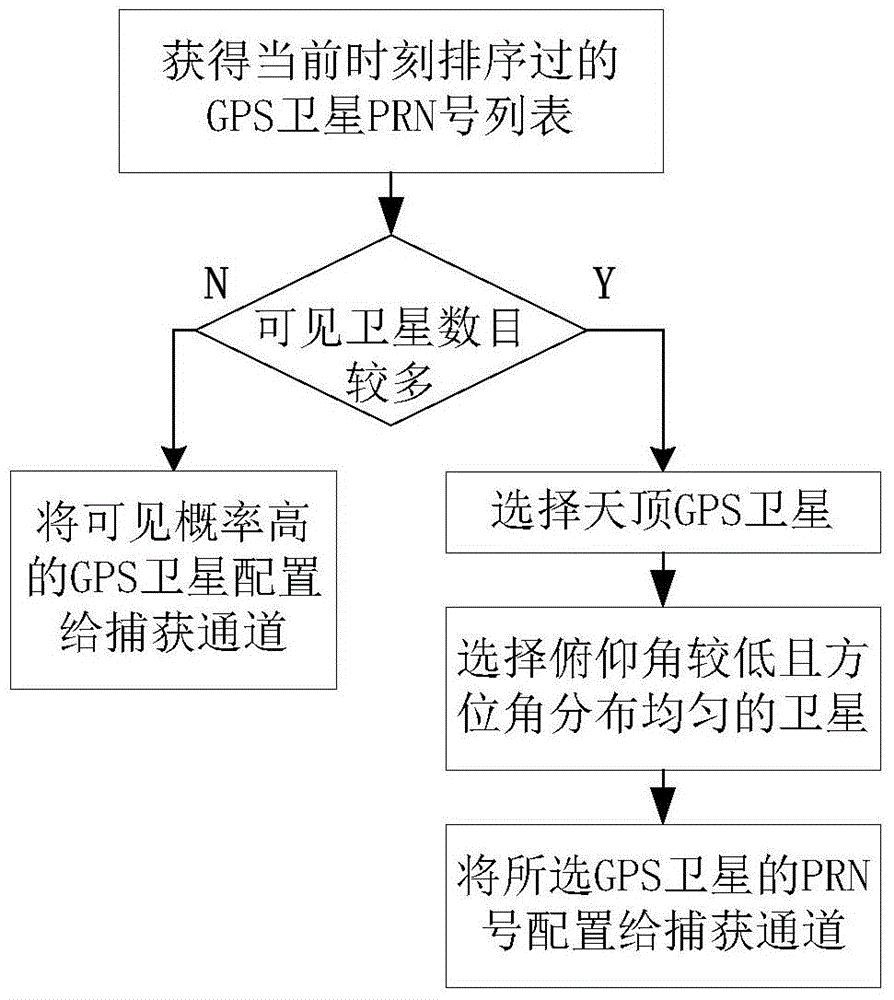
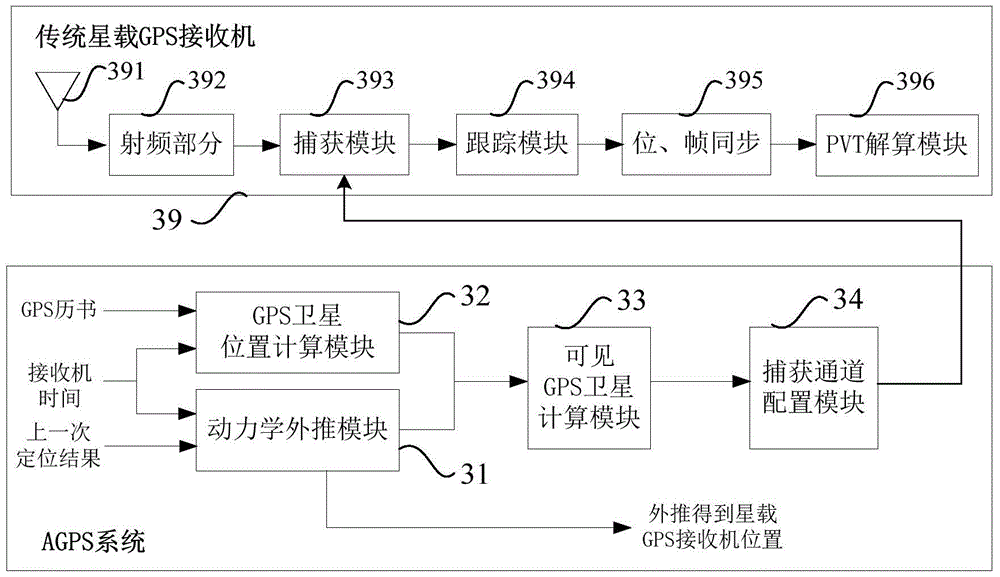
[0026] refer to figure 1 , the flow chart of the spaceborne assisted GPS method based on dynamic orbit extrapolation according to the present invention, said method comprises the following steps: S11: according to the low orbit satellite dynamic model and J2000.0 coordinate system under the spaceborne GPS receiver Extrapolate the orbital position of the latest positioning result, obtain the extrapolated position of the spaceborne GPS receiver and convert it to the ECEF coordinate system; S12: Calculate and obtain the positions of all GPS satellites in the ECEF coordinate system according to the effective GPS almanac; S13: Calculate the same ephemeris The pitch angle of all GPS satellites to the on-board GPS receiver at Yuan time, judge whether each GPS satellite is visible ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com