Evolving tread for a tyre
A tread and tire technology, which is applied in the direction of tire tread/tread pattern, heavy-duty tires, tire parts, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the amount of tread material, affecting the wear speed, and affecting the stiffness of the tread
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
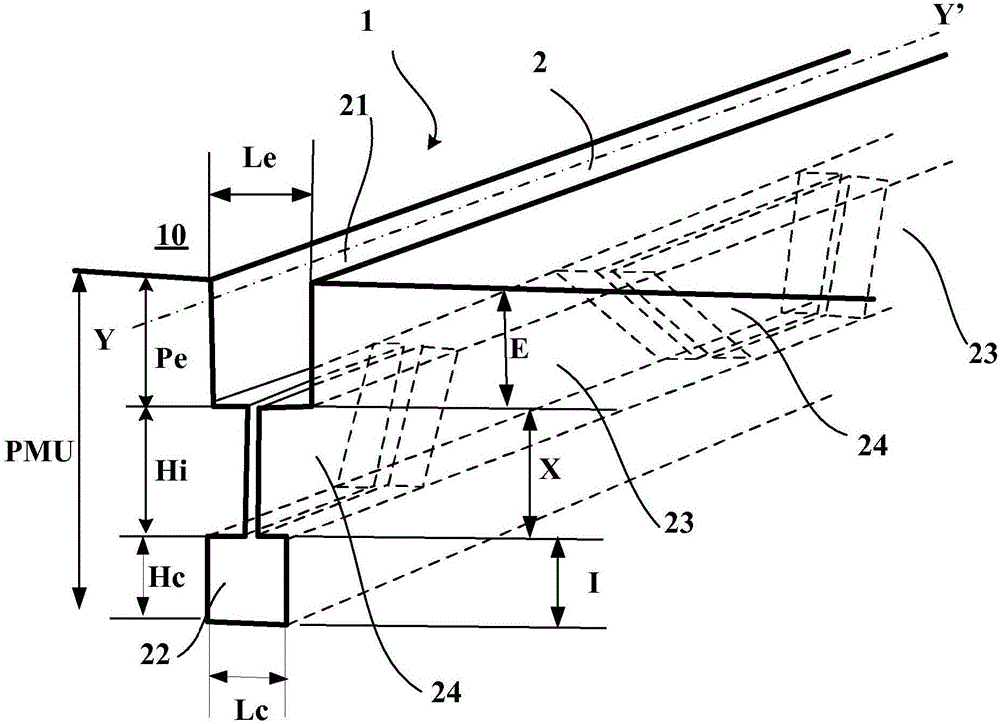
[0035] figure 1 is a partial view of a tread 1 comprising an incision 2 according to the invention extending along the main direction indicated in the drawing by the direction YY'. This tread 1 is intended to fit tires up to size 315 / 70R22.5.
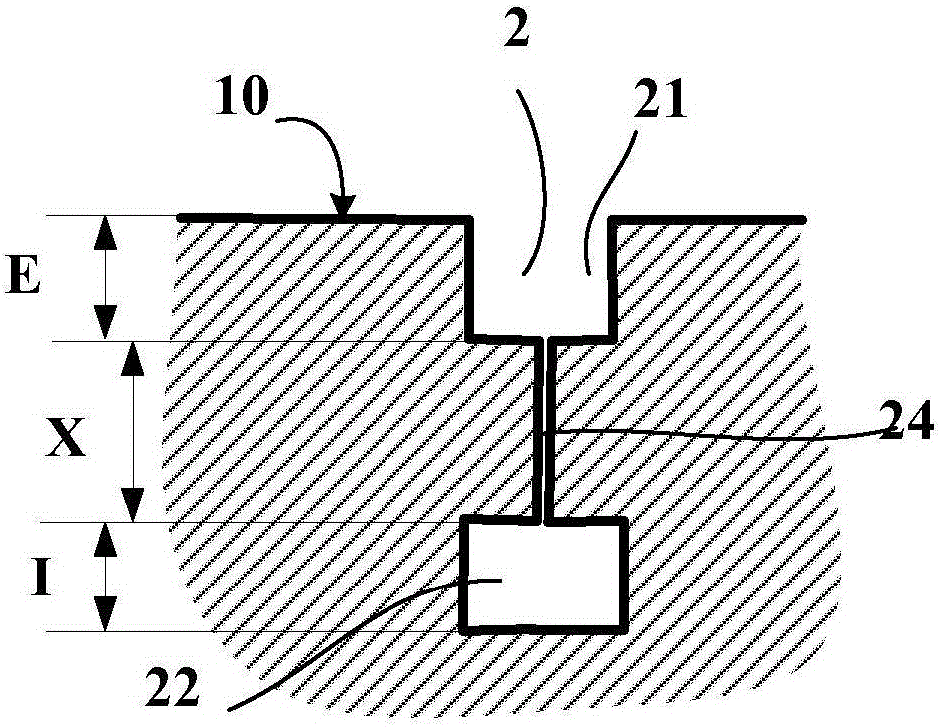
[0036] This incision 2 is formed in a tread 1 which, when new, has a tread surface 10 intended to contact the road when the tire provided with said tread is running. This incision 2 opens into the tread surface 10 in the initial situation, ie when said tread is new and not yet worn. The tread has a material thickness PMU (in this case equal to 14.5 mm) that can be worn away during running, beyond which it is necessary to renew the tread by retreading or replacing the tire.
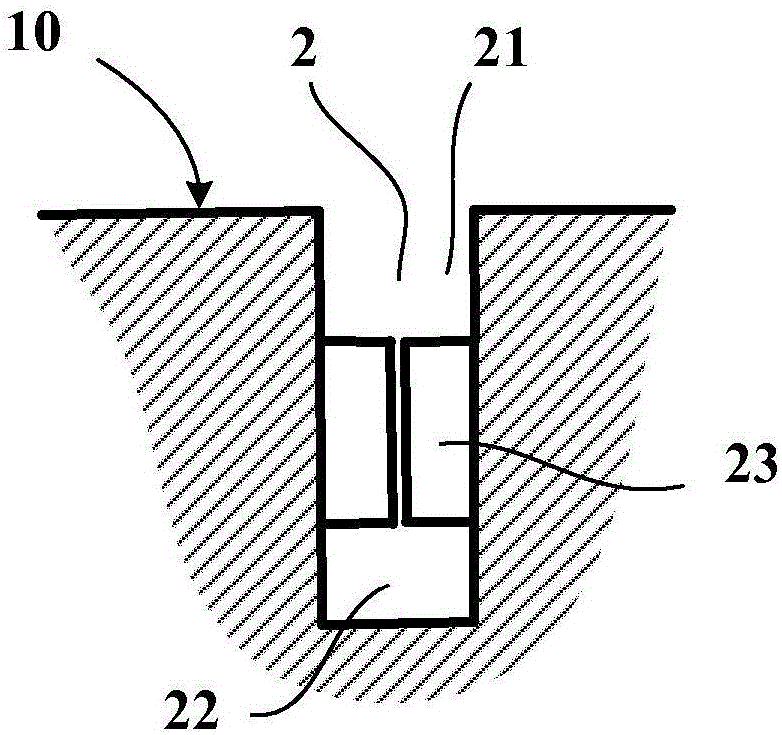
[0037] This cutout 2 comprises in its depth several parts, namely:
[0038] - an outer portion E in the form of a groove 21 opening onto the tread surface 10 when new, having a mean depth Pe here equal to 7.4mm (7.4 / 14.5=51%) and at a width Le on the tread surfa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com