IP address list storage and query method applied to DNS query
A DNS query and IP address technology, applied in the field of IP address list storage and query, to achieve the effect of reducing the number of queries
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
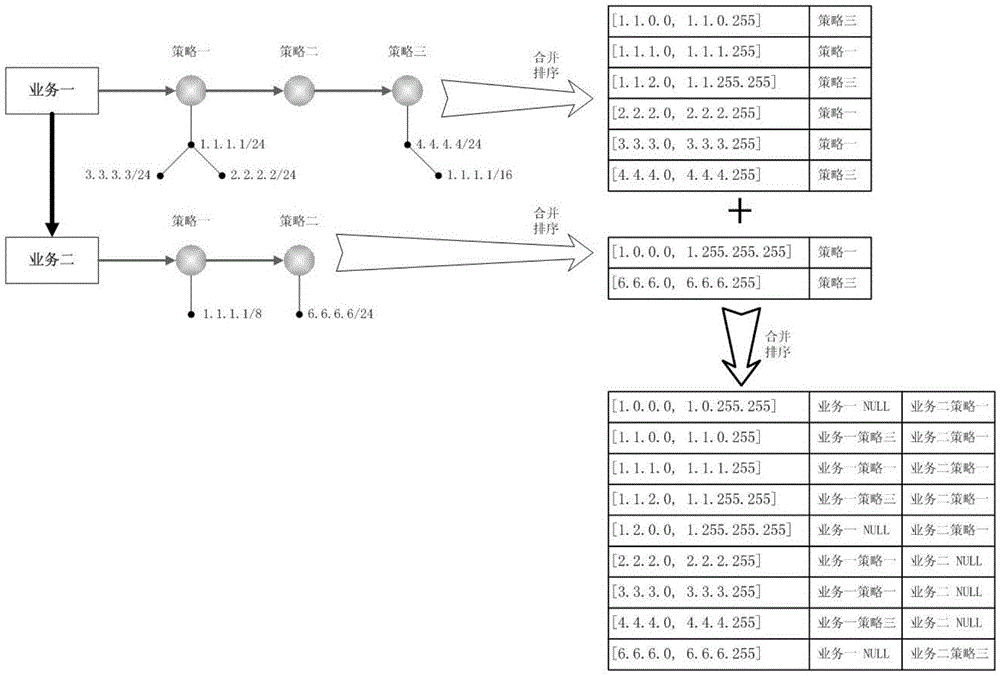
[0037] The merging process of this embodiment is as follows figure 1 , 2 shown, where figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of merging according to the priority principle, figure 2 It is a schematic diagram of merging according to the IP longest matching principle. During the merger process, according to the business requirements, follow the IP longest match principle or match according to the priority. The specific steps are described as follows:
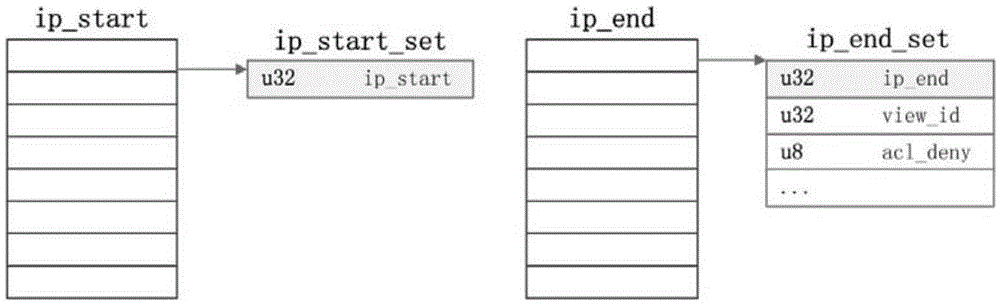
[0038] 1) The IP address list of each policy is deduplicated to build a red-black tree (RedBlackTree), with the IP segment as the key value (node key), and the policy id (policy identification), priority (depending on the specific business , the data requirements of nodes are different) as info (node data);
[0039] 2) Classify priority according to different services: authoritative View sets priority according to the order of configuration, recursive View determines priority according to configured priority, and can confi...
Embodiment 2
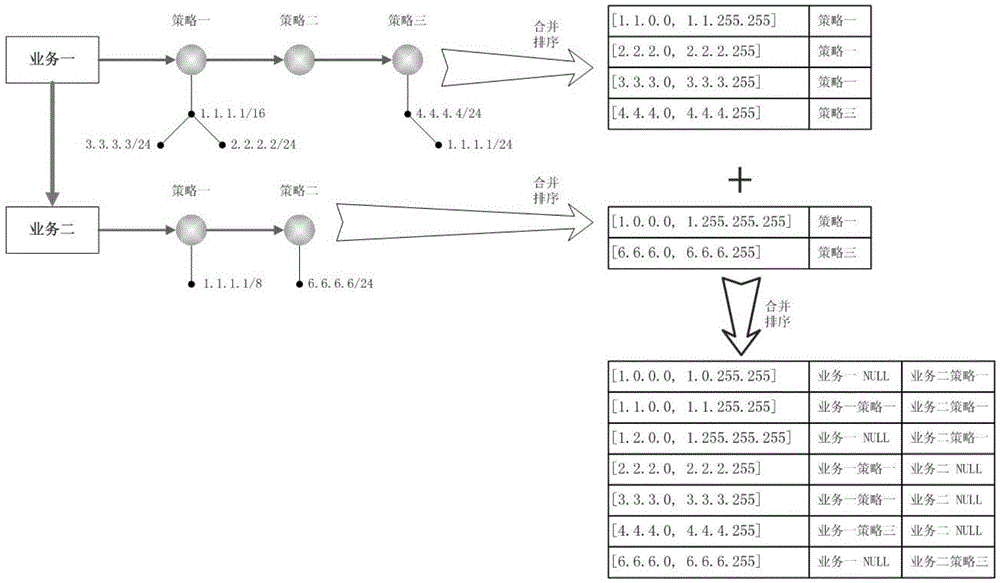
[0047] In this embodiment, the View business is still taken as an example. The specific merging process is as follows: Figure 4 , 5 shown, where Figure 4 It is a schematic diagram of merging according to each IP array, Figure 5 It is a schematic diagram of merging between groups according to the principle of priority. The specific steps are described as follows:
[0048] 1) Build an array for each View IP, and sort the array according to the size of the starting IP. The sorted results are as follows Figure 4 view1 and view2 on the left;
[0049] 2) Merge the IP arrays of view1 and view2 within the group to remove duplicate IP addresses. The result after deduplication is as follows Figure 4 view1 and view2 on the right;
[0050] 3) Split and merge the IP arrays of view1 and view2 according to the priority principle, and the final result (merged array) is as follows Figure 5 shown.
[0051] In the above embodiment, if the arrays are queried using the dichotomy meth...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com