Compound preparation of active ingredients of traditional Chinese medicine for treating non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its use
A technology for fatty liver disease and active ingredients, which is applied to medical preparations containing active ingredients, organic active ingredients, pharmaceutical formulations, etc., and can solve the problems of lack of microscopic analysis of medicinal substances and quality control of components.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
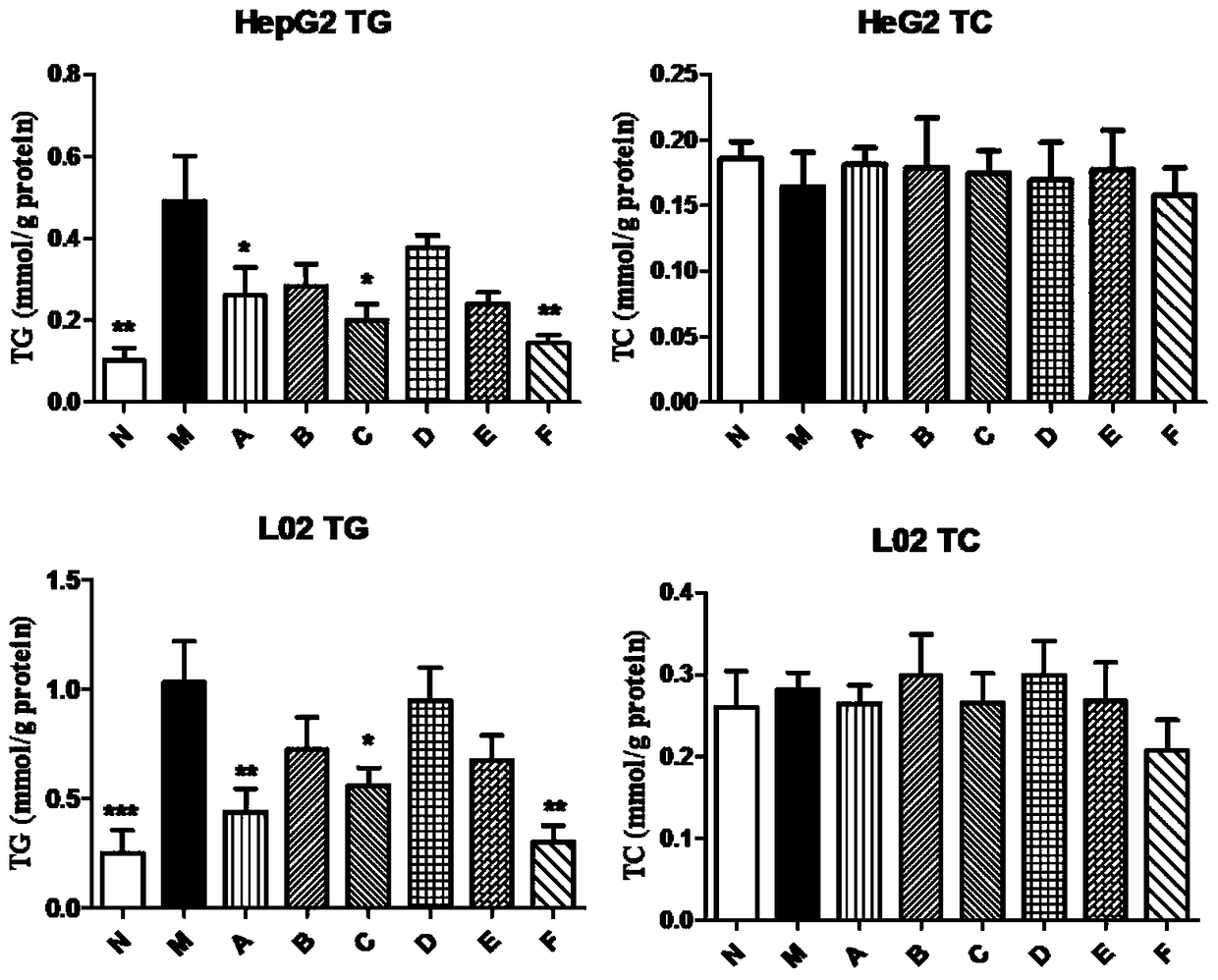
[0031] Embodiment 1 (screening out effective medicinal composition and optimal medicinal composition ratio scheme)
[0032] First determine the safe dose of the medicinal components, and then intervene the fatty degeneration cells with the monomer for 24 hours. (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) activity levels to evaluate the drug efficacy, and then carry out dose compatibility of the effective monomers and screen the optimal ratio scheme according to the above indicators.
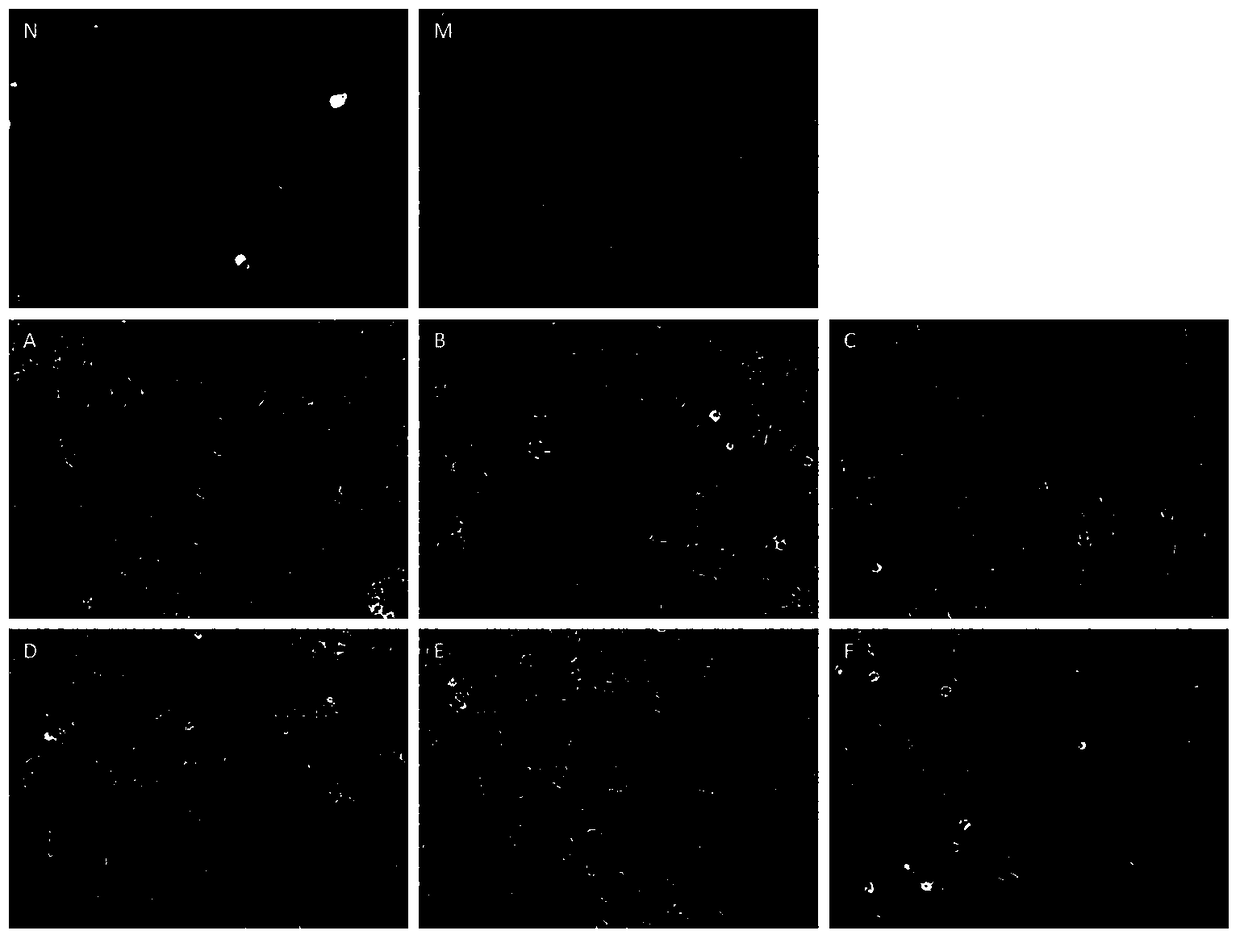
[0033] 1. Establishment of Steatosis Cell Model
[0034] Stimulate HepG2 and L02 cells with 1 mM free fatty acid (FFA), containing different ratios of oleic acid and palmitic acid, for 24 hours, and observed a large number of lipid droplets in the cells by oil red staining with an inverted optical microscope. ALT activity in the cell supernatant was induced by fatty acids. After 24h, it was significantly up-regulated compared with the control, indicating that the simple steatosis model and the ...
Embodiment 2
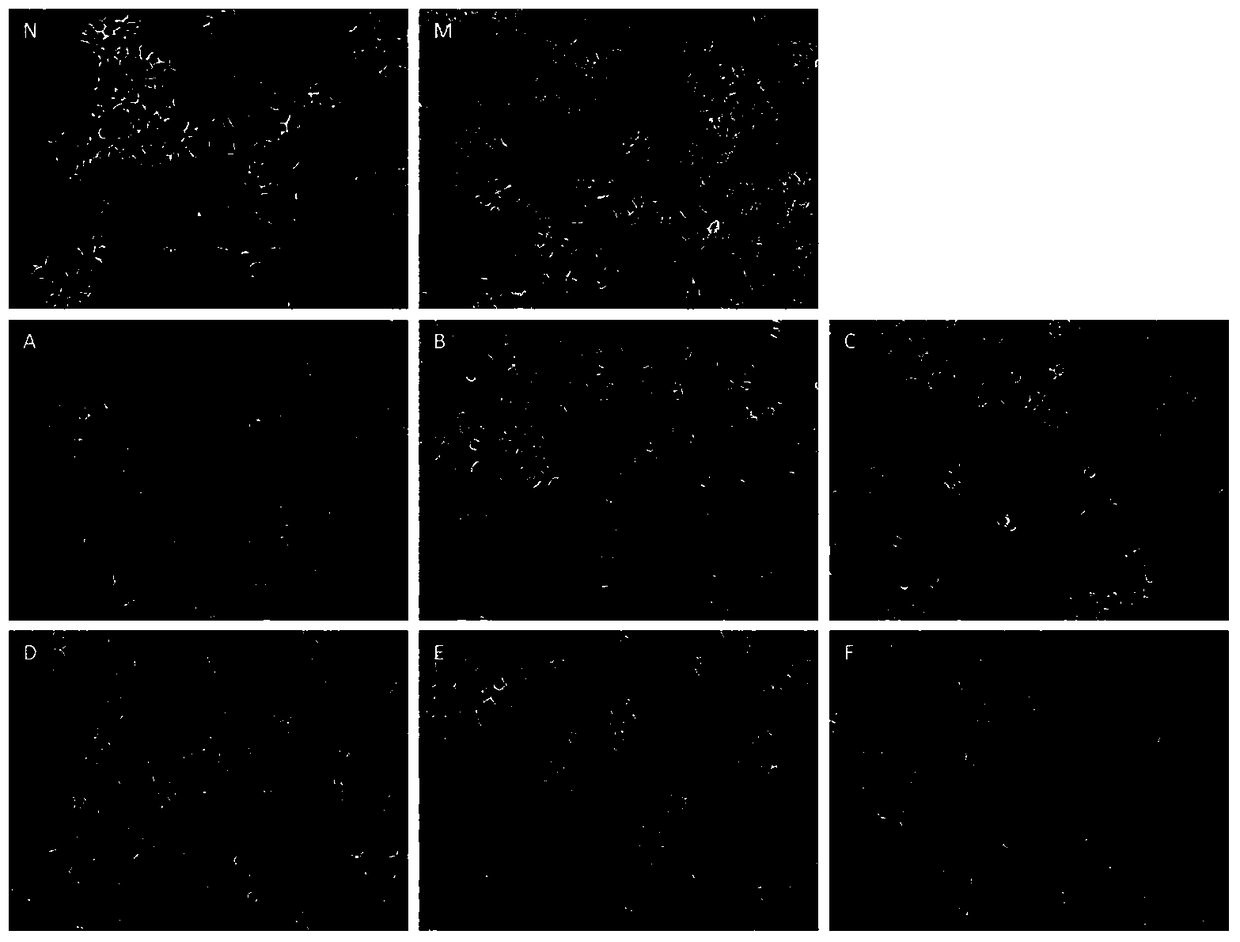
[0045] Example 2 ( Describe the pharmacodynamic mechanism of the optimal drug ingredient ratio scheme)
[0046] Select the most effective drug for lowering lipid and transaminase and the compatibility F to intervene in HepG2 cells with steatosis, and conduct a preliminary study on the mechanism of further pharmacodynamics, mainly including oxidative stress and lipid metabolism-related signaling molecules.
[0047] 1. Mechanisms related to oxidative stress
[0048] Firstly, the effect of the drug on the content of oxygen free radicals in the cells is detected. The fluorescent probe DCFH-DA was used to detect intracellular reactive oxygen species (ROS). The control cells had no obvious green fluorescence, but the cells in the model group had strong green fluorescence, indicating that the steatotic liver cells established with 1mmol / L oleic acid and palmitic acid In the presence of oxidative stress, drug F can significantly reduce the ROS content ( Figure 4 ). Malondialdehy...
Embodiment 3
[0051] Embodiment 3 ( Optimum ratio of ingredients to test drug efficacy in mice)
[0052] SPF grade male C57BL / 6 mice, about 20g, were randomly divided into control group (C), model group (M), high dose of F (HF), medium dose of F (MF), low dose of F (LF) and berberine group (BBR). Except for the control group which was given normal feed, the rest were given 60% high-fat feed. After 3 weeks of modeling, each intervention group was intragastrically administered the corresponding drugs for 4 weeks. Among them, H, middle and low groups were given drug F 52, 26, 13 mg / kg / day respectively, and BBR group was given berberine 100 mg / kg / day. After 4 weeks of drug intervention, the patients were fasted for 8 hours, weighed, the eyeballs were removed, blood was collected, and the serum was separated and frozen for testing. The cervical vertebrae were dislocated and sacrificed, and the liver tissue was weighed. Fix in 10% formaldehyde. Serum and liver indicators were detected.
[...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com