Method for evaluating shallow lake fishery environment by using microbial food web efficiency
A food web and shallow water technology, applied in the direction of testing water, material inspection products, etc., can solve the problems of specific evaluation of the fishery environment, qualitative evaluation methods cannot be given, and cannot play a guiding role in fishery operations, so as to achieve the effect of protecting the environment
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] Embodiment 1: This embodiment provides a method for evaluating the fishery environment of shallow water lakes using microfood web efficiency, and proceeds as follows:
[0037] S1. Determination of phytoplankton primary productivity, bacterial productivity and mesozooplankton productivity in shallow lakes;
[0038] S2. Microfood web efficiency FWEp of shallow lakes = mesozooplankton productivity / (phytoplankton primary productivity + bacterial productivity);
[0039] S3. Evaluate the fishery environment of shallow water lakes through microfood web efficiency FWEp. The smaller the value of microfood web efficiency FWEp, the worse the fishery environment quality of shallow water lakes.
[0040] The microfood web efficiency FWEp will decrease with the increase of lake eutrophication, the smaller the microfood web efficiency is, the worse the fishery environment quality will be.
[0041]In this embodiment, the evaluation criteria for the fishery environment quality of larg...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Embodiment 2: This embodiment provides a kind of method that utilizes microfood web efficiency to evaluate the fishery environment of shallow lake lake, and the step of evaluation is basically the same as in embodiment 1, also is by primary productivity of phytoplankton, bacterial productivity and mesozooplankton After the productivity is measured, the fishery environment of shallow lakes is evaluated by scientific calculation methods. The difference is that in this example, the primary productivity of phytoplankton, bacterial productivity and medium-sized zooplankton productivity in shallow lakes are estimated by empirical models. method, as follows:
[0066] (1) Determination of phytoplankton chlorophyll a in shallow lakes to obtain the concentration Chla of chlorophyll a.
[0067] The method for measuring phytoplankton chlorophyll a is specifically:
[0068] Experimental supplies:
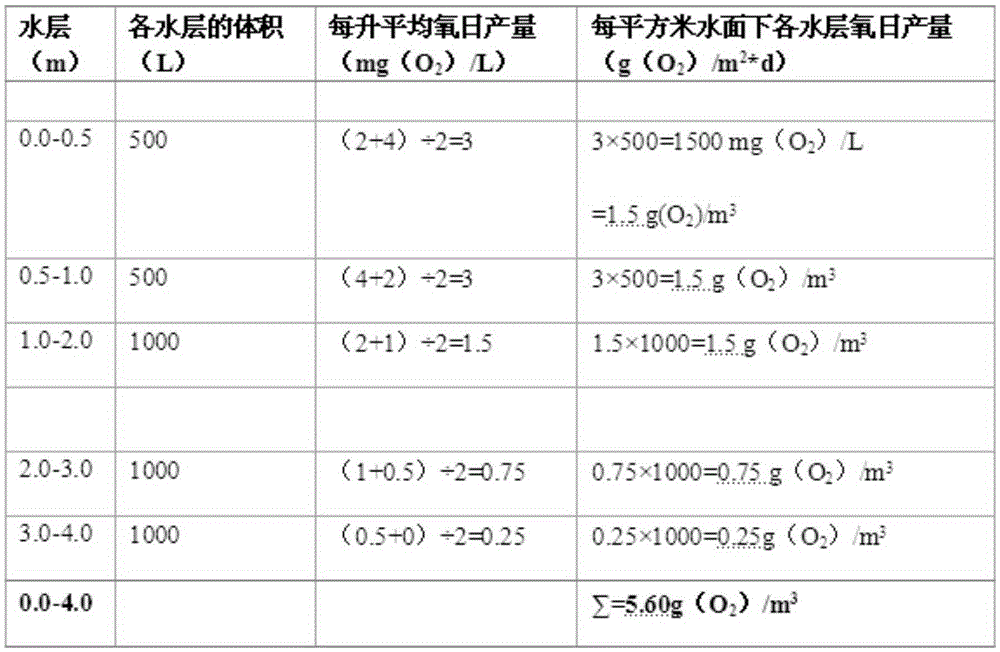
[0069] Model 721 spectrophotometer (or similar products), suction filter (47mm stai...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com