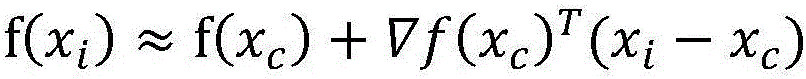Adaptive rendering method using linear prediction
An adaptive rendering and linear prediction technology, applied in the field of adaptive rendering, can solve the problems of high computing overhead and achieve the effect of reducing computing overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0050] The present invention will be described in detail below in conjunction with specific embodiments.
[0051] Such as figure 1 As shown, an adaptive rendering method using linear prediction, including:
[0052] Step 1, reconstruct the image using a local linear model.
[0053] First define a filter window The filter window is centered on pixel c. A filter window can be viewed as a collection of all pixels within the window.
[0054] Define another prediction window Including Note the filter window There is a global fixed size, which is 19*19 in this embodiment. in the forecast window In , the real image f(x) is predicted using a linear model with variable k.
[0055] Within the prediction window, a linear model is defined by a first-order Taylor polynomial centered at pixel c as follows:
[0056] (T indicates that the item is predicted by the least square method)
[0057] where x i Represents a feature vector at pixel i; x c Represents a feature vector ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com