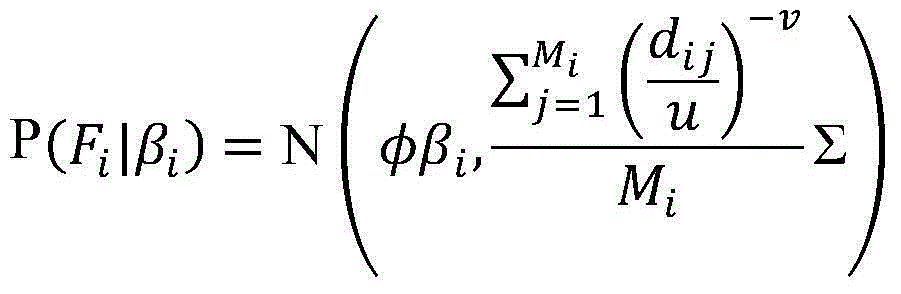Probability linear speaker-distinguishing identifying method based on priori knowledge structured covariance
A technology for speaker identification and linear identification, which is applied in the field of speaker identification based on probabilistic linear identification analysis based on prior knowledge normalization and covariance, which can solve problems such as erasure and achieve the effect of improving the effect.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0031] The drawings are for illustrative purposes only, and should not be construed as limitations on this patent; in order to better illustrate this embodiment, some parts in the drawings will be omitted, enlarged or reduced, and do not represent the size of the actual product;
[0032] For those skilled in the art, it is understandable that some well-known structures and descriptions thereof may be omitted in the drawings. The technical solutions of the present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
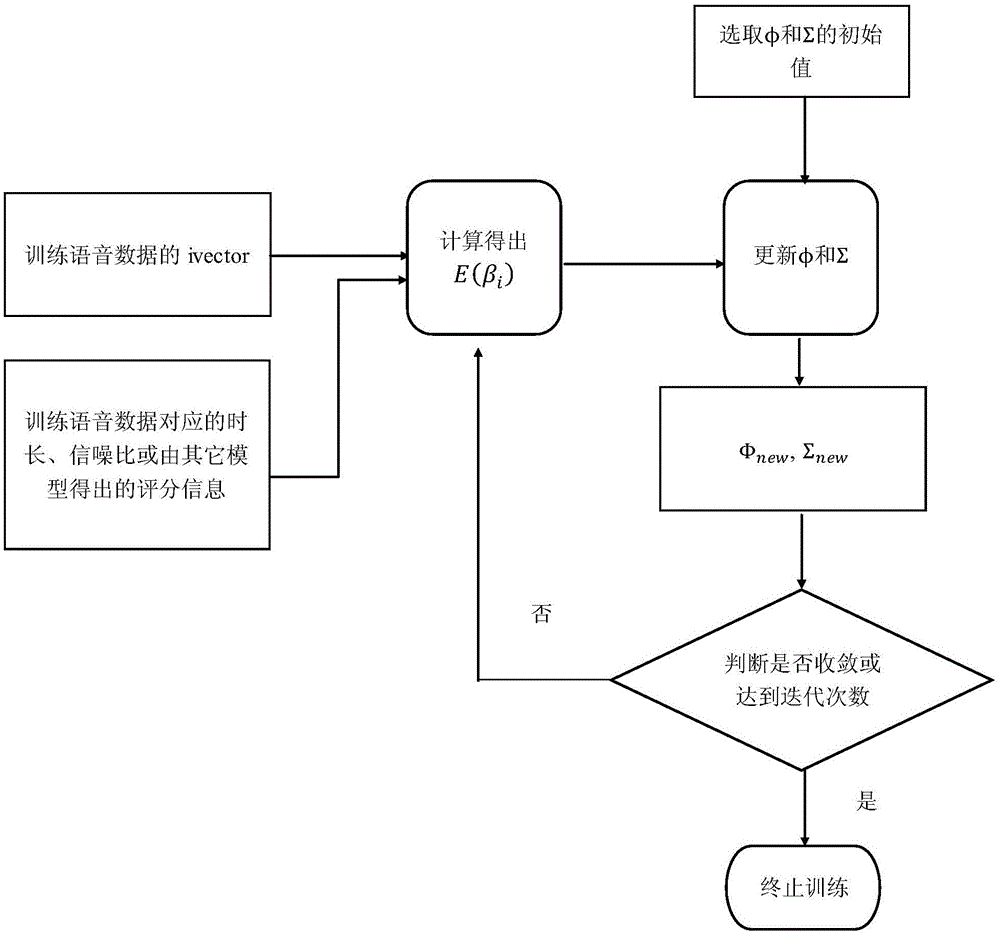
[0033] figure 1 In the present invention, the inherent physical information of the training speech, such as duration, signal-to-noise ratio, and scoring information obtained from other models, is used as a regularization process for the prior knowledge of this model training. In this embodiment, the duration of the training speech is selected as the prior knowledge. Covariance regularization.
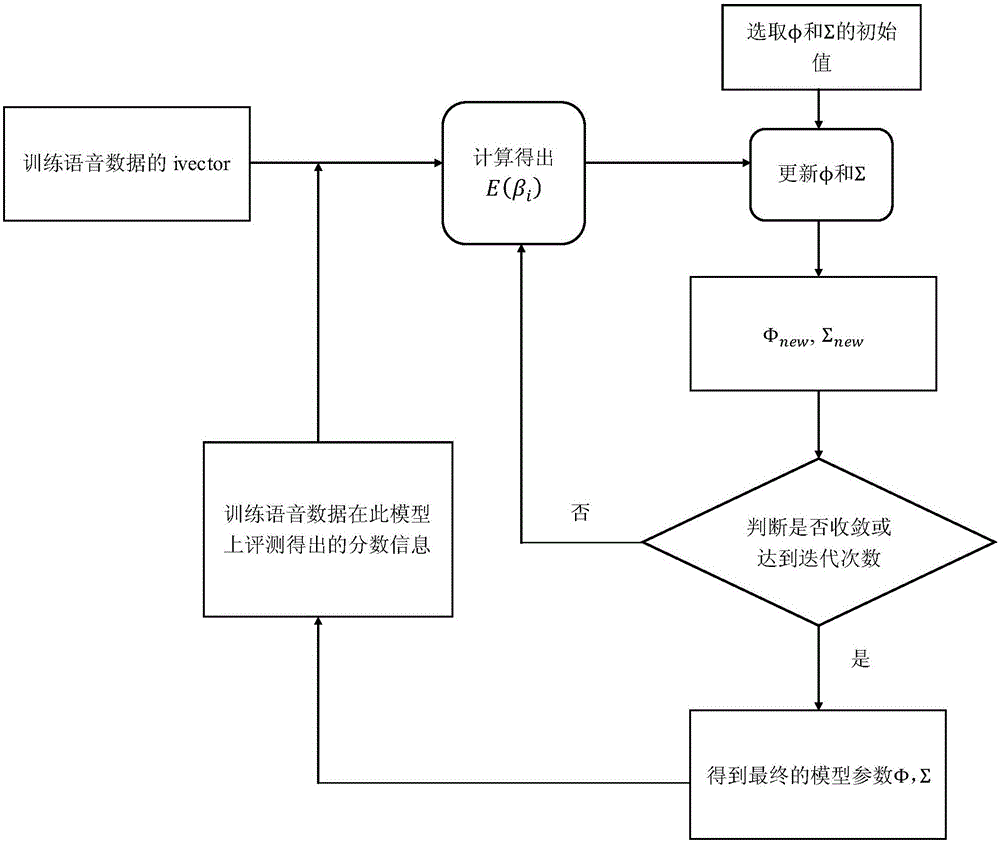
[0034] figure ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com