Spun-laid webs with at least one of lofty, elastic and high strength characteristics
A fabric, tensile strength technology, used in textiles, fabrics, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve problems such as sticky hands, difficult, expensive, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
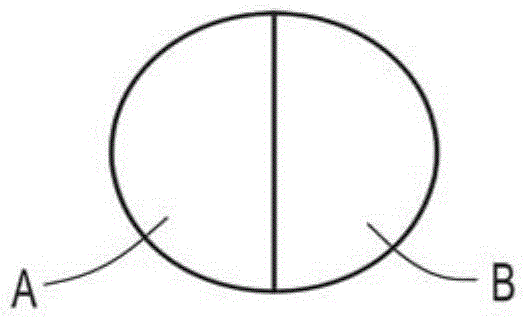
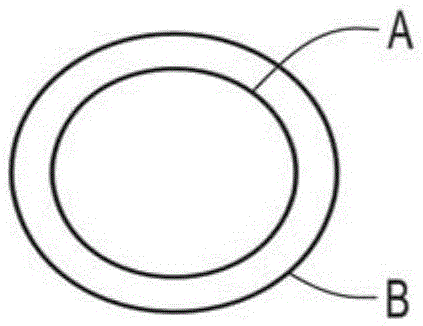
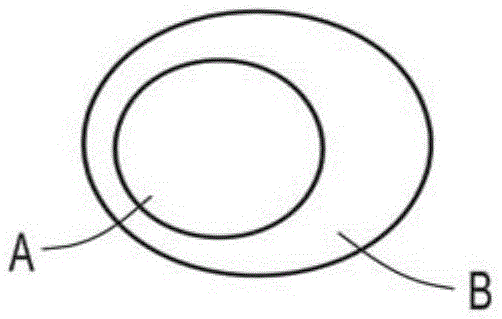
[0058] Slightly eccentric core-sheath fibers of continuous filaments spun into fabrics (e.g., with Figure 1C elaborating the geometry of the fiber) using the figure 2 A similar system is formed as shown. The core-sheath fibers consist of polylactic acid (PLA) polymer as the sheath ( Figure 1C The polymer component B) and polypropylene as the core ( Figure 1CThe polymer component A) in. In particular, PLA polymers are commercially available from NatureWorks Corporation (Minnesota) under the trade designation PLA6302, and polypropylene polymers are commercially available from Lyondell Bassell Industries (Texas) under the trade designation PPPH-835. The resulting eccentric core-sheath fibers include a slightly non-circular or irregularly shaped core. The cross-sectional view of the collection of fibers formed is shown in image 3 as shown in the image.
[0059] Spun fabrics made from this fiber were completely free of bonding on the porous belt. Instead, the fabric is ...
Embodiment 2
[0065] Continuous filaments are spun into fabrics using similar figure 2 The system shown is prepared where side-by-side two-components are used to prepare fabrics (e.g. Figure 1A shown). The side-by-side components (Components A and B) were the same PLA and polypropylene components as used in Example 1. A cross-sectional view of the fiber assembly is shown in Figure 4 as shown in the image. Corresponding to the activation using a boiling water tank (as in Example 1 or a similar activation treatment station), the spun fabric showed very similar properties to the fabric described in Example 1 (increase in fabric thickness or Z-dimension, density reduction, and enhanced fabric strength, fabric uniformity and fabric elasticity). While there is some fibrillation in the fibers forming the fabric (eg, partial separation of polymer component A from polymer component B in bicomponent fibers), it does not negatively affect the properties achieved after activation of the fabric. ...
Embodiment 3
[0067] use with figure 2 A similar system as shown produces a plurality of different continuous filament spun fabrics, wherein the fabric includes two types of bicomponent fibers side-by-side, solid (such as Figure 1A shown) and hollow (as Figure 1E shown), and sheath-core bicomponent fibers (such as Figure 1B and / or 1C). The polymer components (components A and B) used to form each fabric were the same polylactic acid (PLA) and polypropylene (PP) components used in Example 1, but used in different fabrics with different The volumetric two-component ratio. After each continuous filament spun fabric is formed or activated, each activated fabric is subjected to a series of tests to determine certain properties of the fabric, such as fabric loft, fabric strength, and fabric elasticity. Test data for each fabric is provided in Tables 1-5.
[0068] Table 1 - Formed continuous filament spunbond web
[0069]
[0070] Table 2 - Tensile Strength Evaluation
[0071]
[...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com