Method and quality control molecular based mouse embryo assay for use with in vitro fertilization technology
An embryo, assisted reproductive technology technology, applied in the field of quality control analysis of clinical assisted reproductive technology
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0101] Example 1: Evaluation of regulators of pluripotency
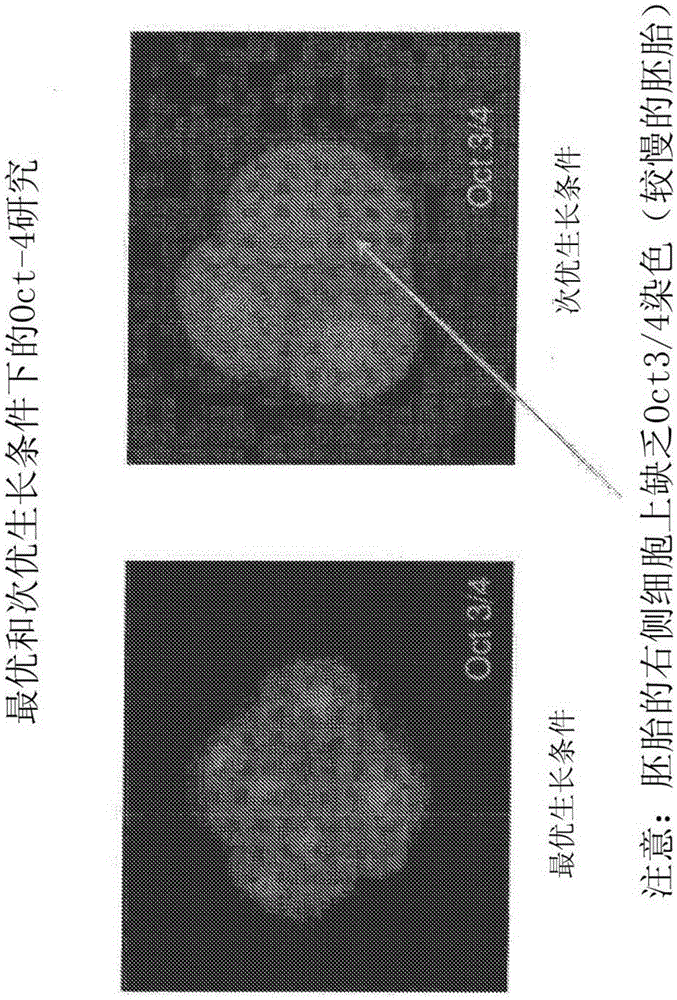
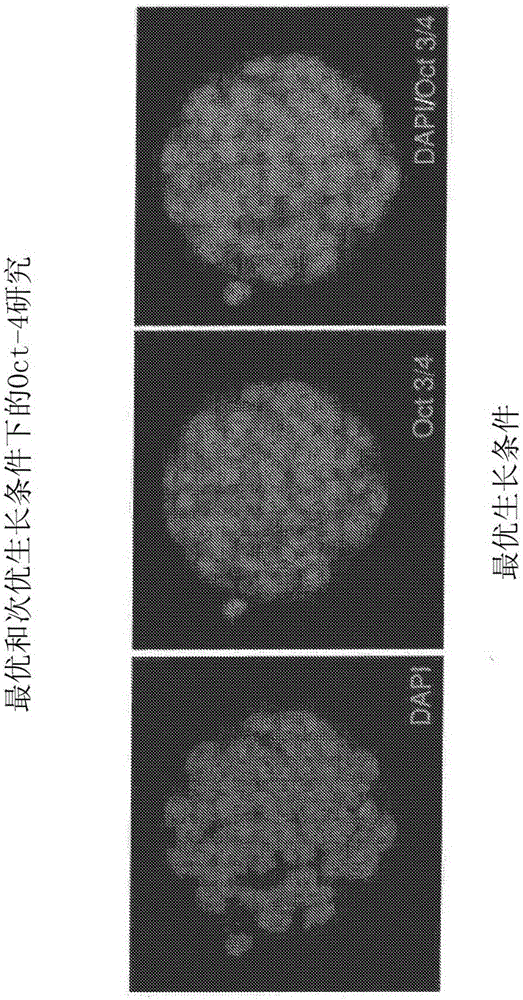
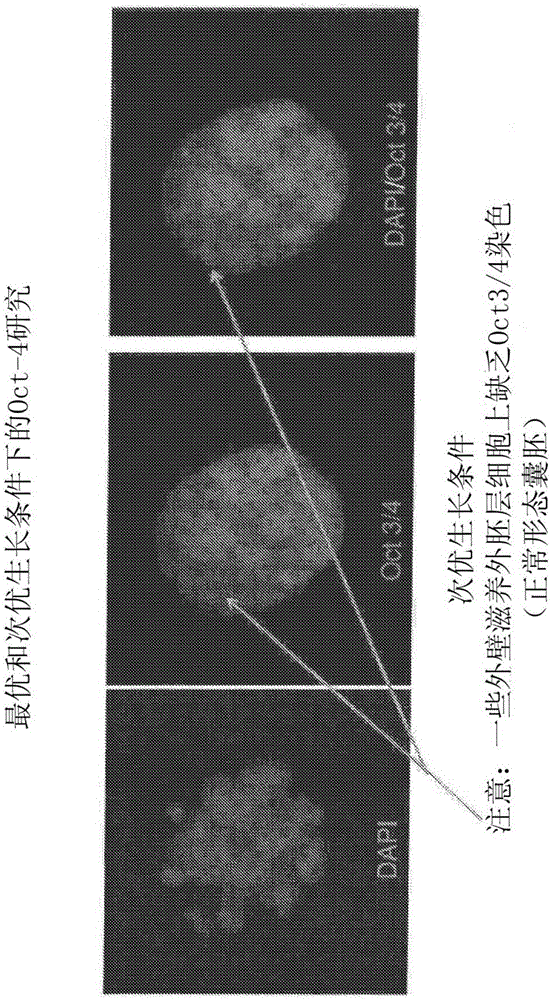
[0102] Several factors such as the toxicity and sterility of the media or materials used in ART can affect the development of the embryo. The following examples describe assays for assessing embryo viability under optimal and suboptimal culture conditions. This example shows embryos in which regulators of pluripotency were visualized using fluorescence microscopy. Markers of pluripotency for evaluating embryonic development at the one-cell or two-cell stage of development include, for example, SOX2, Oct-4, Nanog, and their upstream mediators and downstream effectors, the upstream mediators and Downstream effectors play a role in ensuring normal embryonic development.
[0103] To test media, media supplements, or ART consumables, collected transgenic embryos were first incubated in 50 μL droplets of control media (the media identified to promote optimal blastocyst development) or test media. In each case, embryos w...
Embodiment 2
[0114] Example 2: Molecular Mouse Embryo Analysis
[0115] Transgenic mice containing reporter genes linked to pluripotency markers were used to perform molecular-based mouse embryo analysis (mMEA) under optimal and suboptimal conditions. Transgenic male mice expressing enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP) under the control of the POU protein domain class 5 transcription factor 1 (Pou5fl, also known as Oct-4) promoter and distal enhancer (B6; CBA -Tg(Pou5f1-EGFP)2Mnn / J; Jackson Laboratory).
[0116] Transgenic male mice were mated with superovulated wild-type (B6D2F1) female mice. Single-cell embryos were collected and cultured in groups of 3 to 4 embryos per 20 μL droplet of medium, or a single embryo per 10 μL droplet of medium, depending on the experiment performed. Embryos were cultured for 96 hours under optimal or suboptimal conditions. Fluorescence shows the expression of the Oct-4-EGFP transgene.
[0117] a. Comparison of morphological development and Oct-4 ex...
Embodiment 3
[0122] Example 3: Molecular Mouse Embryo Analysis for Evaluating Blastocyst Development in the Presence of Different Quality Oils
[0123] Transgenic mouse embryos containing CDX2-GFP were used to perform experiments in the presence of oils of different qualities ((1) good oil, (2) 5% low-quality oil, (3) 7.5% low-quality oil, (4) 10% low-quality oil, and (5) Molecular-based mouse embryo analysis (mMEA) under the condition of 15% inferior oil). Eighteen embryos were tested for each of the oil qualities listed above. Embryos were assessed morphologically for blastocyst development at 48 and 96 hours using a stereomicroscope, and also at 48 and 96 hours using a fluorescent microscope for GFP expression. Using conventional MEA procedures, any embryos (expanded and hatching blastocysts) with a 96-hour score of 80% or higher passed the test, and as such, the parameters of the test were considered achievable. As shown below, speciation analysis alone is not as sensitive as the mol...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com