A high-performance magnetoresistive device and its manufacturing process
A magnetoresistive device, high-performance technology, applied in the fields of magnetic field-controlled resistors, the manufacture/processing of electromagnetic devices, semiconductor devices, etc., can solve the problems of small input resistance and cannot be practically applied, and achieve the effect of large input impedance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
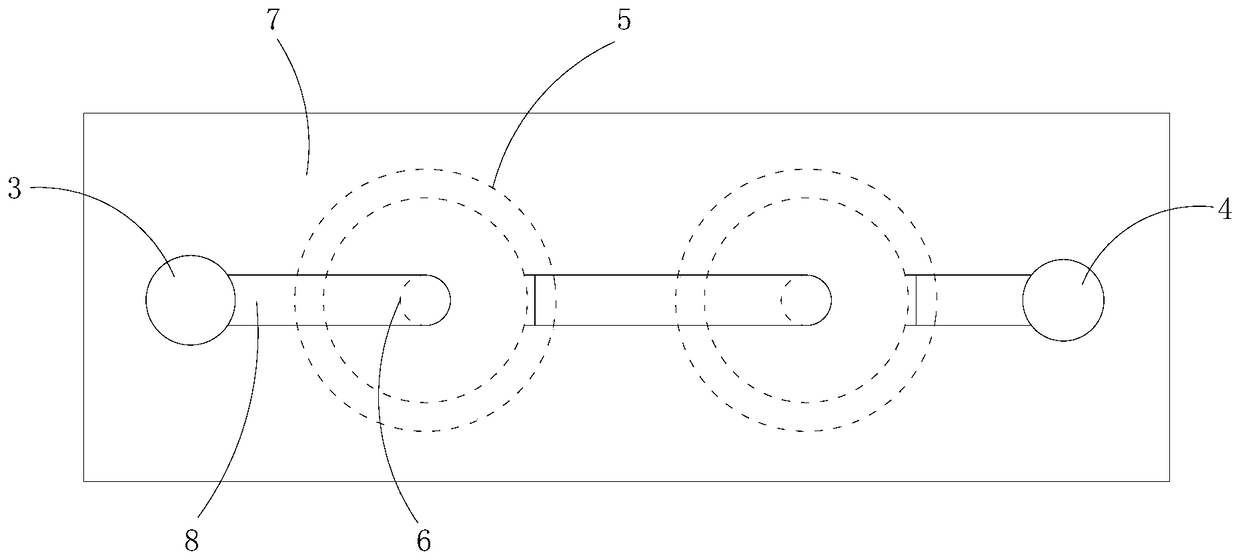
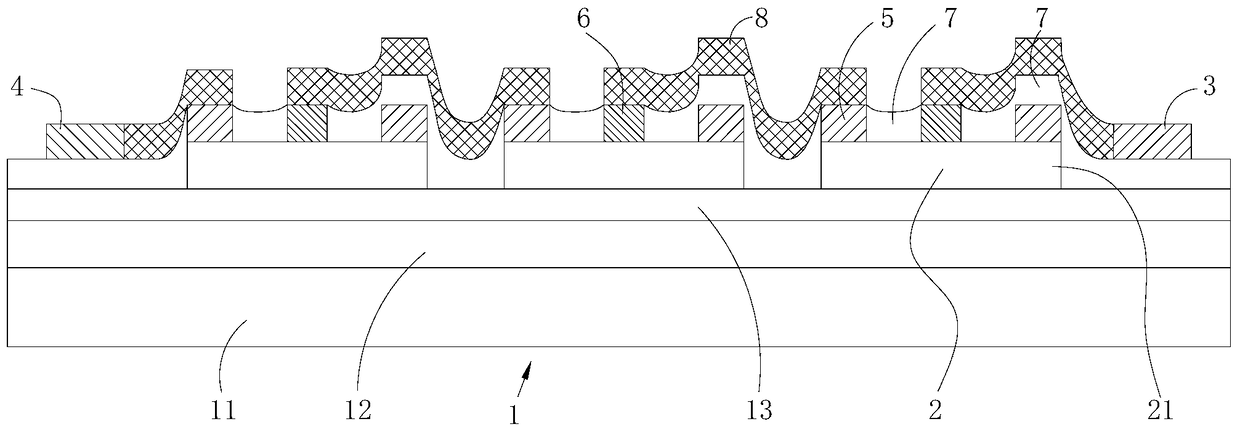
[0034] Refer to attached figure 2 (refer to attached image 3 ), a high-performance magnetoresistive device in this embodiment, which includes a substrate 1 (attached figure 2 covered under the insulating film), a plurality of InSb thin film disks 2 arranged in sequence on the substrate 1 (attached figure 2 covered under the insulating film), the ring electrode 5 on the InSb thin film disk 2 (attached figure 2 In the figure, the part where the ring electrode is covered under the insulating film is indicated by a dotted line), the center electrode 6 on the InSb thin film disk 2 and inside the ring electrode 5 (attached figure 2 Covered by the connecting electrode 8 ), on the ring electrode 5 and partly covering the insulating film 7 of the ring electrode 5 .
[0035] The insulating film 7 covers each ring electrode 5, and a plurality of first openings and a plurality of second openings are opened above each ring electrode 5 so that each ring electrode 5 has a part from ...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Refer to attached image 3 , the difference between a high-performance magnetoresistive device in this embodiment and the first embodiment is only that: the number of InSb thin film disks 2 and connecting electrodes 8 is different from that of the first embodiment.
[0048] In this embodiment, the first electrode 3 is a negative electrode, and the second electrode 4 is a positive electrode.
[0049] The substrate 1 in this embodiment includes a substrate layer 11 , a transition layer 12 , and an insulating layer 13 arranged in sequence from bottom to top. The thickness of the substrate layer 11 is 100 μm-1000 μm, and the material is ceramic, silicon, ferrite or mica. The thickness of the insulating layer 13 is 0.01 μm to 10 μm, and the material is In 2 o 3 or SiO 2. The material of the transition layer 12 is a compound containing at least one metal element in the same group as In including In. The compound contains at least Sb, and the compound only contains metal ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com