Fault feature extraction method of weak transient zero-sequence current on background of strong noise
A zero-sequence current and fault feature technology, applied in the field of power system distribution network fault line selection, can solve the problems of the grounding resistance of the fault point affecting the fault zero-sequence current, the complex structure of the power distribution network, and the inconspicuous fault characteristics.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
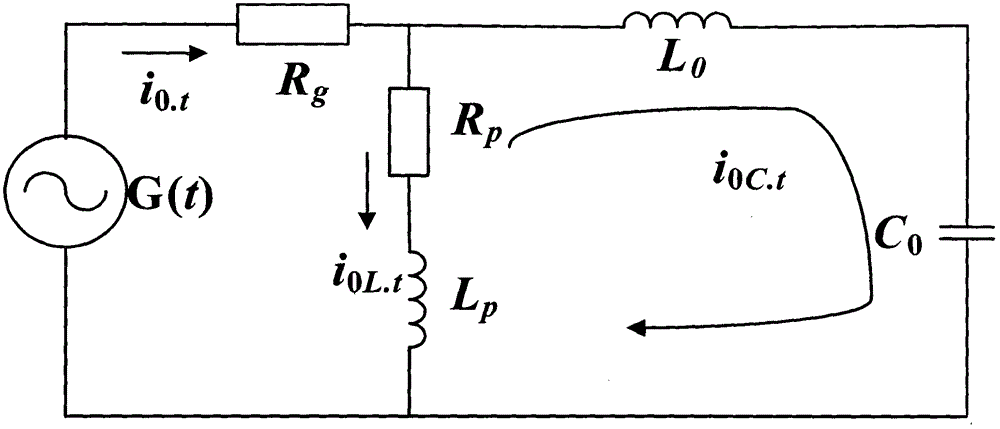
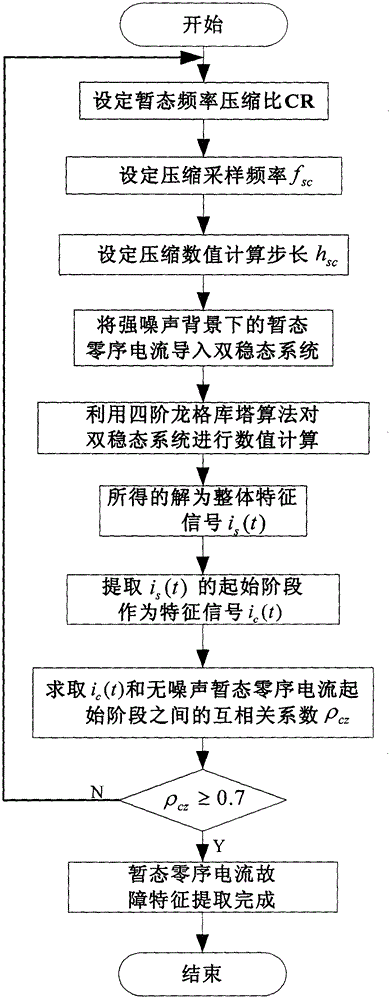
[0062] 1 Detection of transient zero-sequence current signal
[0063] image 3 It is a flow chart of the weak transient zero-sequence current fault feature extraction method under the strong noise background of the present invention. In order to check whether the variable-scale bistable system can detect the transient zero-sequence current (Transient Zero-SequenceCurrent, TZSC), the ideal transient zero-sequence current (TZSC) is defined. state zero sequence current i z (t) for
[0064] i z (t)=x 1 (t)+x 2 (t)+x 3 (t)+x 4 (t)+Г(t)(8)
[0065] x 1 (t)=5.6cos(2π×50t+60°)(9)
[0066] x 2 (t)=40e -56t cos(2π×250t+30°)(10)
[0067] x 3 (t)=72e -102t cos(2π×315t)(11)
[0068] x 4 (t)=10e -5.5t (12)
[0069] In formula (8): x 1 (t) is a power frequency signal with a smaller amplitude; x 2 (t) is the fifth harmonic with larger amplitude; x 3 (t) is a non-integral harmonic with a large amplitude; x 4 (t) is the attenuation DC component; Г(t) is the noise. It is w...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com