Magnetic brake
A technology of electromagnetic brakes and brake discs, applied in the direction of brakes, brake types, brake components, etc., can solve the problems of large force on the rotating body, braking impact, and the impossibility of applying industrial robotic arms, etc., to achieve the maximum installation space The effect of minimal constraints and compact structure production
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
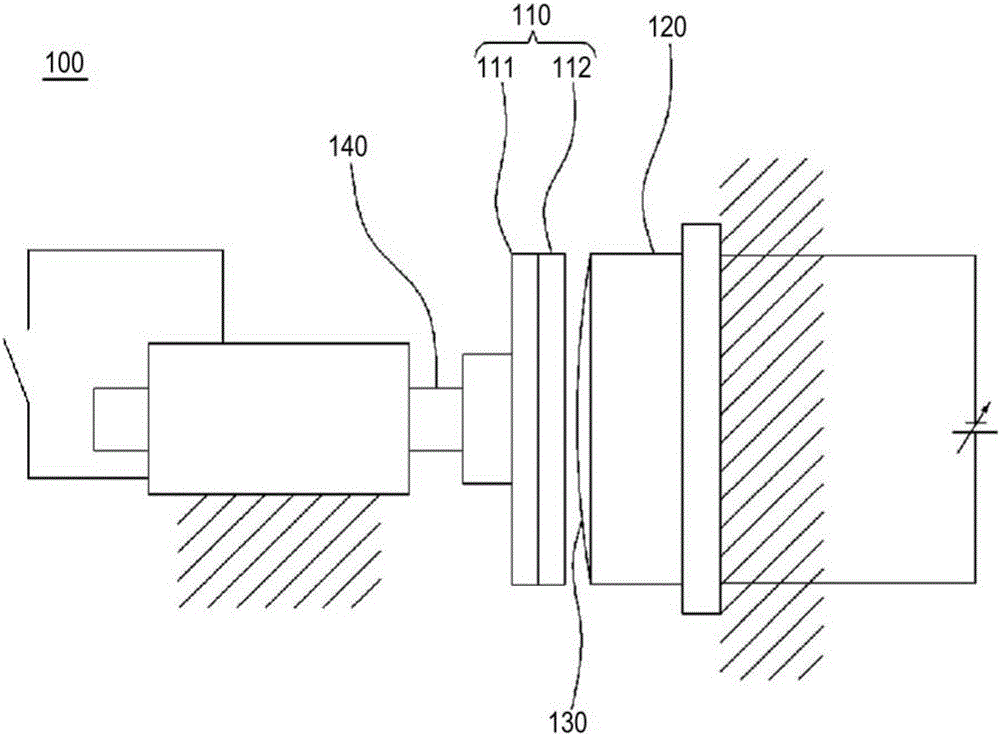
[0035] refer to figure 1 , the electromagnetic brake according to the first embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0036] figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the electromagnetic brake of the first embodiment of the present invention, figure 2 is another schematic diagram of the electromagnetic brake according to the first embodiment of the present invention.
[0037] if refer to figure 1 and figure 2 , The electromagnetic brake 100 of the first embodiment of the present invention includes a brake disc portion 110 , a brake shoe portion 120 , and a buffer means 130 .
[0038] The brake disc portion 110 is axially mounted on the rotating body 140 so as to be able to rotate in conjunction with the rotating body 140 . Wherein, preferably, it is slidably mounted on the rotating body 140 in an axial manner, so that the brake disc portion 110 moves toward the brake shoe along the rotating body 140 when the power is connected to the brake shoe portion 120 . ...
Embodiment 2
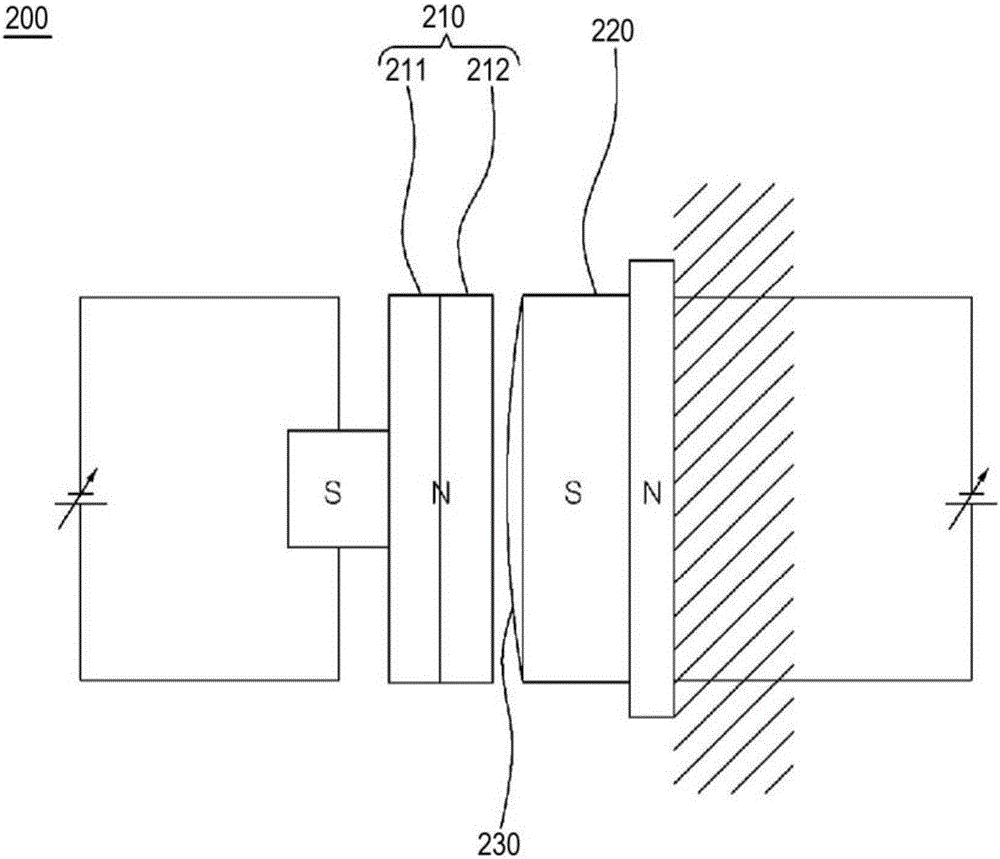
[0050] refer to image 3 and Figure 4 , the electromagnetic brake according to the second embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0051] image 3 is a schematic diagram of an electromagnetic brake according to a second embodiment of the present invention, Figure 4 is another schematic diagram of the electromagnetic brake according to the second embodiment of the present invention.
[0052] The electromagnetic brake of this embodiment is the same as the electromagnetic brake of the first embodiment except for a part of the brake disc unit, and thus detailed descriptions of other constituent elements other than the part of the brake disc unit are omitted.
[0053] if refer to image 3 and Figure 4 , the brake disc portion 210 of the electromagnetic brake 200 according to the second embodiment of the present invention is mounted on the rotating body in a shaft manner so as to be able to rotate in conjunction with the rotating body (not shown in the figure...
Embodiment 3
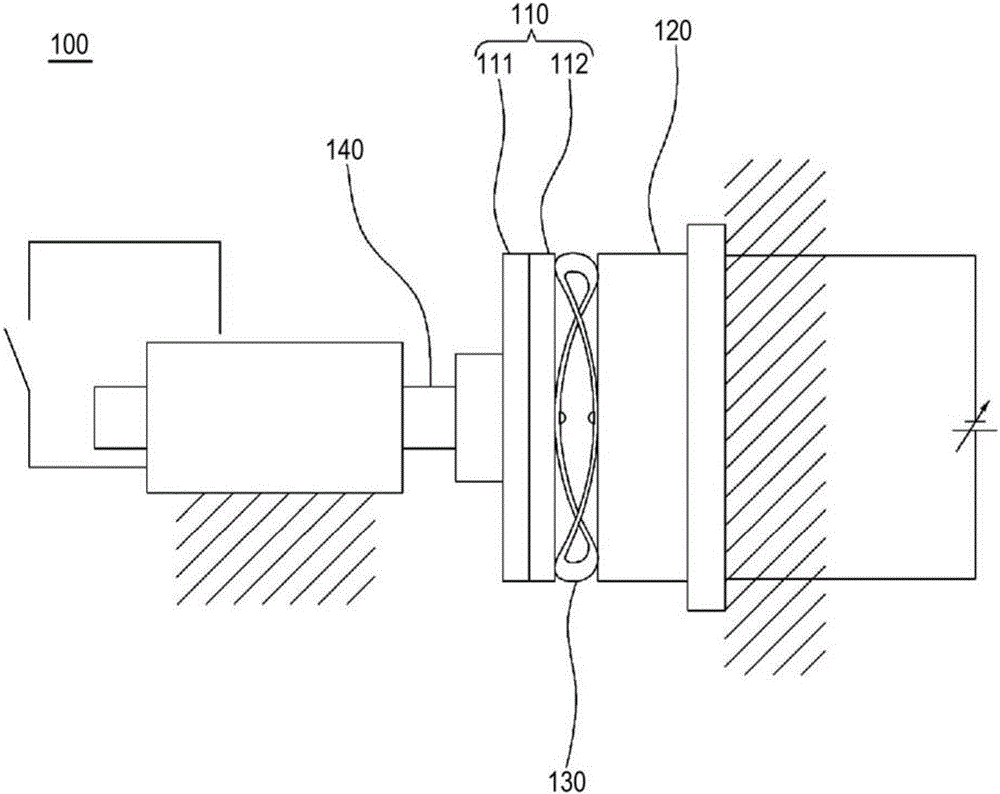
[0063] refer to Figure 5 and Figure 6 , the electromagnetic brake according to the third embodiment of the present invention will be described.
[0064] Figure 5 is a schematic diagram of an electromagnetic brake according to a third embodiment of the present invention, Figure 6 It is a front view for explaining the structure of a shoe part.
[0065] The electromagnetic brake of this embodiment is the same as the electromagnetic brake of the first embodiment except for a part of the brake shoe part, so detailed descriptions of other constituent elements except for a part of the brake shoe part are omitted. For example, the same / similar constituent elements are assigned the same reference numerals. On the other hand, this embodiment may not include the buffering means disclosed in the first embodiment.
[0066] if refer to image 3 The brake shoe portion 320 of the electromagnetic brake 300 according to the third embodiment of the present invention is formed by concen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com