Composite structural products
A technology for composite structures and products, applied in the field of composite structure products containing continuous fiber tensile elements and/or open mesh woven elements, which can solve the problems of non-conformity, expensive filling products, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1 - Composite Parts with Tensile Parts
[0055]A composite part is formed having opposing first and second planar surfaces and rib elements extending from the second surface. The composite part was formed from polypropylene and 40 wt% long fiber dispersion (RTP80107, available from RTP Company). The fiber dispersion had an average length of about 12 mm and an average diameter of about 20 microns. The tensile part is embedded within the composite part rib and along its entire length. Tensile parts are continuous fiber bundles or elements formed from thousands of parallel and coextensive glass fibers held together with polypropylene resin. The continuous fiber bundle is 60 wt% glass fibers. The diameter of the continuous fiber bundle is about 0.1 inches or about 2500 microns. The composite part weighed 11.7 g.
[0056] Comparative parts were formed using polypropylene and 40 wt% long fiber dispersion (RTP 80107 from RTP Company) within the rib element or with...
Embodiment 2
[0060] Example 2 - Composite part with impact part
[0061] Composite parts were formed by injection molding polypropylene and 40 wt% long fiber dispersion (RTP 80107, available from RTP Company) with open mesh woven elements in a 4 inch diameter mold. The fiber dispersion had an average length of about 12 mm and an average diameter of about 20 microns. The impact part is a 2oz / yd 2 Open mesh weave element with 8 fiber bundles / inch fiberglass mesh (Saint-Gobain Adfors, France).
[0062] A comparative part was formed using polypropylene and 40 wt% long fiber dispersion (RTP 80107, available from RTP Company) without an impact part (open mesh woven element).
[0063] result
[0064] Impact strength tests (Instrumented Dynatup test) were performed on both the composite part of Example 2 and the comparative part of Example 2. Compared to the comparative part of Example 2, the composite part withstands 2-3 times the impact force before breaking.
[0065] Further samples were f...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Example 3 - Composite Parts with Tensile Parts and Impact Parts
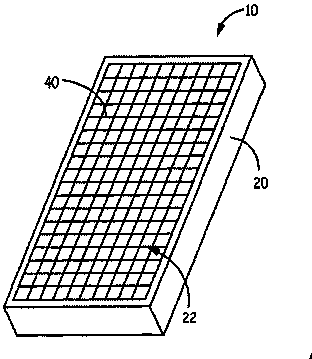
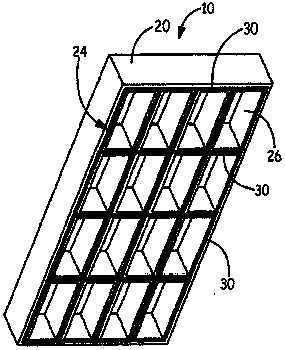
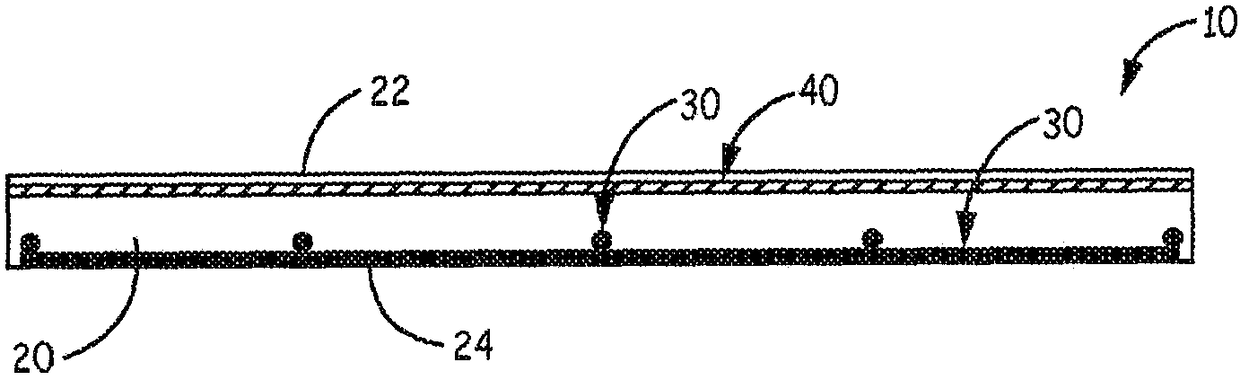
[0069] Such as Figure 1-3 Stencils are used as shown. Die measures 8 inches wide by 18 inches long and 1 inch thick. Five ribs are parallel to the width and five ribs are parallel to the length. The width ribs are perpendicular to the length ribs.
[0070] Polypropylene and either 40 wt% long fiber dispersion (RTP 80107 from RTP Company) or 30 wt% long fiber dispersion (RTP 80105 from RTP Company) or 20 wt% long fiber dispersion (RTP 80103 from RTP Company) were used , forming a composite article (with stretched components). A tensile member (described in Example 1) was embedded within each rib element. The comparative examples did not include tensile members.
[0071] result
[0072] Table 2 below reports the results of the bend test (three point bend test over a 15" span).
[0073] Table 2
[0074] Material Description
Bend test (pounds until failure)
RTP 80107 40% Fiber
...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com