Patents
Literature
111results about How to "Minimal wear" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
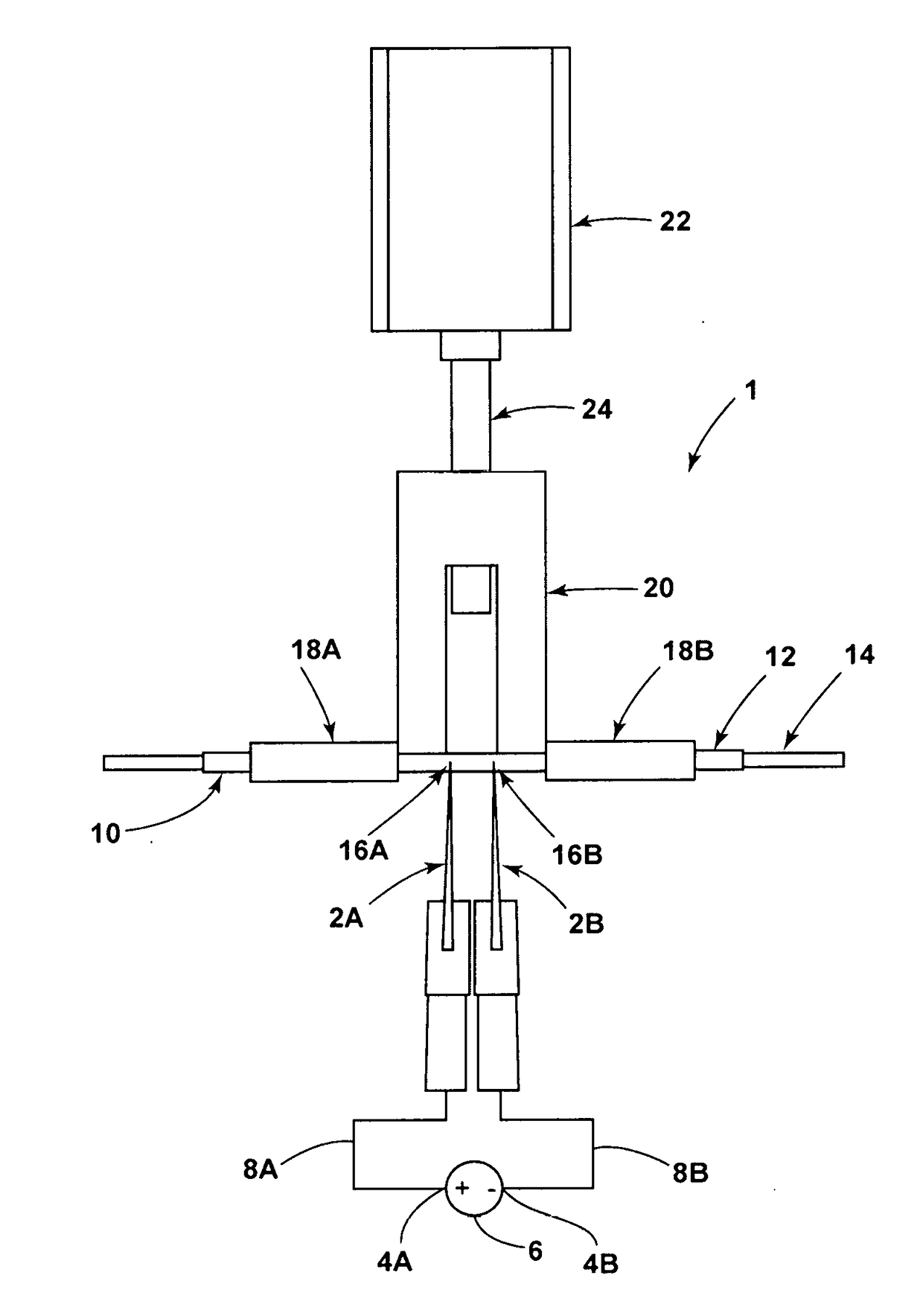
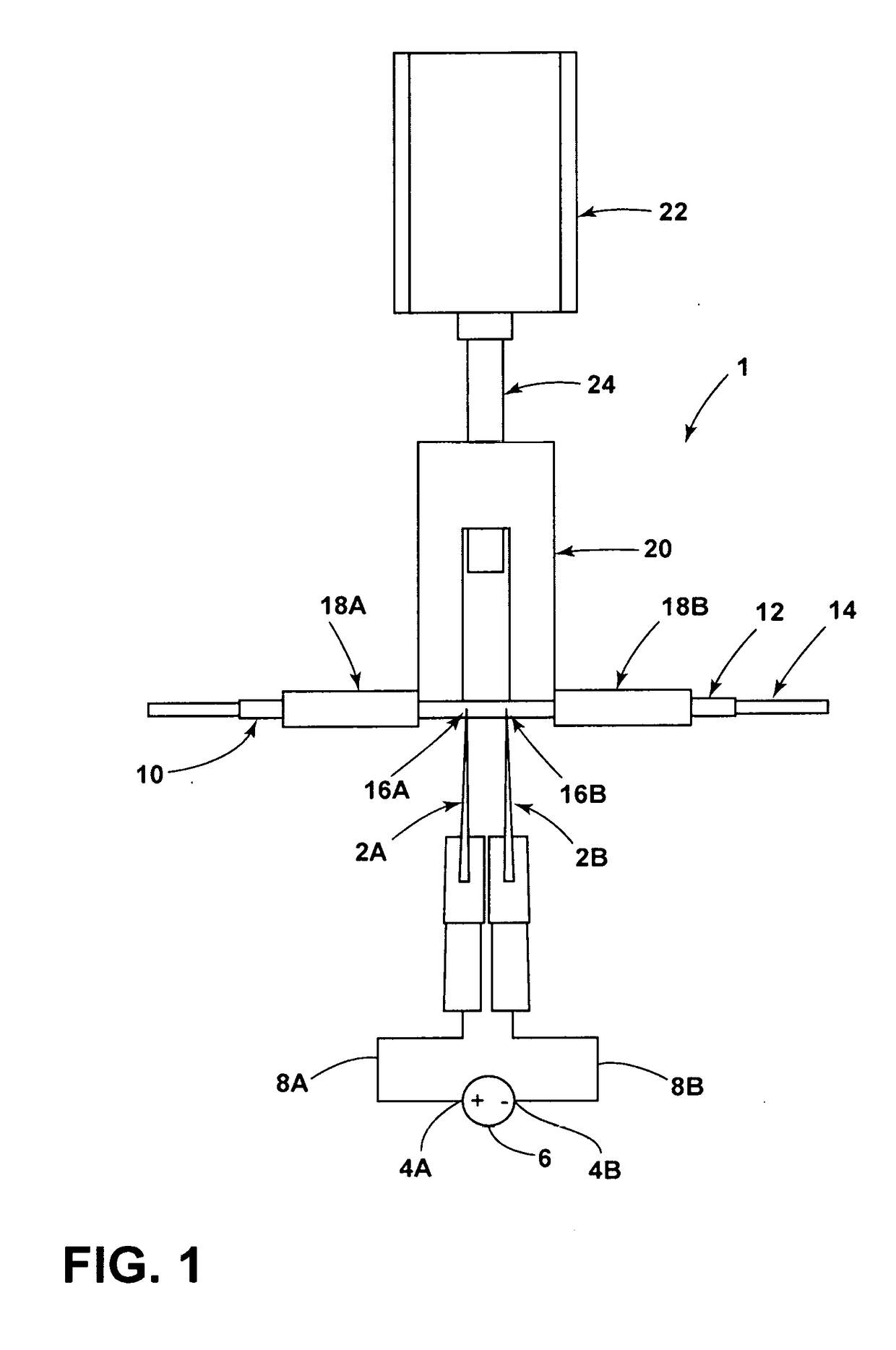
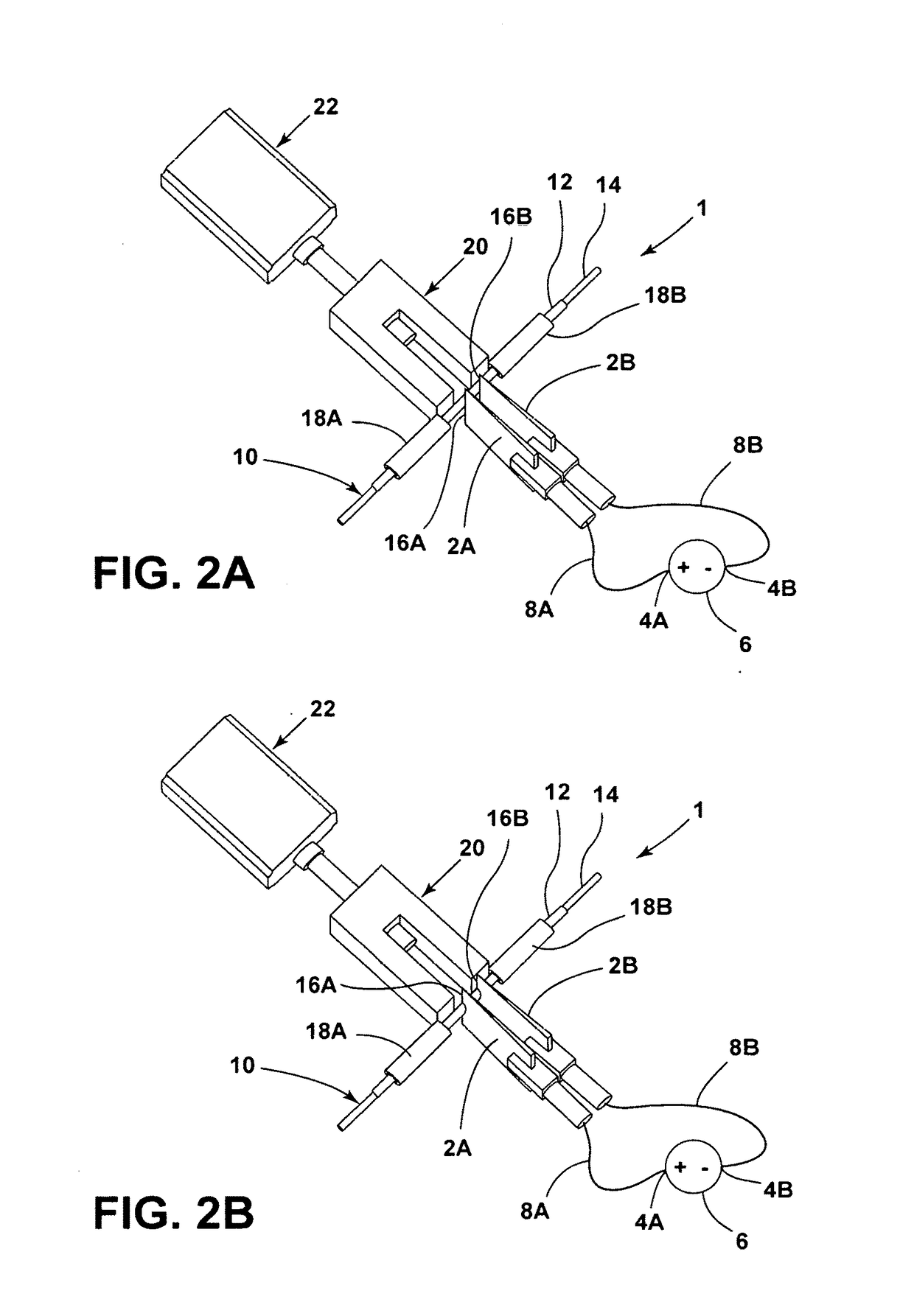
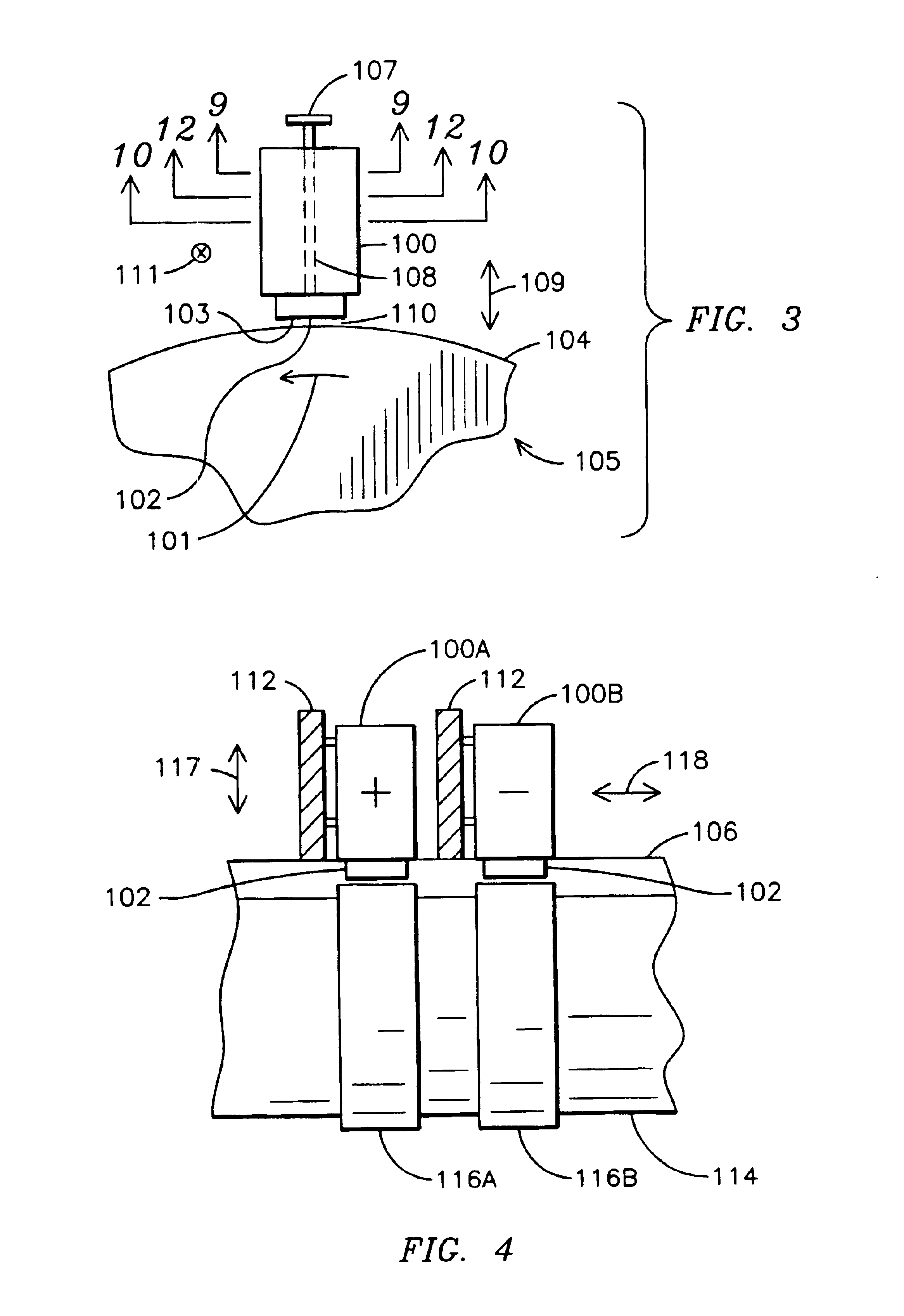
Cutting mechanism for carbon nanotube yarns, tapes, sheets and polymer composites thereof
ActiveUS20170129182A1Easy to cutRobust cutting method3D object support structuresManufacturing data aquisition/processingPower flowCarbon nanotube yarn
A cutting mechanism includes electrodes that are utilized to cut or score a non-conductive outer material of a filament or sheet. The electrodes contact a conductive reinforcing material of the filament or sheet to complete an electric circuit. Electric current flows through and heats the conductive material to oxidize or otherwise separate / cut the conductive material and any remaining non-conductive material.
Owner:NAT INST AEROSPACE ASSOC +1
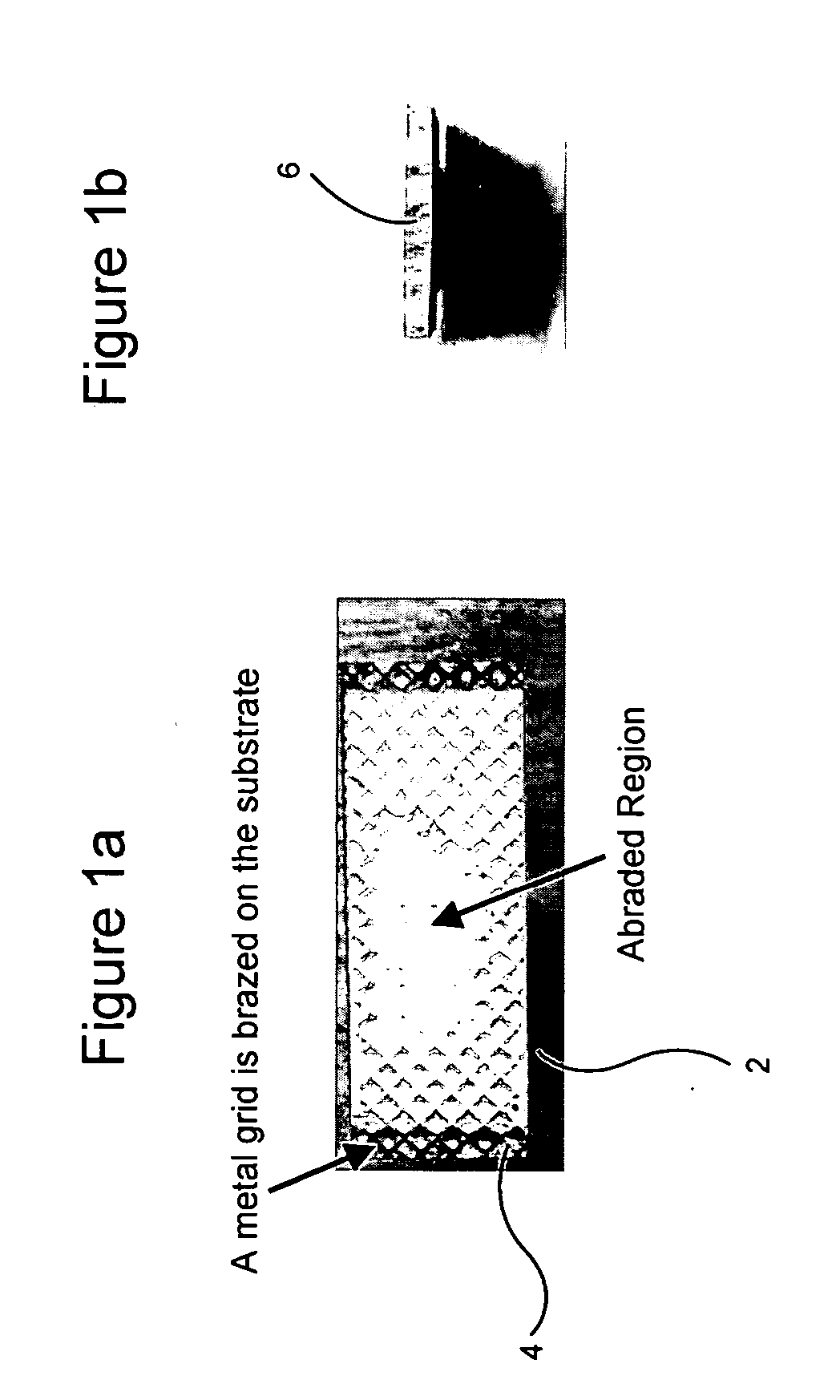
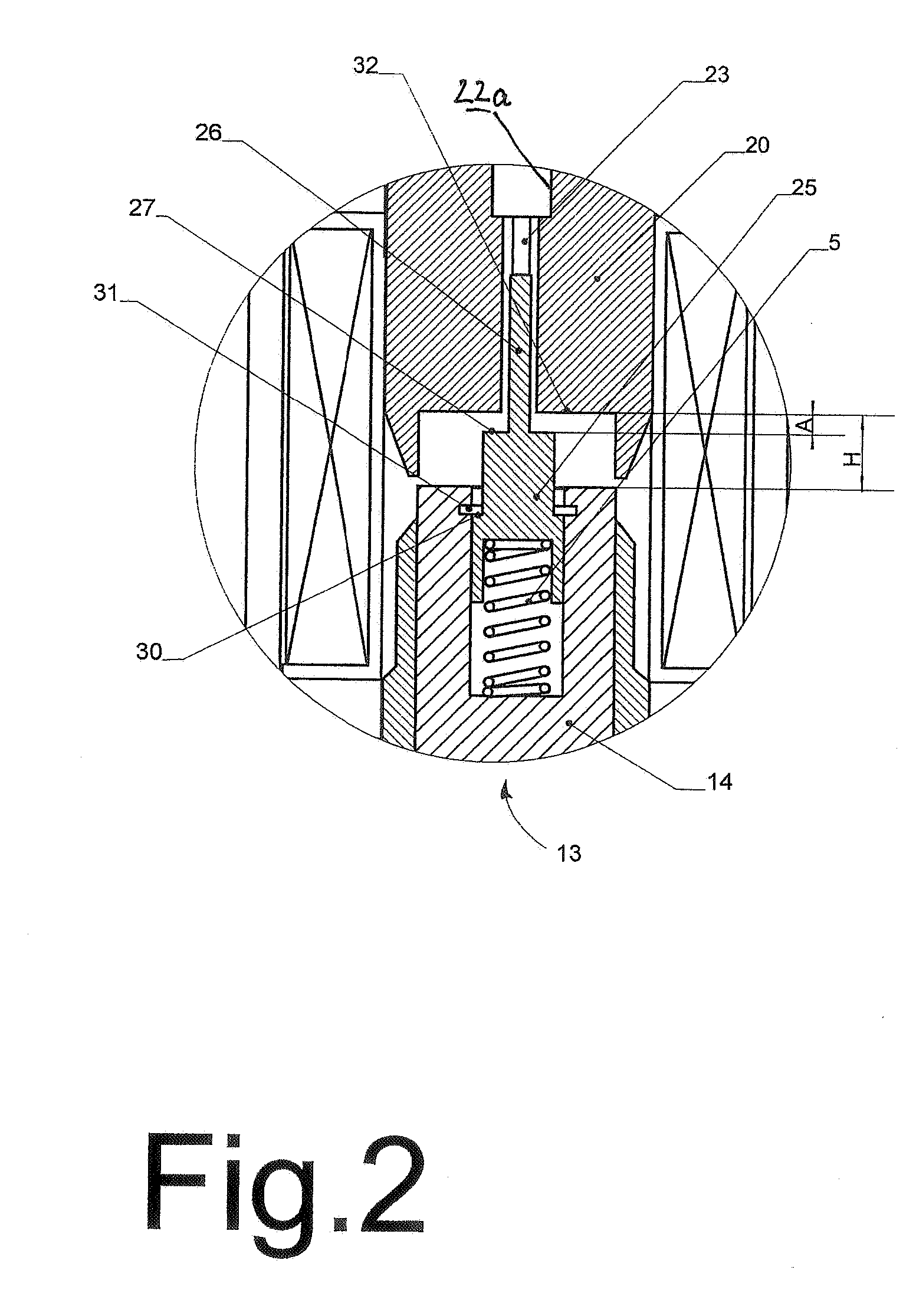
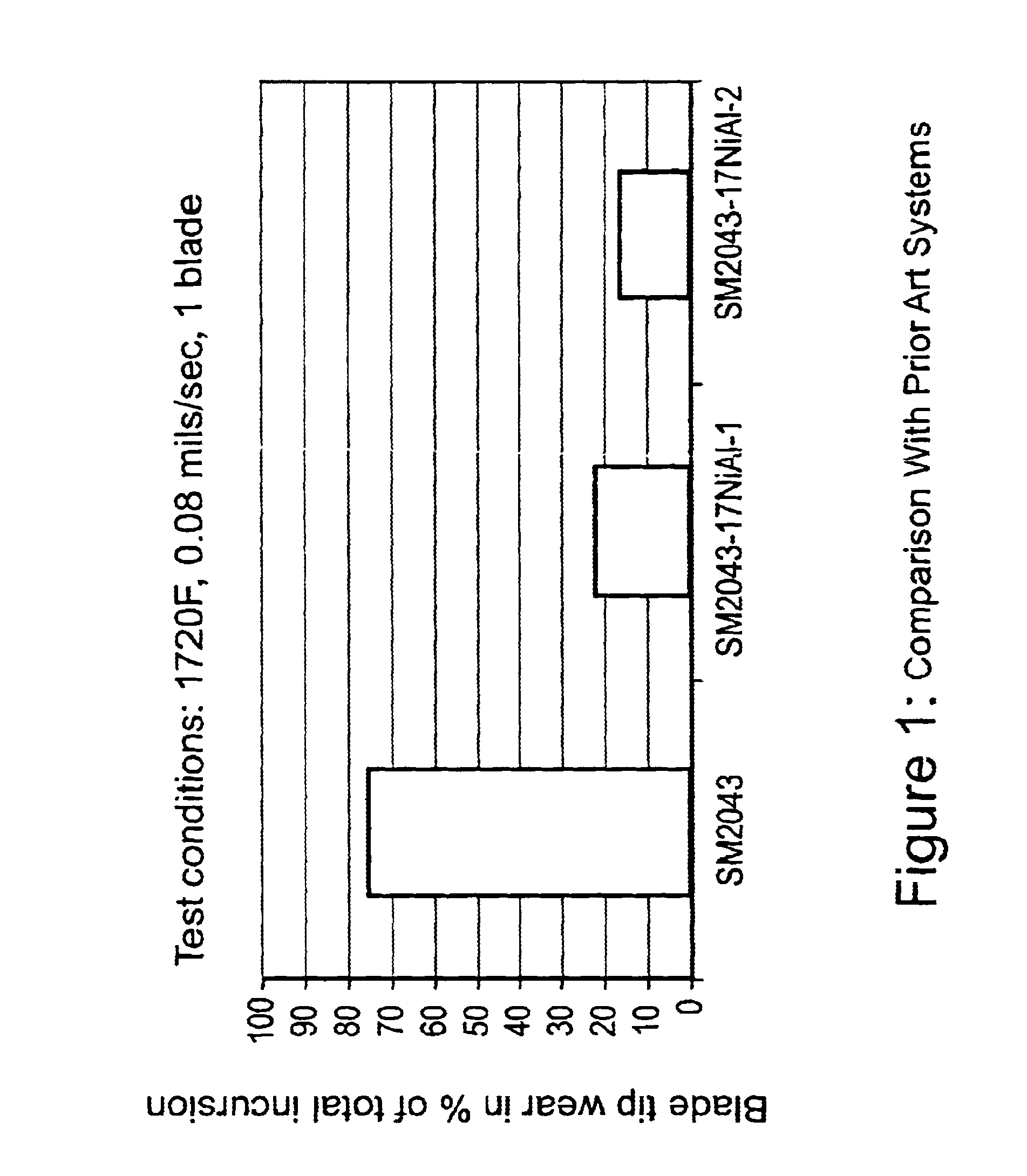
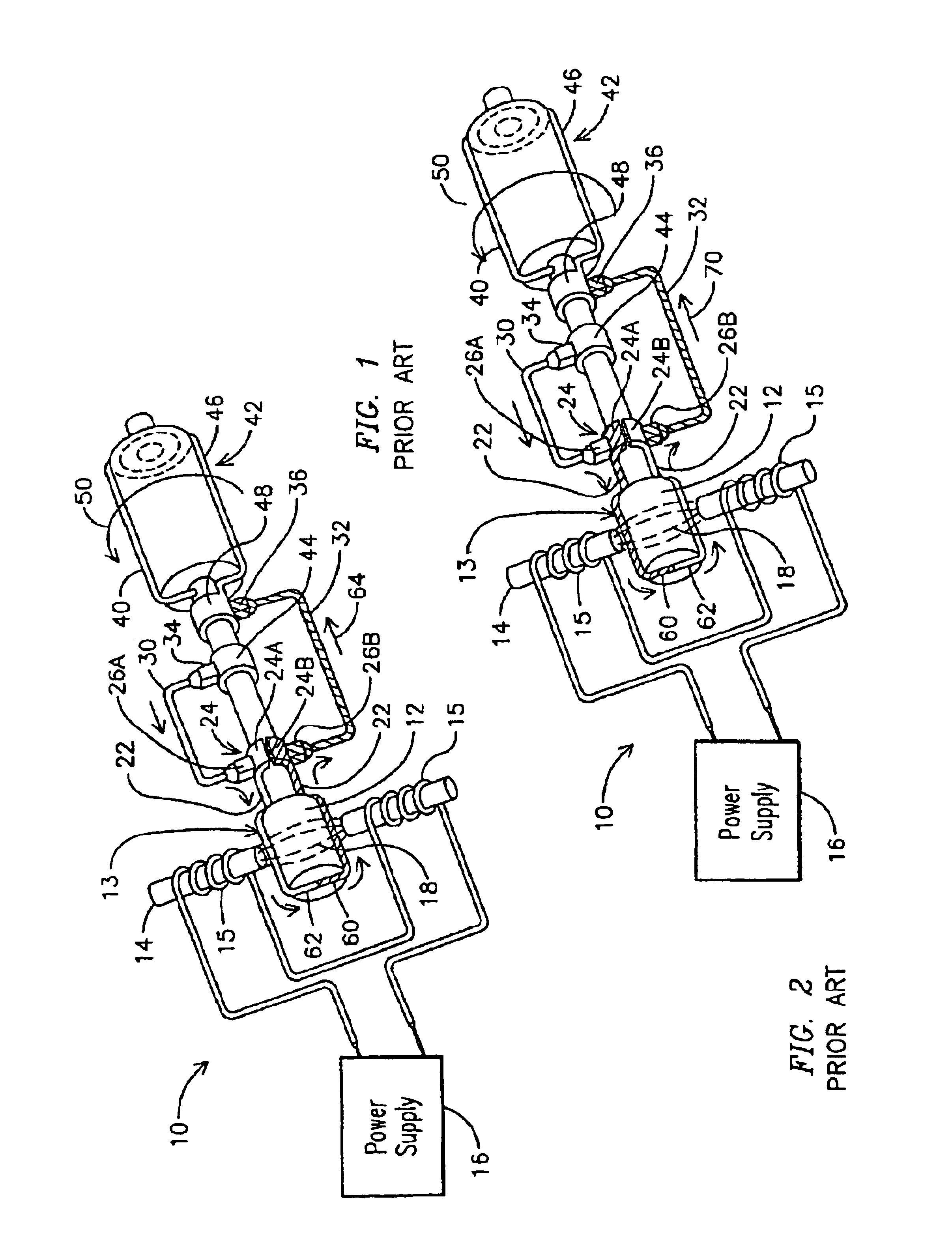
7FAstage 1 abradable coatings and method for making same
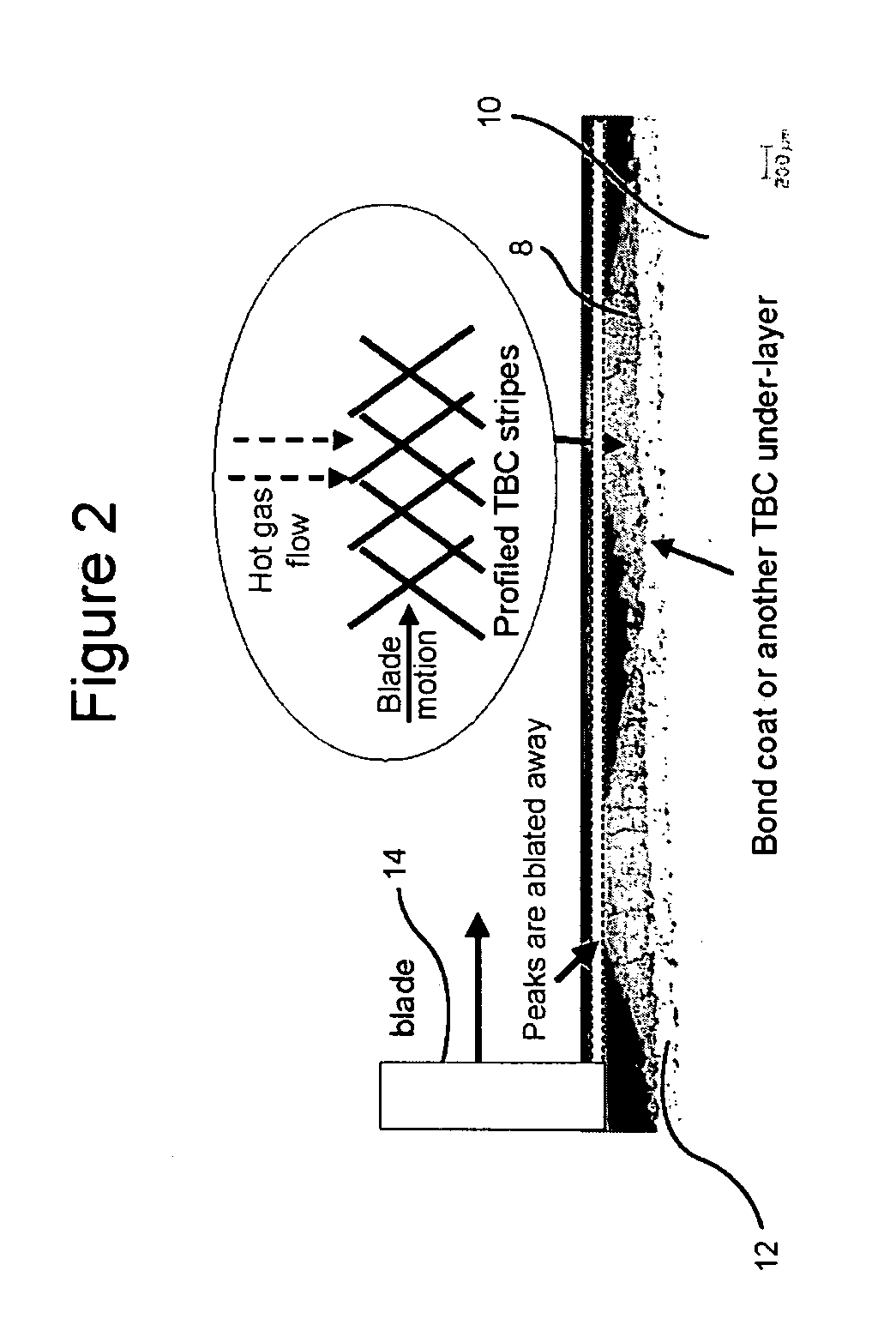
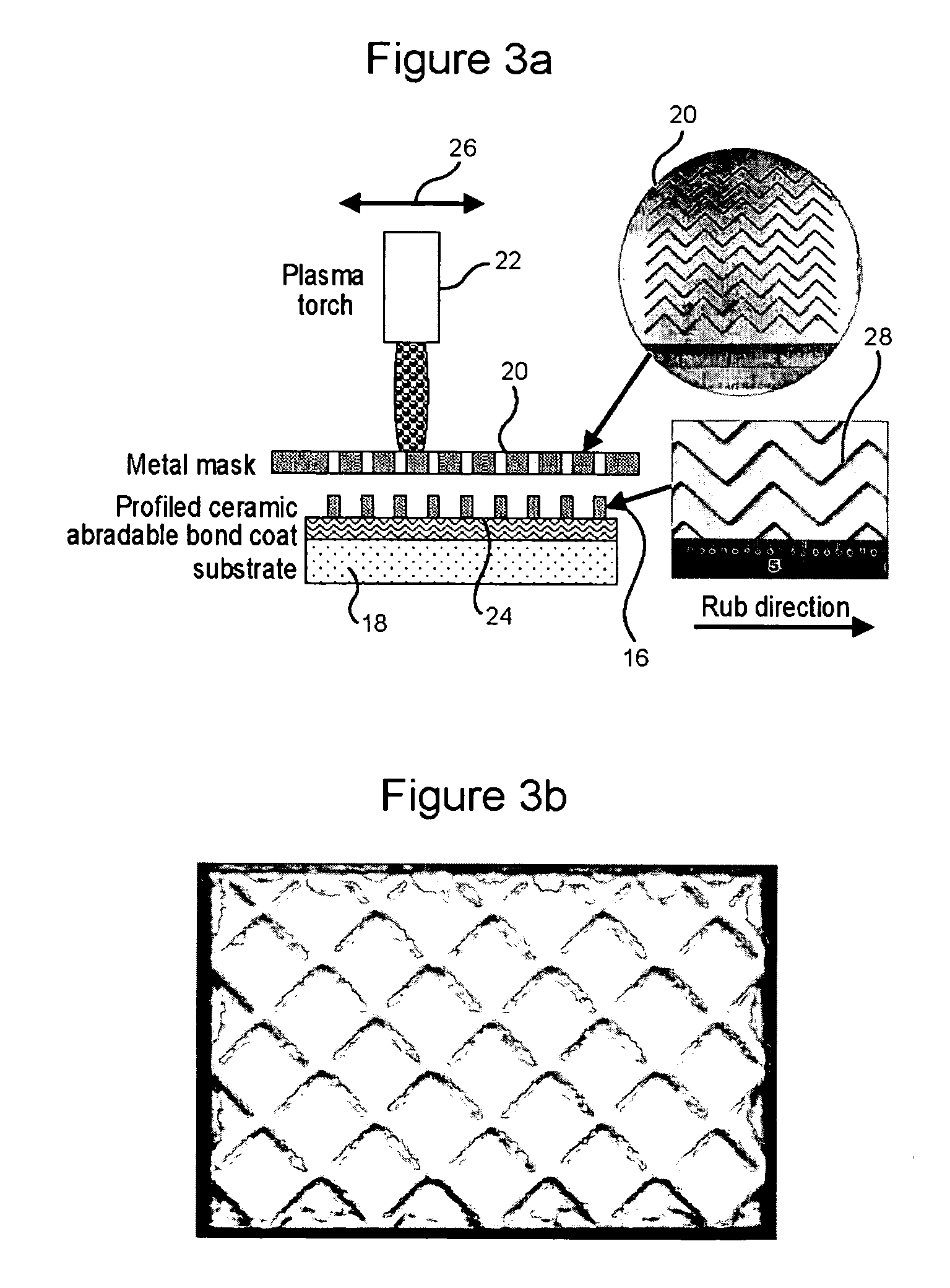
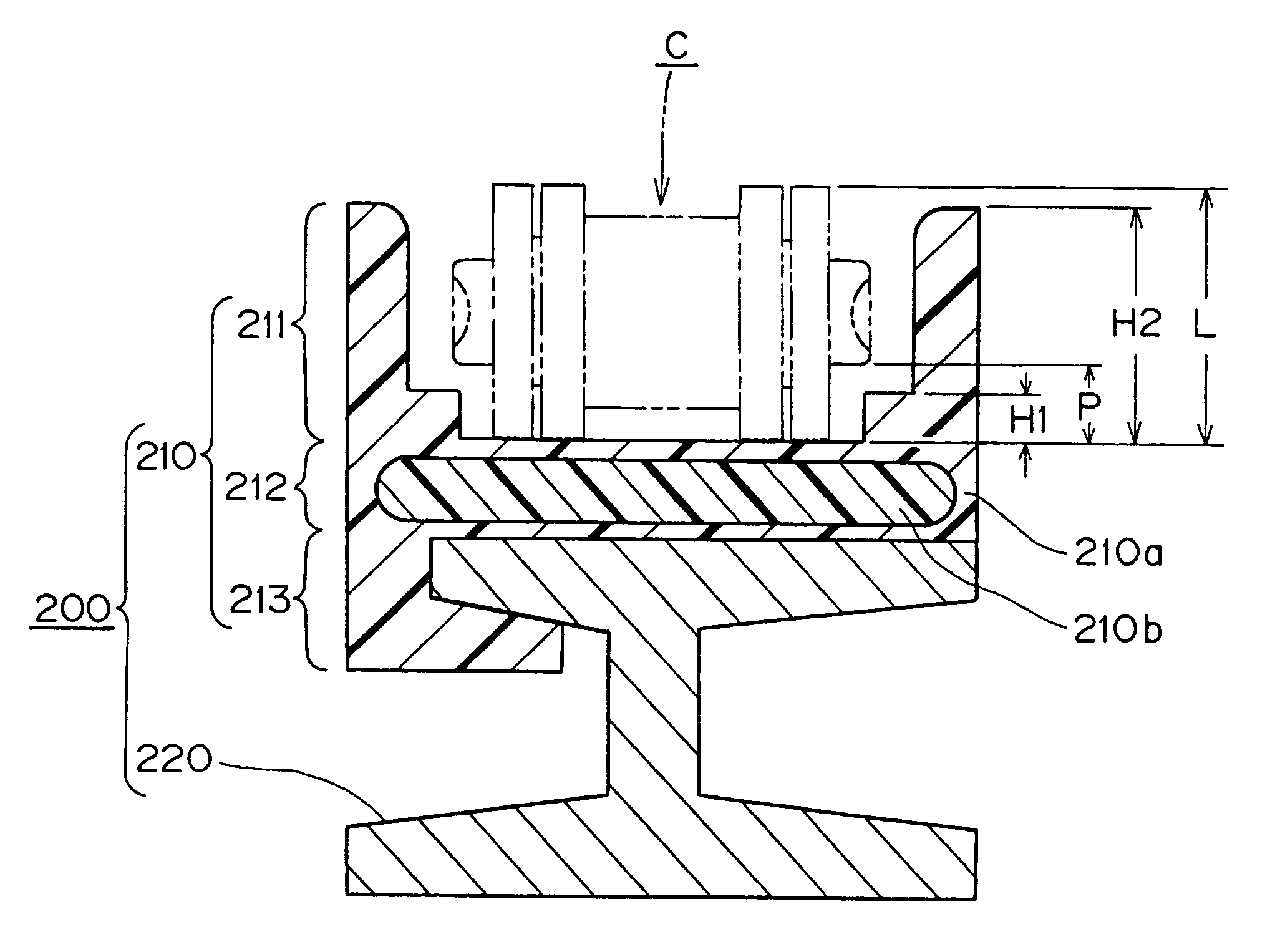
InactiveUS20050003172A1Minimal wearReduce gas leakageMolten spray coatingEngine manufactureLeading edgeGrid pattern
A method of applying a profiled abradable coating onto a substrate in which an abradable ceramic coating composition is applied to a metal substrate using one or more coating application techniques to produce a defined ceramic pattern without requiring a separate web or grid to be brazed onto the substrate. The invention is particularly designed to withstand the higher operating temperatures encountered with the stage 1 section of 7FA+e gas turbines to allow for increased coating life without significant deterioration in structural or functional integrity. Typically, the grid pattern coating begins approximately 0.431″ after the leading edge of the shroud, and ends approximately 1.60″ before the trailing edge of the shroud. In the case of diamond-shaped patterns, the grid pattern will be about 0.28″ long and 0.28″ wide, with an overall thickness of about 0.46.″ The coatings thus provide the required levels of abradability and leakage performance and may be applied as a chevron or diamond pattern with the shape oriented such that the diagonals run perpendicular and parallel to the sides of the shroud.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
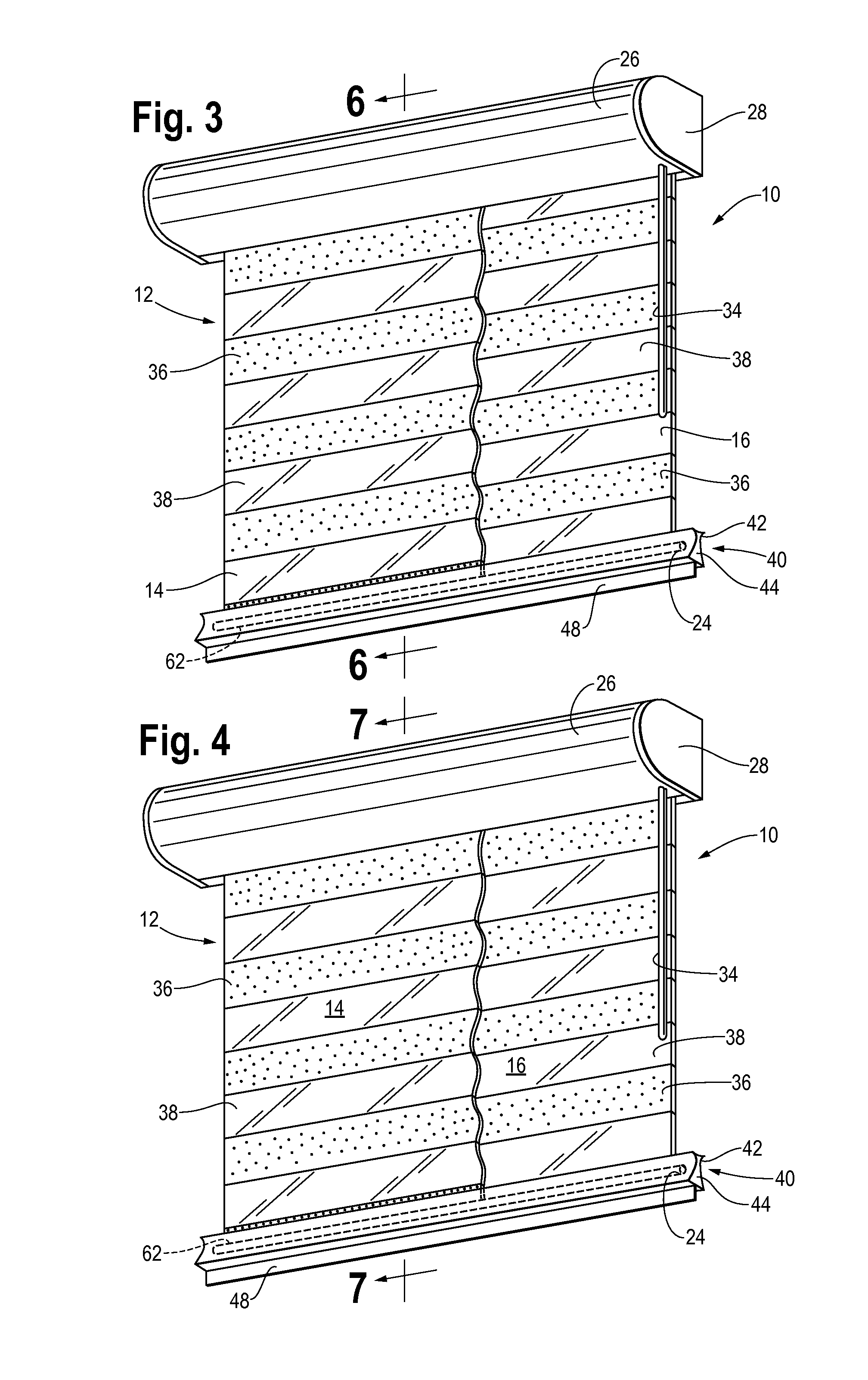
Dual Panel Window Shade Apparatus with Improved Bottom Weight Bar and Rail
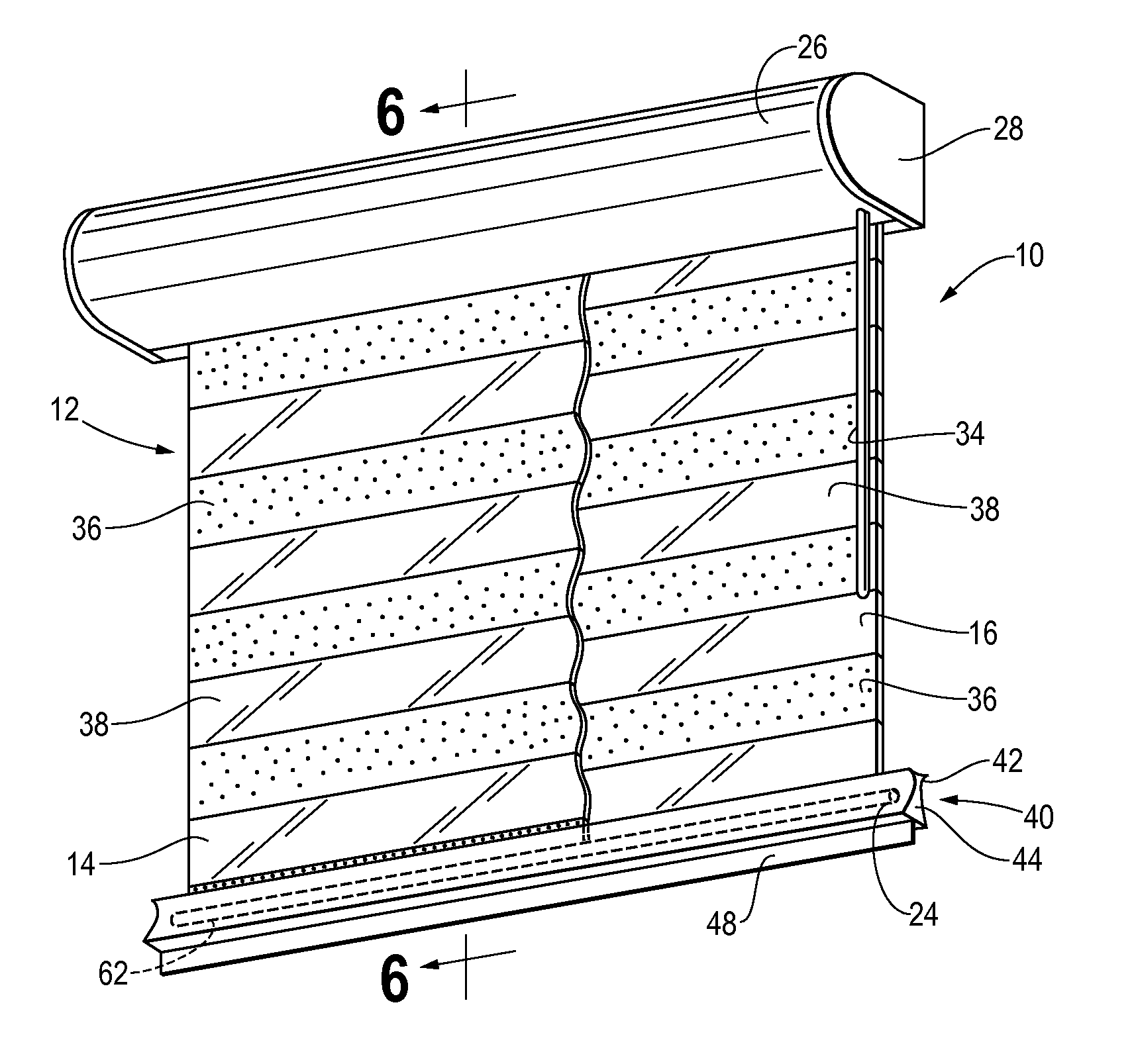
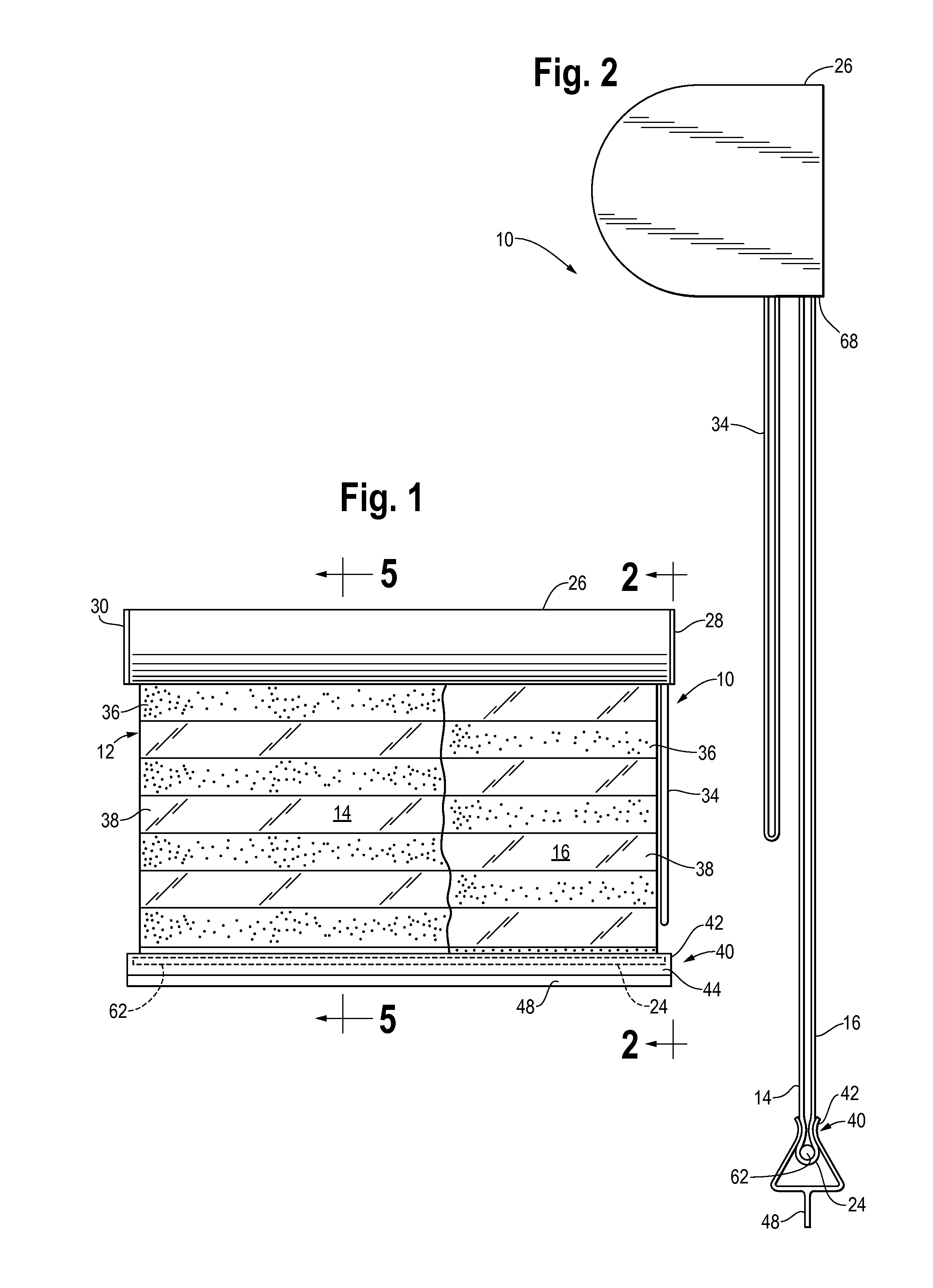
InactiveUS20120043029A1Minimal wearShutters/ movable grillesLight protection screensLight transmissionSurface plate
A dual panel adjustable light transmission shade apparatus for adjusting the amount of light passing through a window comprises a spool rotatably mounted in a canopy, and an opening in the canopy. A single piece of material forms opposed facing front and rear panels, and a bight is formed at the bottom of the panels. An upper portion of each panel is fastened to the spool at spaced apart locations on the outer surface of the spool. One of the panels moves generally vertically upward and the other panel moves generally vertically downward when the spool is rotated in one direction. A weight bar is lodged in the bight at the bottom of the panels to apply a downward force on the panels, and the weight bar rotates in the bight only when the panels are adjusted relative to each other.
Owner:GASKILL ROBERT D +1
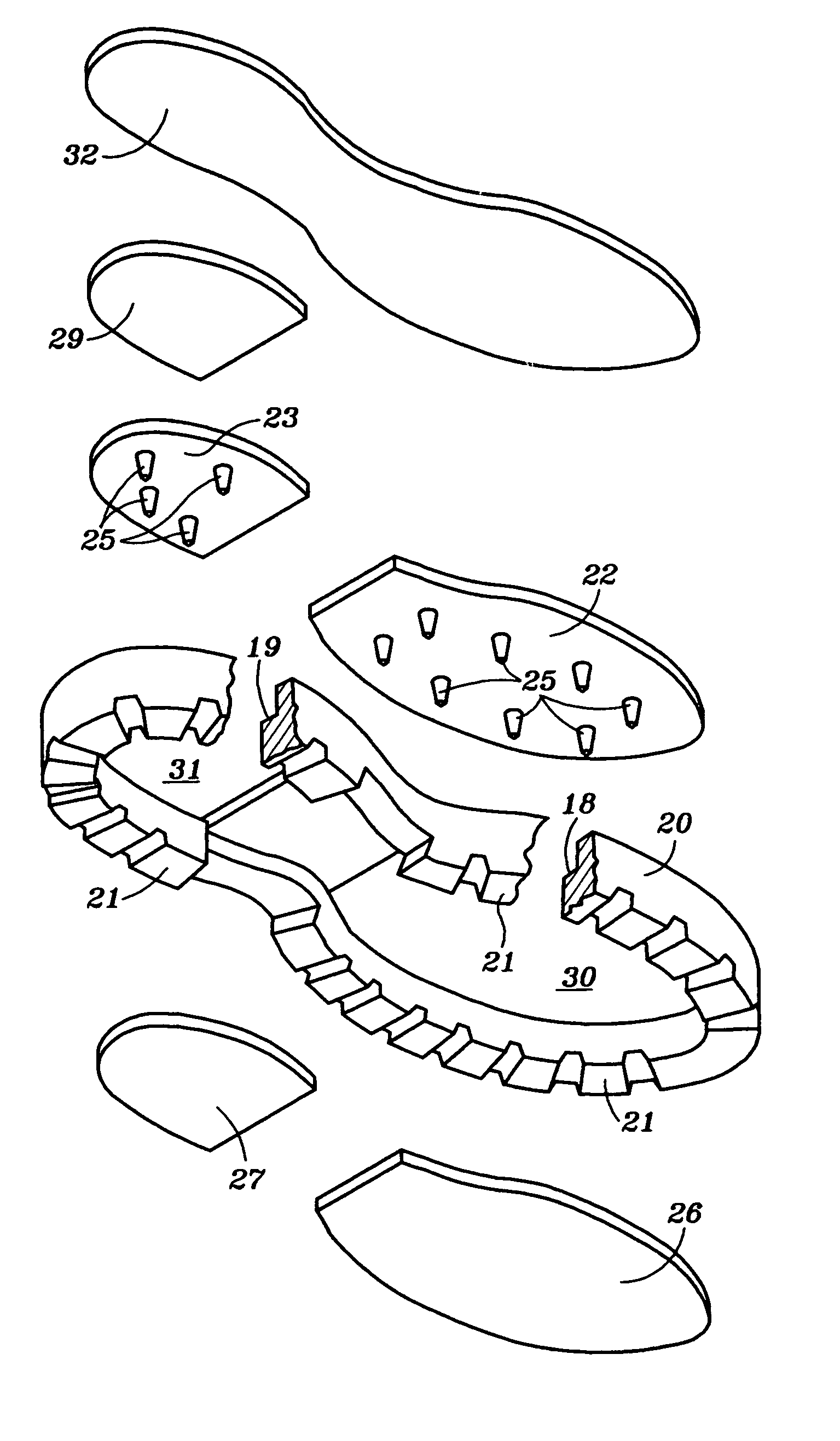
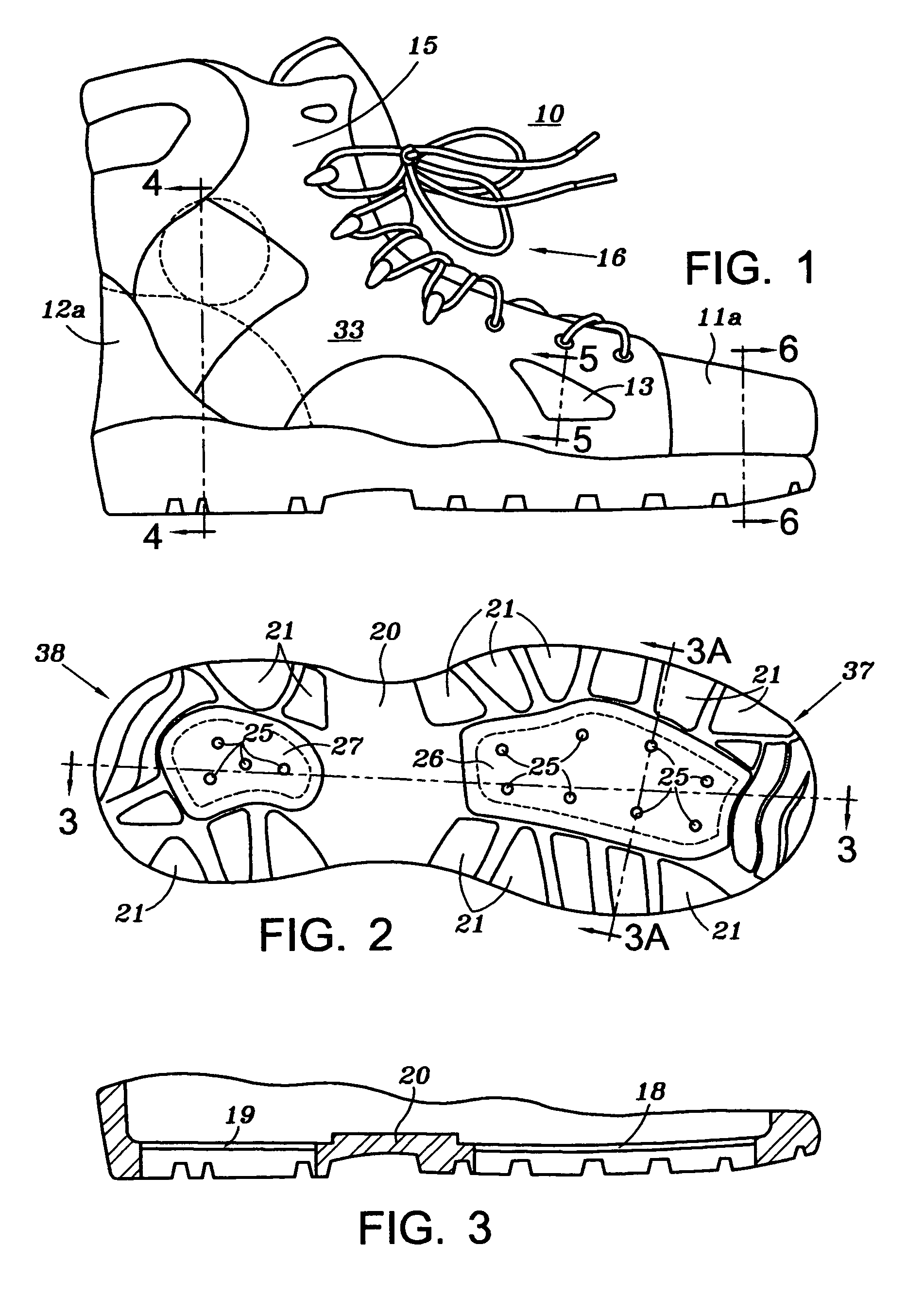
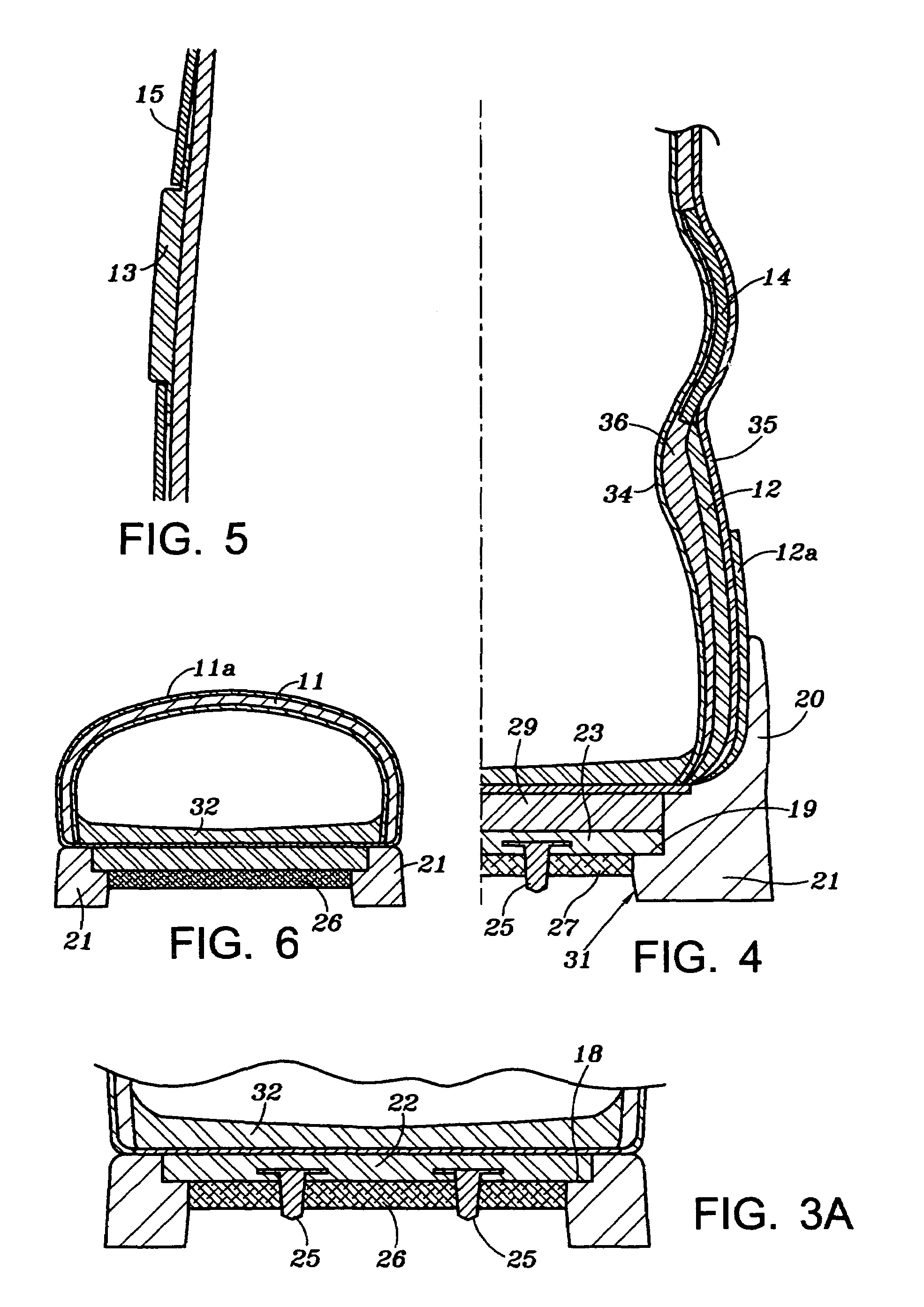
Field and stream boot
A field and stream boot for traversing rivers, lakes and stream beds, as well as, outdoor trails which includes; an upper construction with a hard heel, a hard toe, an ankle cup, and a metatarsus rigid panel that provide foot protection from outdoor or underwater terrain and obstacles; and an outsole construction where the outsole has peripheral intermittent tread surrounding a heel array of tungsten carbide spikes overlain with felt with the spike protruding through the felt but not below the peripheral intermittent tread, and surrounding a forefoot array of tungsten carbide spikes overlain with felt with the spikes protruding through the felt but not below the peripheral intermittent tread. The tread may be in the form of lugs, cleats or other gripping ribs or ridges.
Owner:MYERS ROBERT J
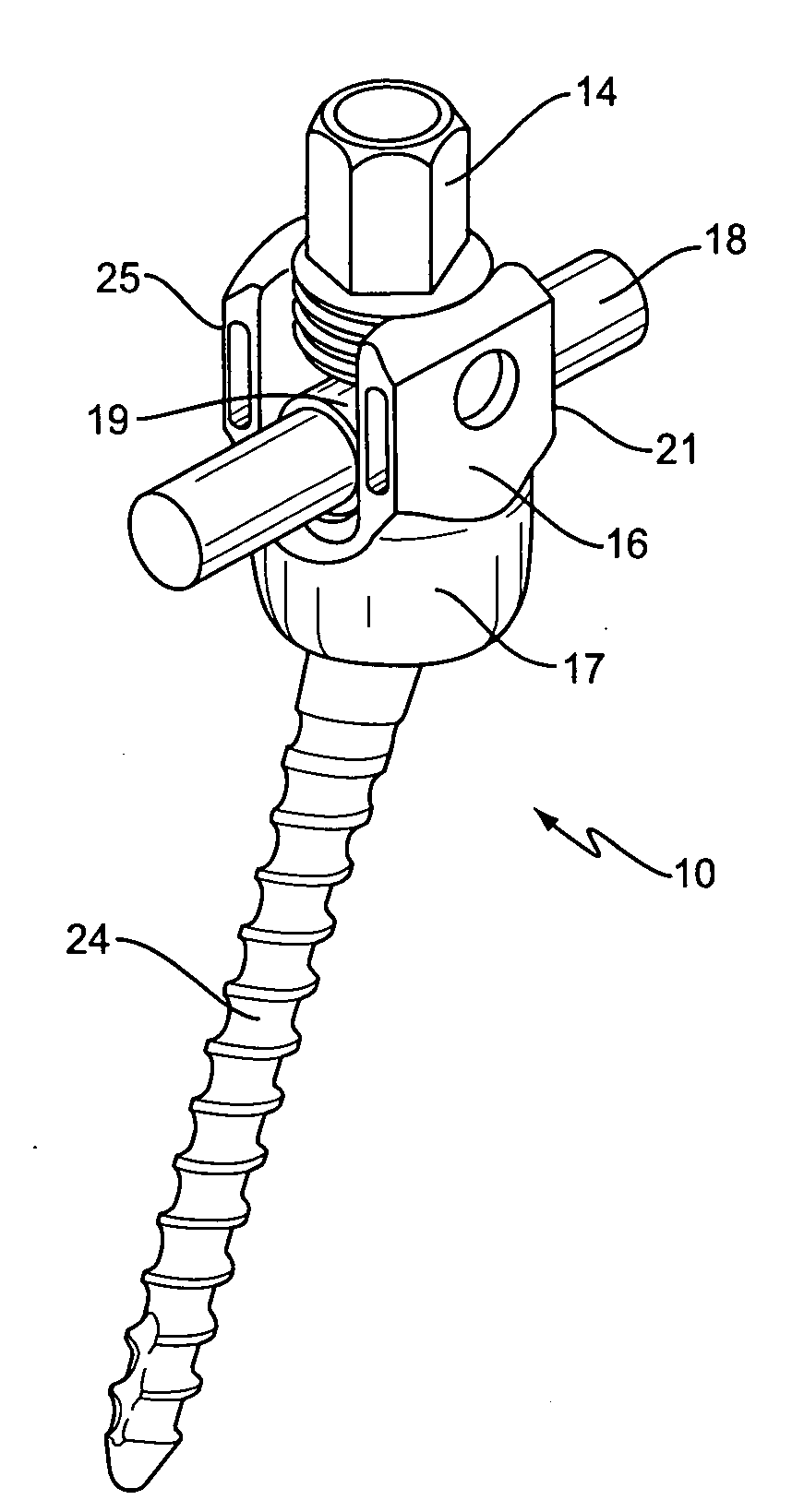
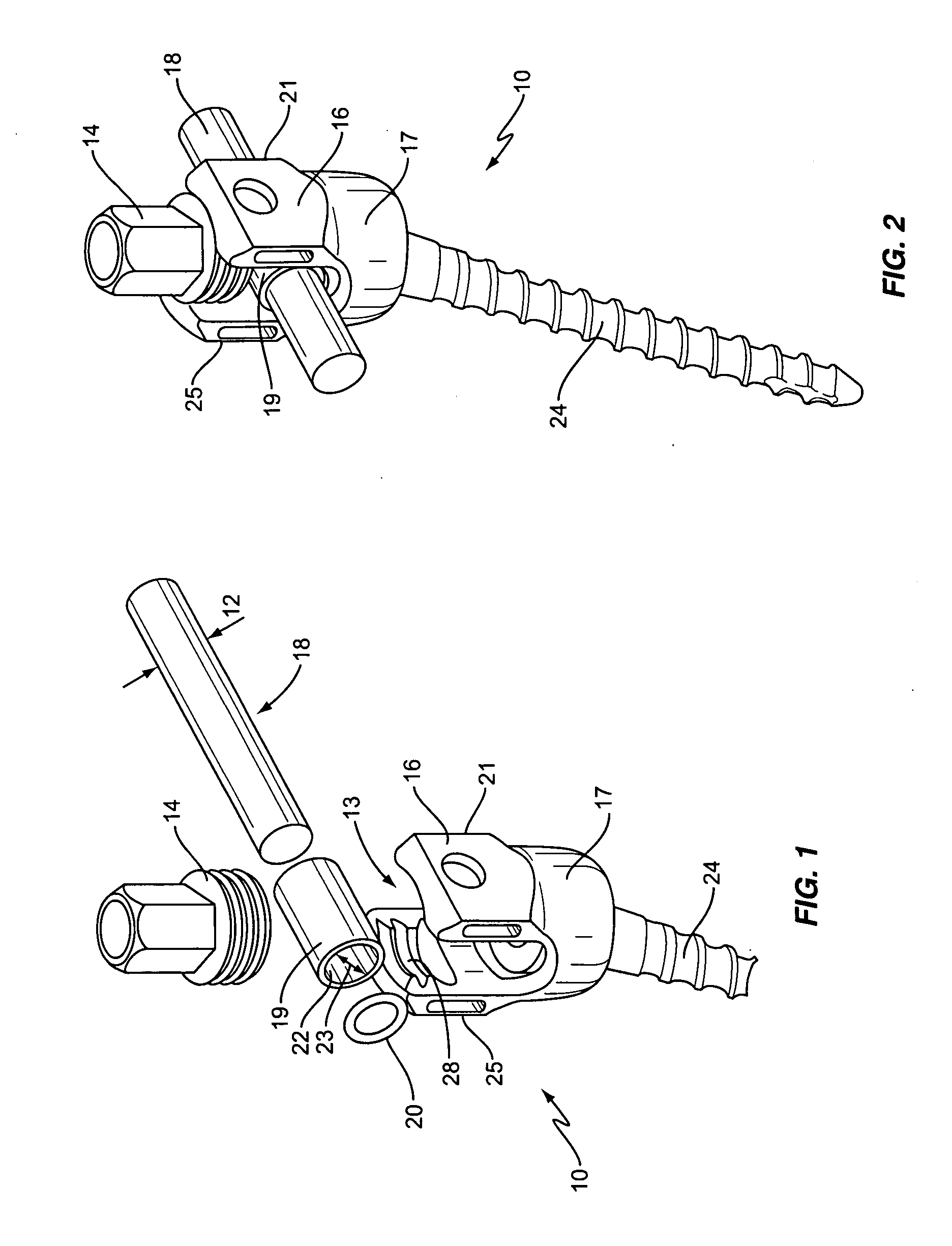
Spinal rod translation device
InactiveUS20100262190A1Reduce wearAvoid clamping forceSuture equipmentsInternal osteosythesisCompression memberIliac screw
A rod translation device is described that minimizes the wear between a spinal rod and a bone anchor in a spinal implant. In one embodiment, the rod translation device is a sleeve that is slid onto the outside diameter of the spinal rod. At least one compressible member, such as an O-ring, may be placed within the inside diameter of the sleeve to prevent direct contact of the outside diameter of the spinal rod to the inside diameter of the sleeve. Once the spinal rod is secured within the implant any translation of the spinal rod decreases wear debris between the outside diameter of the spinal rod and the pedicle screw.
Owner:WARSAW ORTHOPEDIC INC
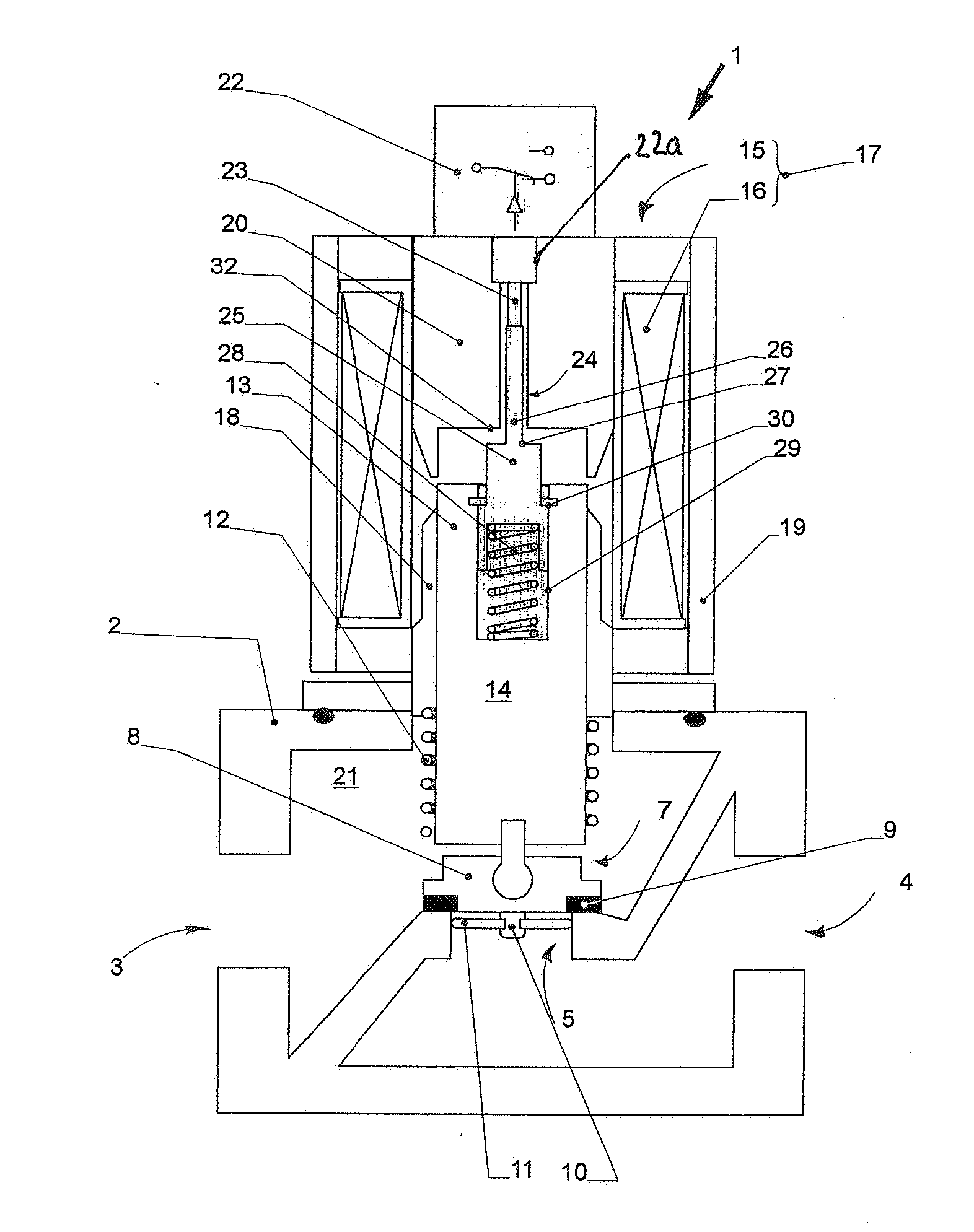
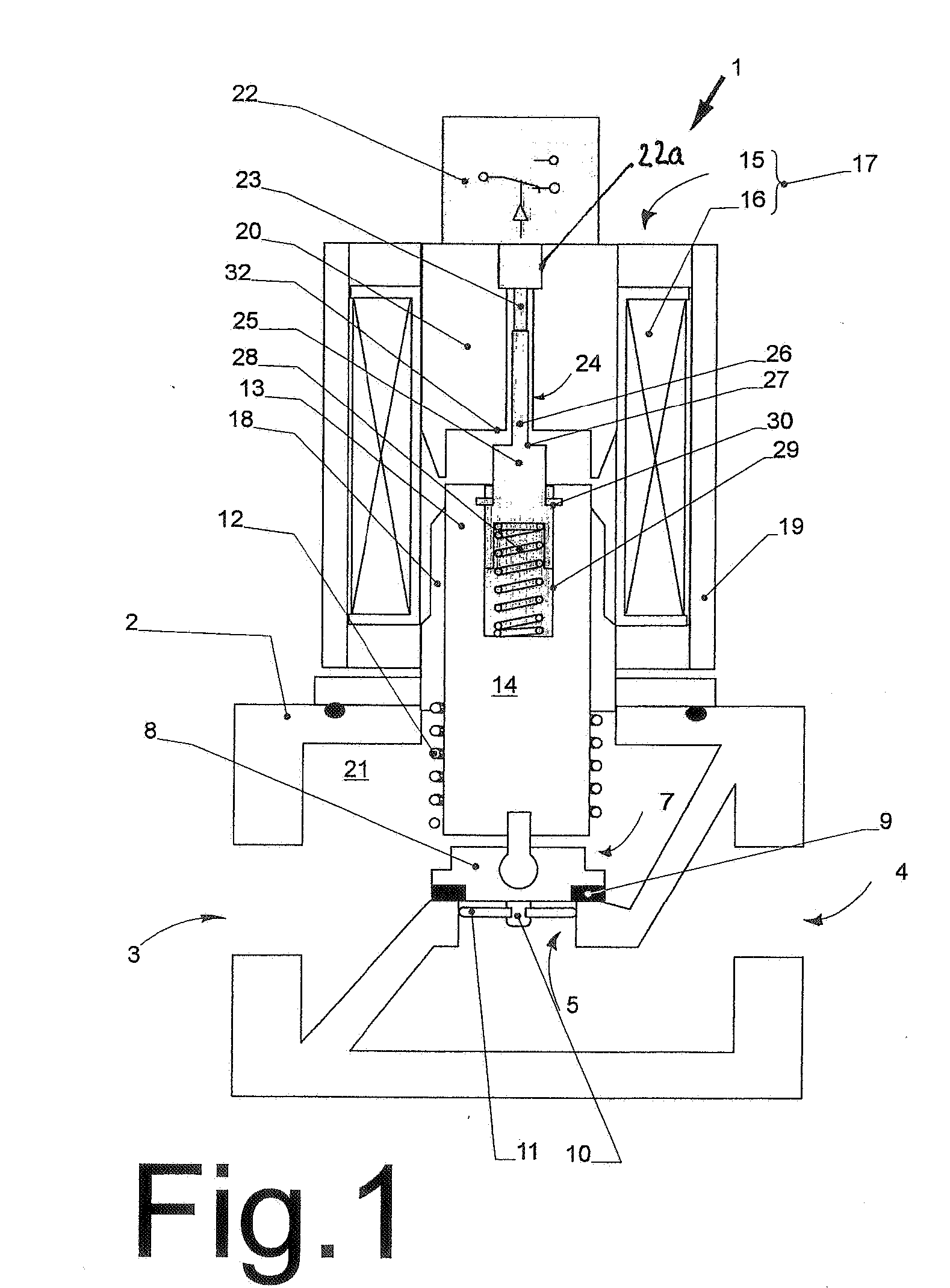
Valve with end position switching
InactiveUS20060272712A1Avoid destructionImprove sealingOperating means/releasing devices for valvesPipeline systemsEngineeringTappet
For detecting closing or opening of a valve activated preferably by a solenoid actuator, a switch activated by a tappet spring mounted on an armature of the actuator is provided. A stop and an associated surface limit the stroke of the tappet with reference to the switch. Preferably, a valve closing element opens the gas flow only when the armature has already executed a part of its opening stroke. The trigger point of the switch is set in this first part of the opening stroke of the armature, in which the valve closing element has not yet opened. The stroke limiting of the tappet for activating the switch is also preferably set in this region of the opening stroke of the armature. However, the stop limits the stroke of the tappet independent of the opening stroke size of the armature, so that the same switch can be used for different valves with different nominal diameters and opening strokes.
Owner:KARL DUNGS
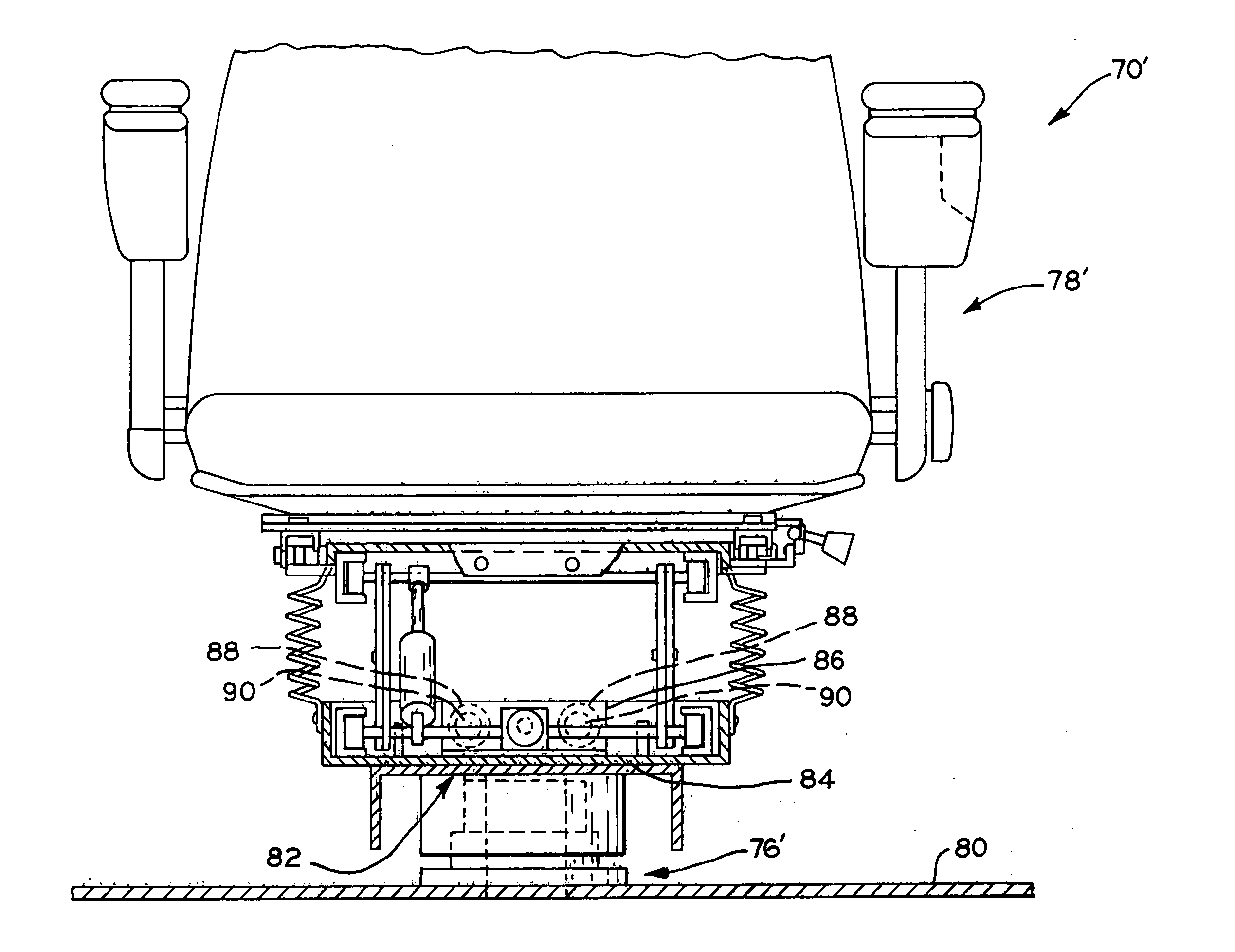
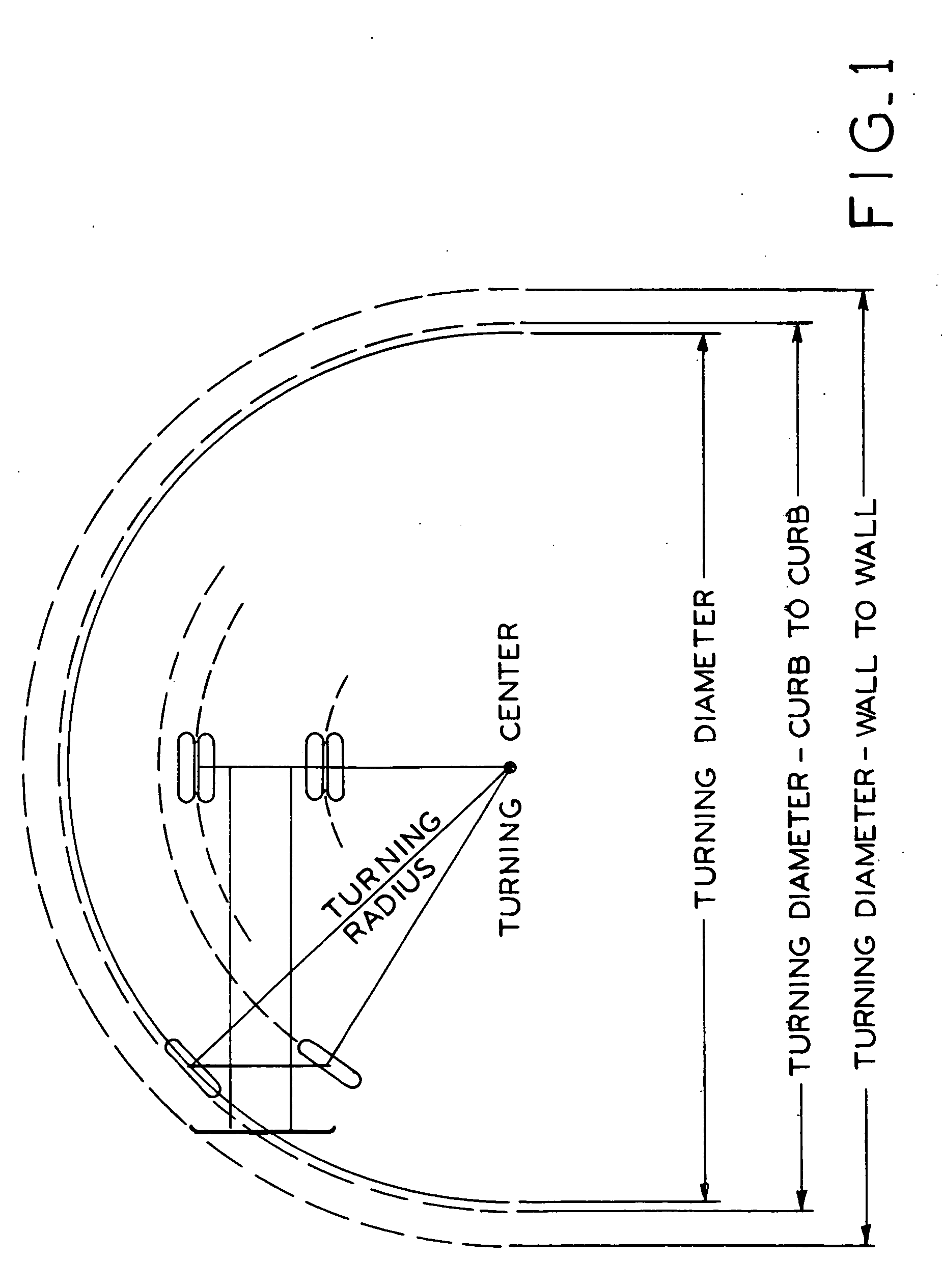
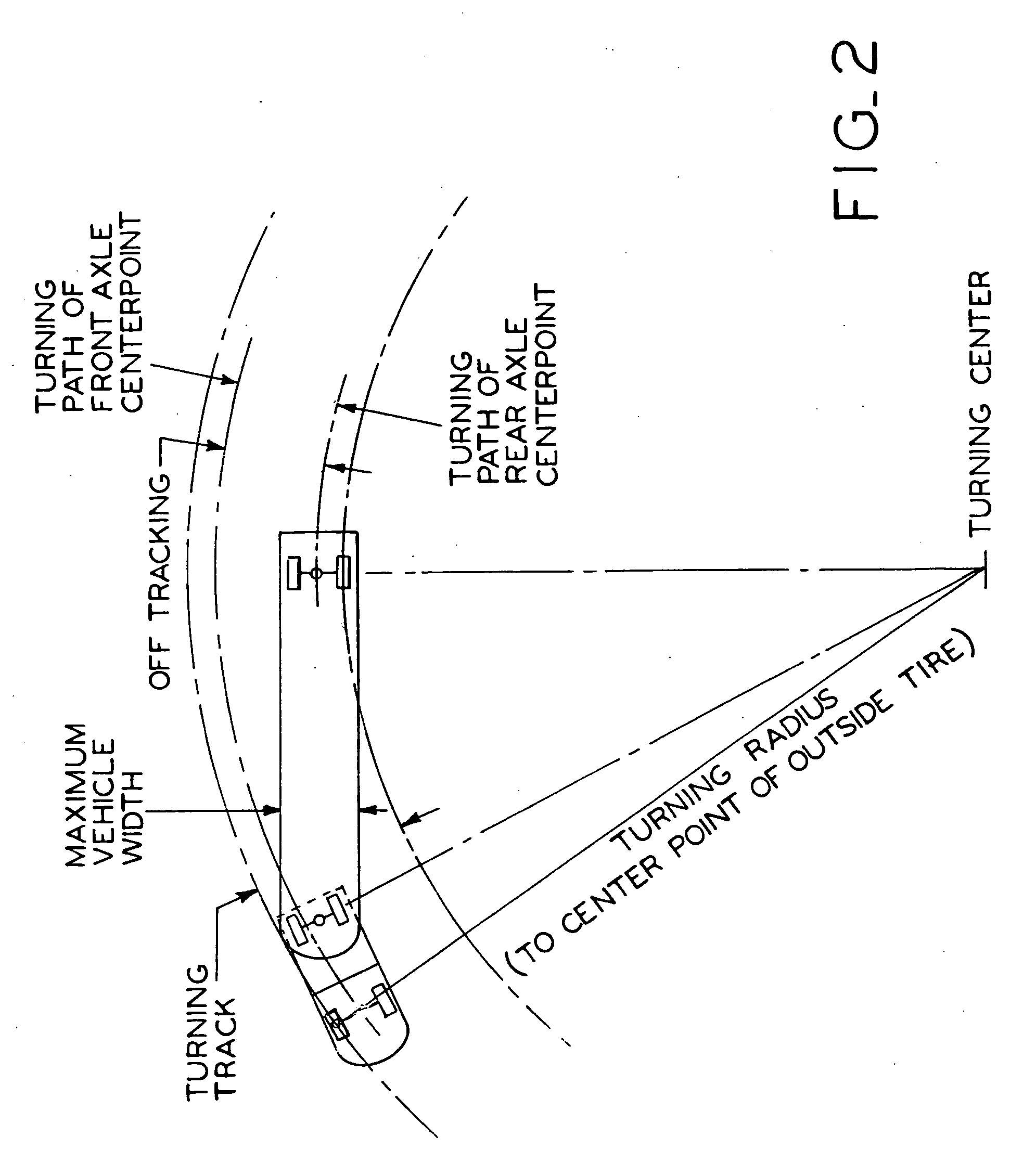
Differential steering application for trailer spotter vehicles
InactiveUS20060207822A1Reduce the overall diameterMinimal effortVehicle seatsVehicle mounted steering controlsVehicle frameHydraulic pump
A trailer spotter vehicle having a seat and a control console which are relatively rotatable with respect to the vehicle frame, and a differential drive system which permits the vehicle to turn within a very small turning radius. The rotatable seat and control console allow the operator to steer the vehicle without having to substantially turn their body or use mirrors to observe the path of the vehicle. To drive the vehicle in a forward direction, hydraulic pumps transmit pressurized hydraulic fluid to the trailer spotter wheels to rotate them in a first direction. In order to drive the vehicle in reverse, the flow of hydraulic fluid to the wheels is reversed to rotate the wheels in an opposite direction. To pivot the vehicle, the first wheel is driven in the first direction and the second wheel is driven in the opposite direction.
Owner:TAYLOR KERMIT O
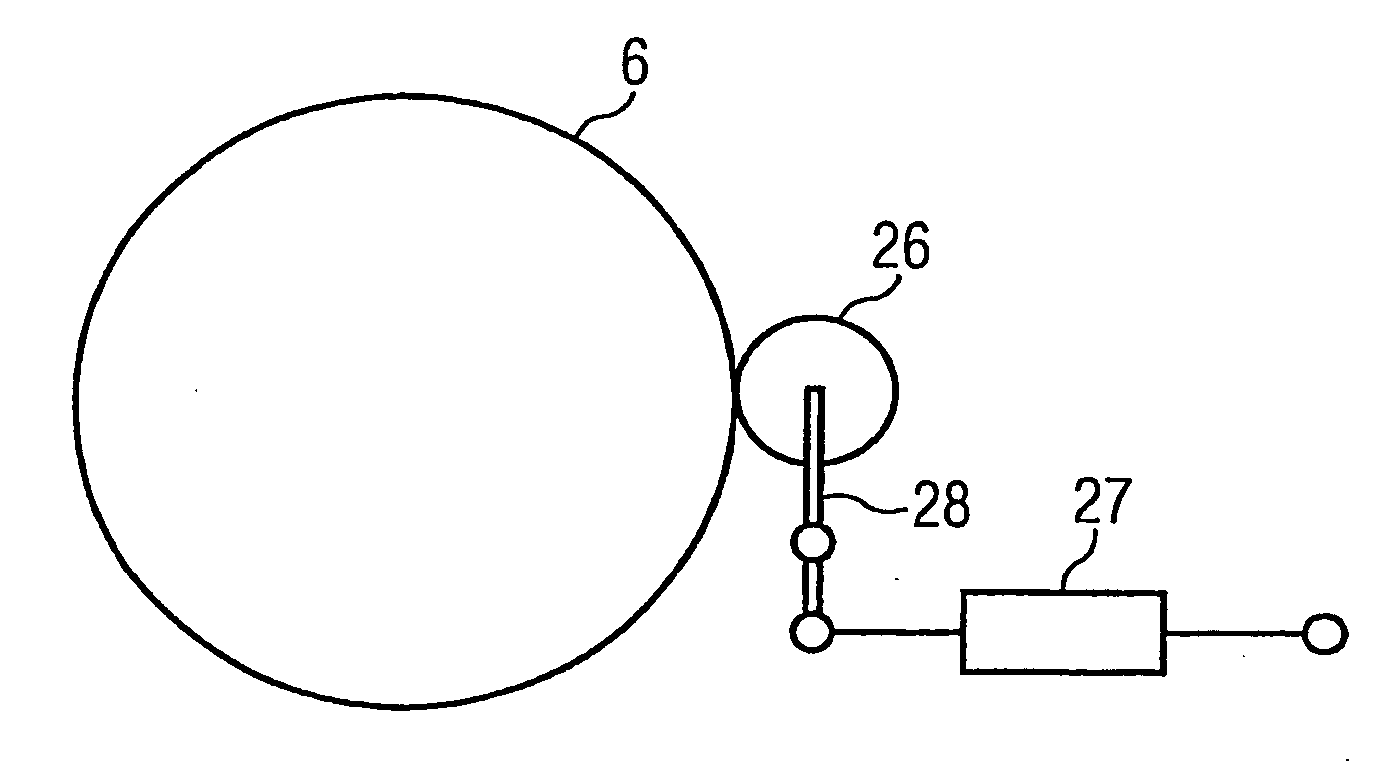
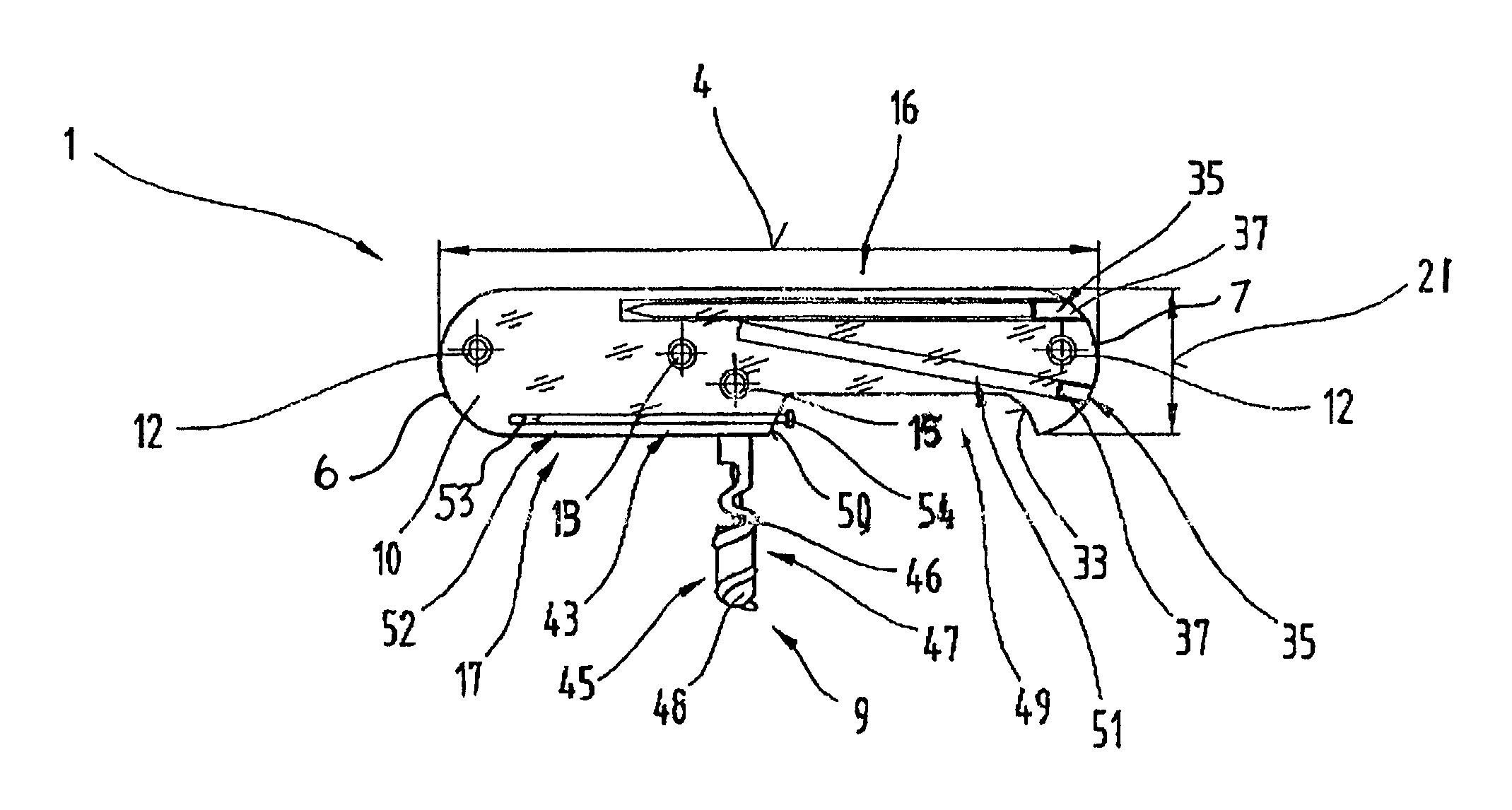
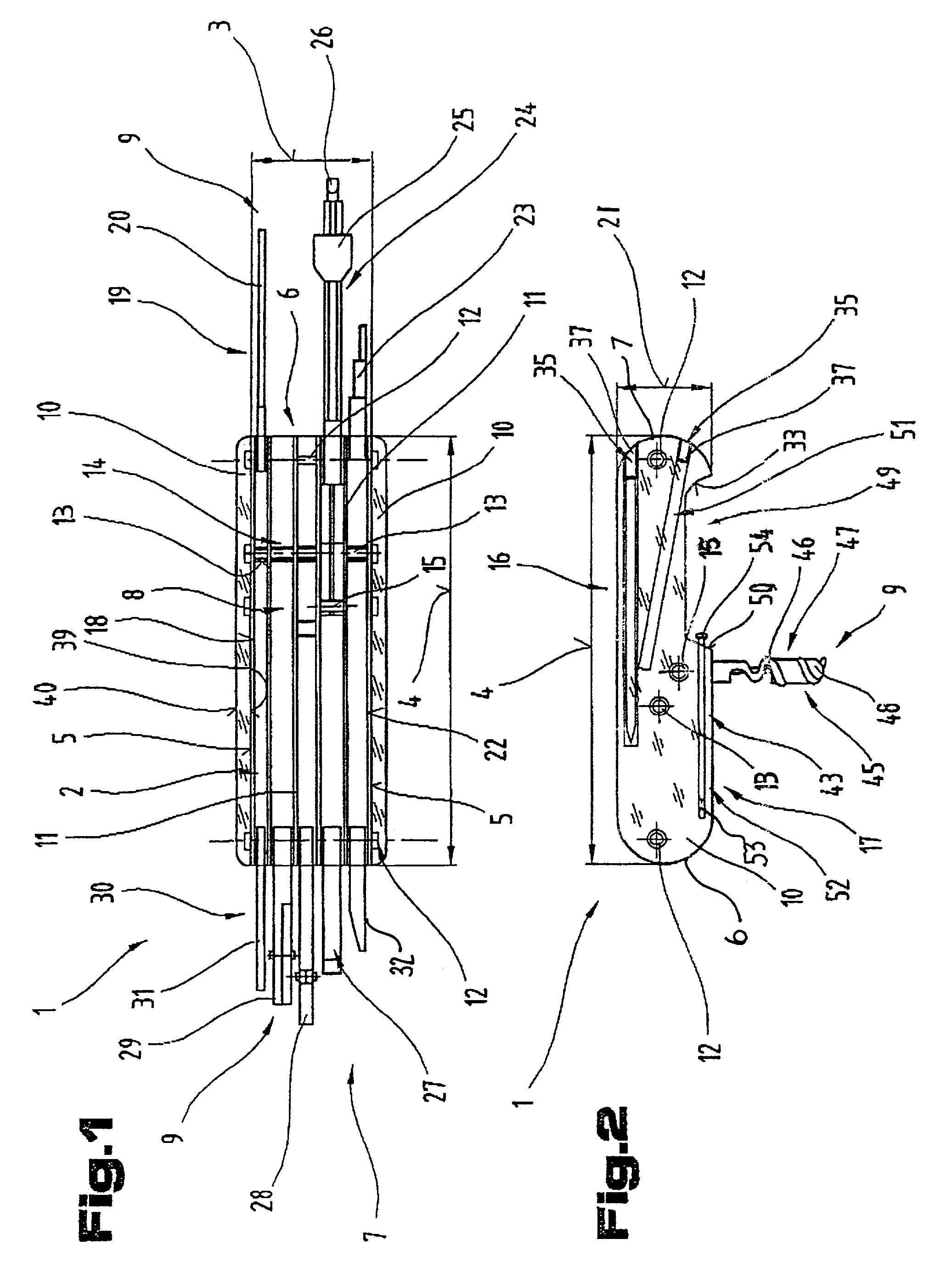
Rope Winding System for Winding and Unwinding Steel Ropes of Cranes
ActiveUS20070228202A1Reliable and goodEasy to operateFilament handlingPortable liftingClassical mechanicsSteel rope
The present invention relates to a rope winding system (1) for winding and unwinding a steel rope (4) of a crane (7). A rope winding system (1) according to the present invention has a rope drum (6), onto which the steel rope (4) can be wound in a plurality of layers, and a magnetic system (7) which is configured to generate a magnetic field over a section of the steel rope (4) with its magnetic flux being deflected by a movement of the steel rope (4) in such a way that the steel rope (4) is braked. A crane (7) is also discloses which is equipped with such a rope winding system (1) for winding and unwinding a steel rope (4).
Owner:TADANO DEMAG GMBH
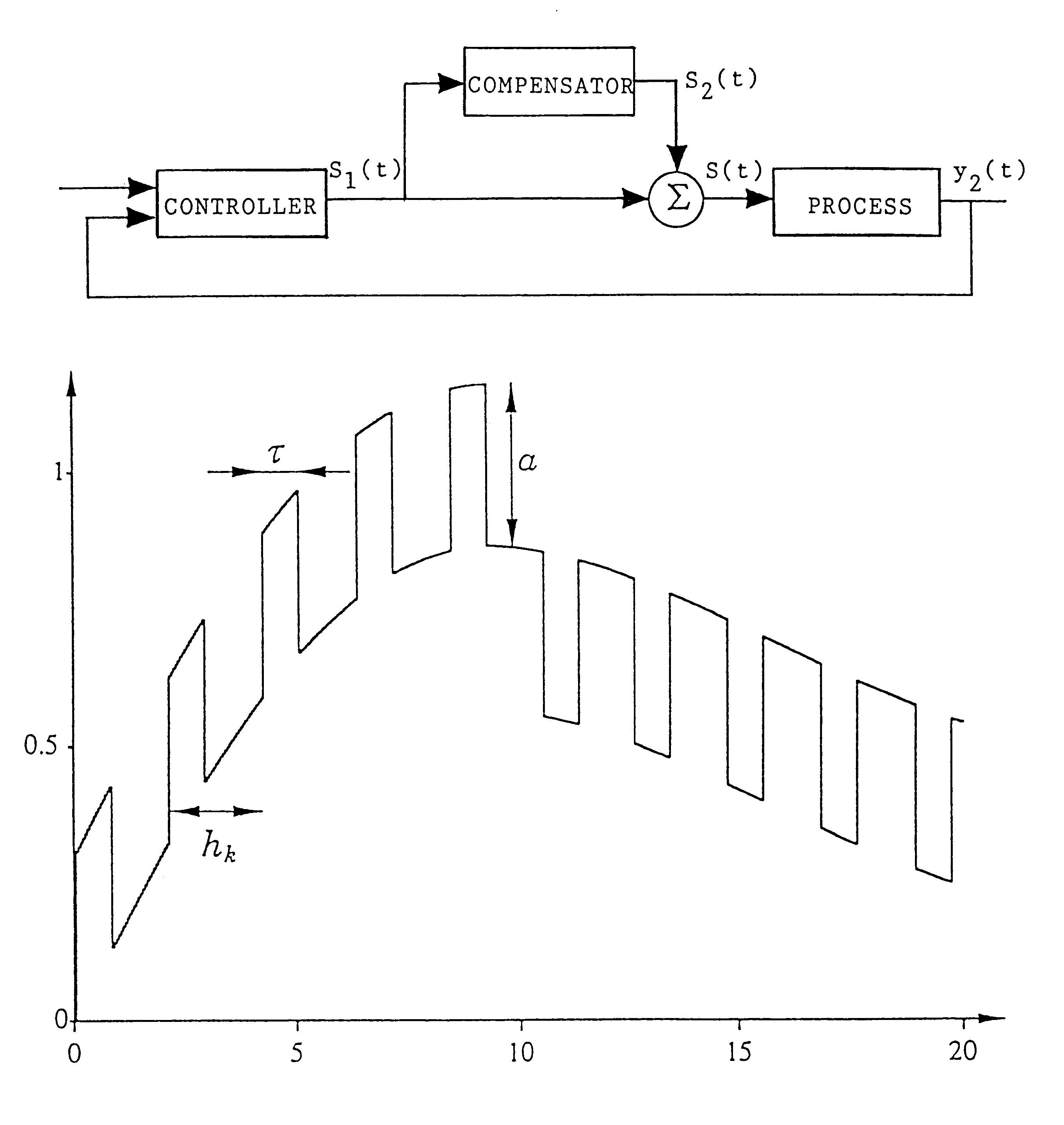
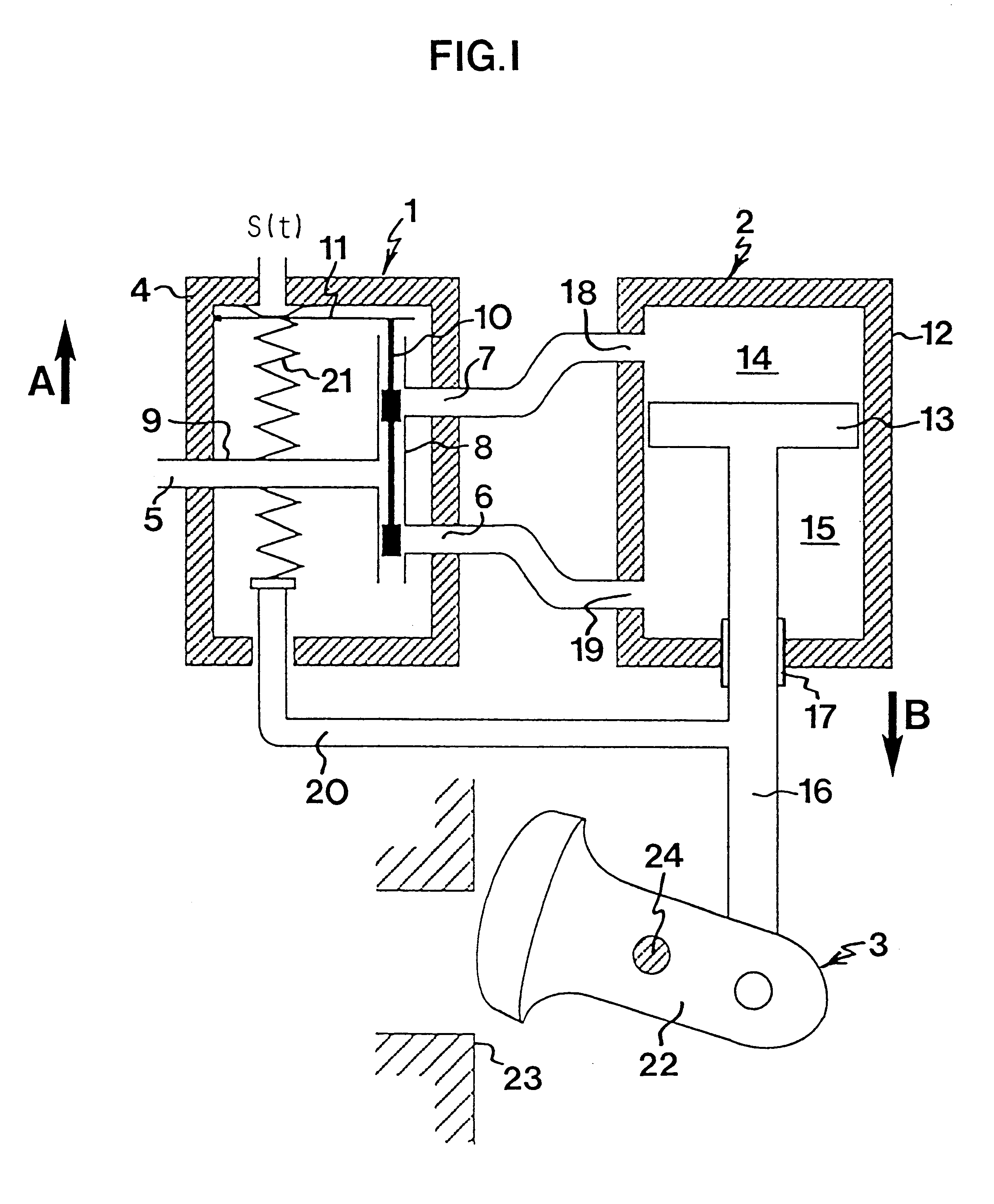
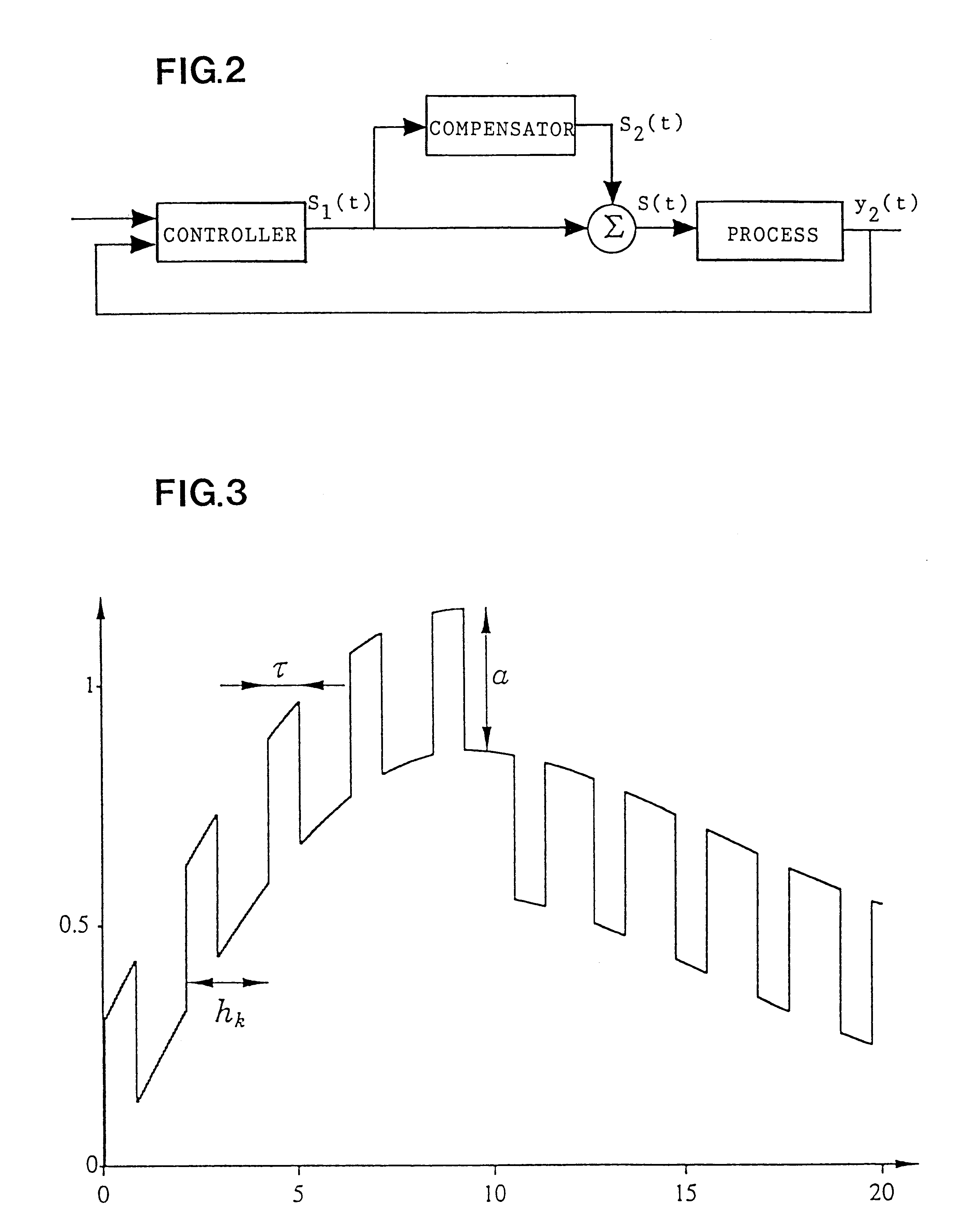
Method and control system for compensating for friction
InactiveUS6285913B1Reduce impactMinimal wearProgramme controlOperating means/releasing devices for valvesControl systemControl signal
A method for compensating for static friction in an actuating device includes the steps of generating an actual signal y2(t) corresponding to a quantity which is controllable by the actuating device, generating a set value signal y1(t) generating a control signal s1(t) based on the set value signal y1(t) and the actual value signal y2(t), and supplying the control signal to the actuating device for controlling the same. The method also includes the steps of generating an intermittent signal s2(t) compensating for friction, sensing the sign of the derivative with respect to time of the control signal s1(t), giving the signal s2(t) compensating for friction the same sign as the derivative, and adding the signal s2(t) compensating for friction to the control signal s1(t) before supplying the same to the actuating device.
Owner:ALFA LAVAL AUTOMATION
High temperature abradable coating for turbine shrouds without bucket tipping
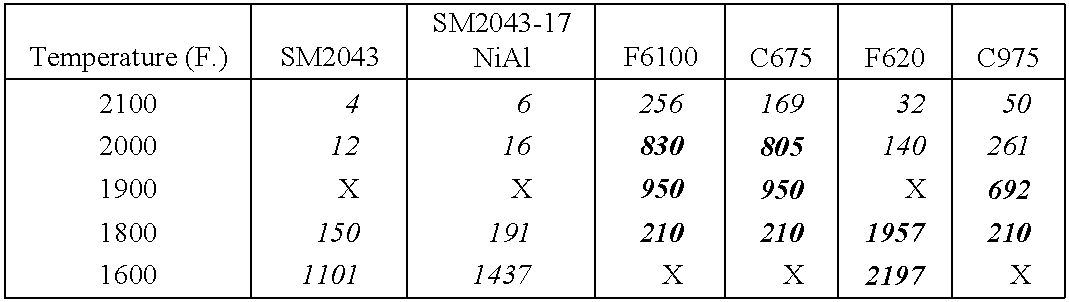
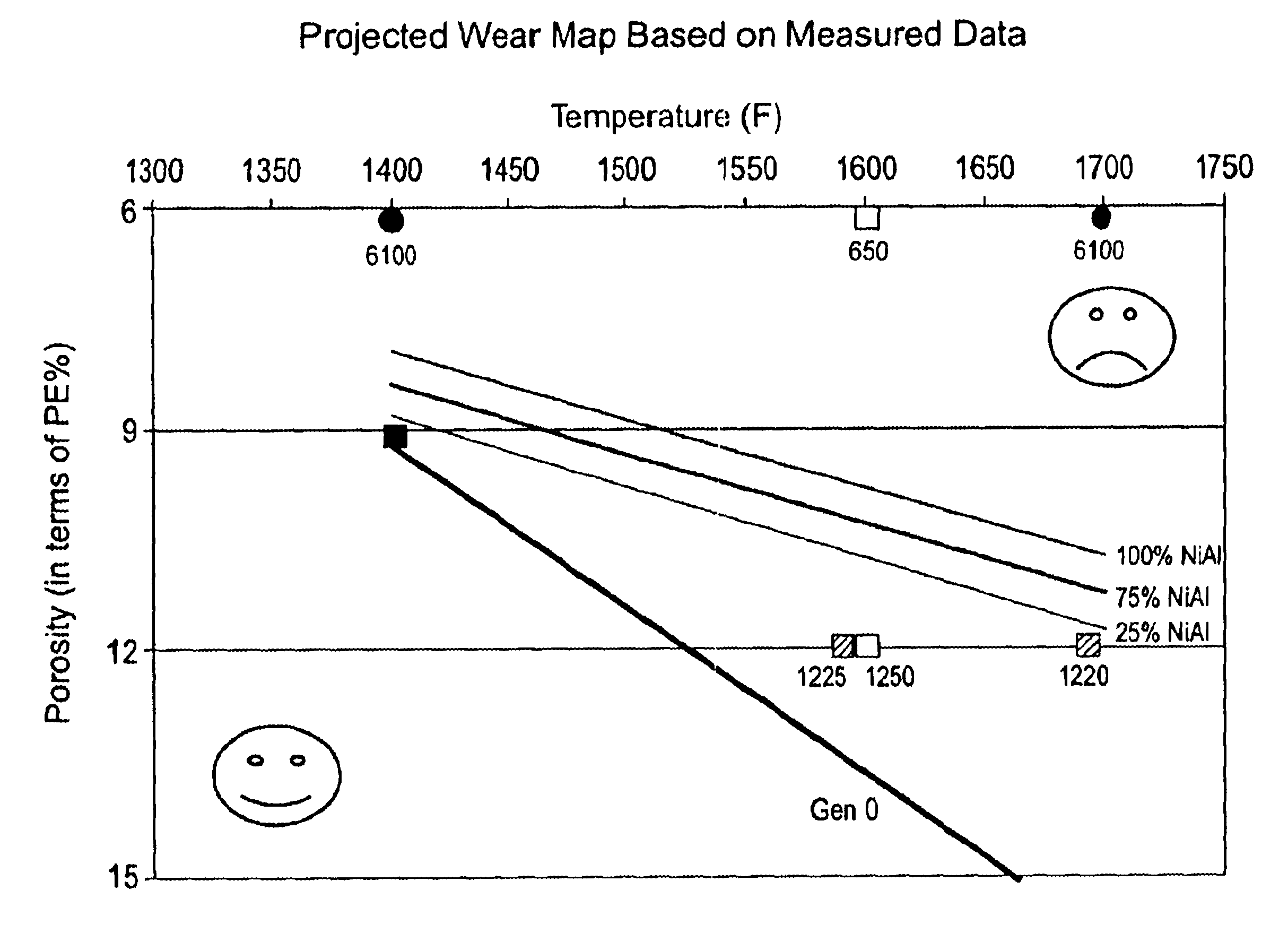
InactiveUS6660405B2Reduce gas leakageImprove turbine efficiencyLiquid surface applicatorsMolten spray coatingPolyesterPorous coating
An abradable coating composition for use on shrouds in gas turbine engines (or other hot gas path metal components exposed to high temperatures) containing an initial porous coating phase created by adding a "fugitive polymer" (such as polyester or polyimide) to the base metal alloy, together with a brittle intermetallic phase such as .beta.-NiAl that serves to increase the brittle nature of the metal matrix, thereby increasing the abradability of the coating at elevated temperatures, and to improve the oxidation resistance of the coating at elevated temperatures. Coatings having about 12 wt % polyester has been found to exhibit excellent abradability for applications involving turbine shroud coatings. An abradable coating thickness in the range of between 40 and 60 ml provides the best performance for turbine shrouds exposed to gas temperatures between 1380.degree. F. and 1850.degree. F. Abradable coatings in accordance with the invention can be used for new metal components or to repair existing equipment.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Apparatus and methods for parallel processing of multiple reaction mixtures
InactiveUS6913934B2Reduce wearEasy to handleProcess control/regulationProgramme-controlled manipulatorEngineeringParallel processing
Owner:UNCHAINED LABS
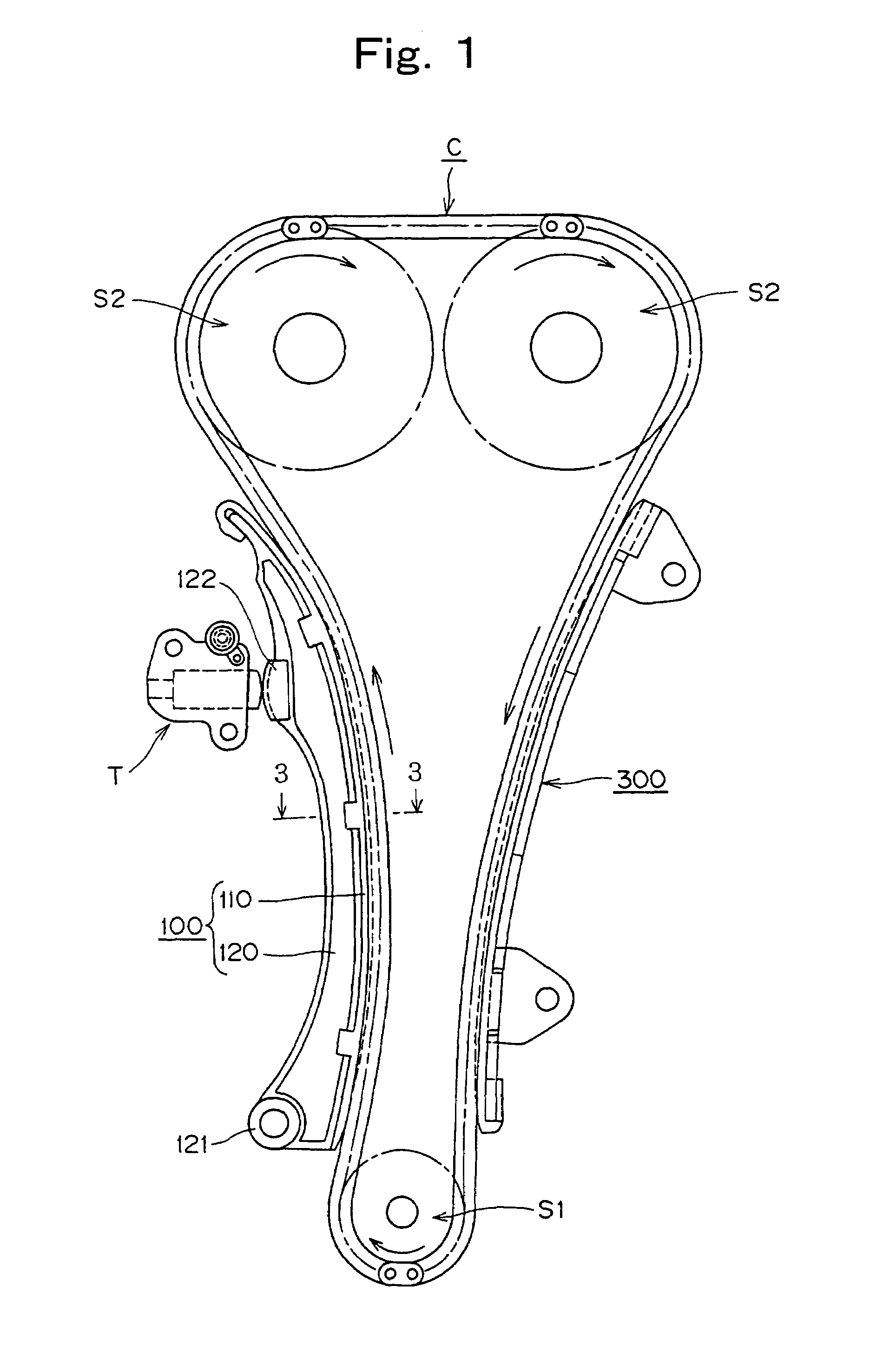
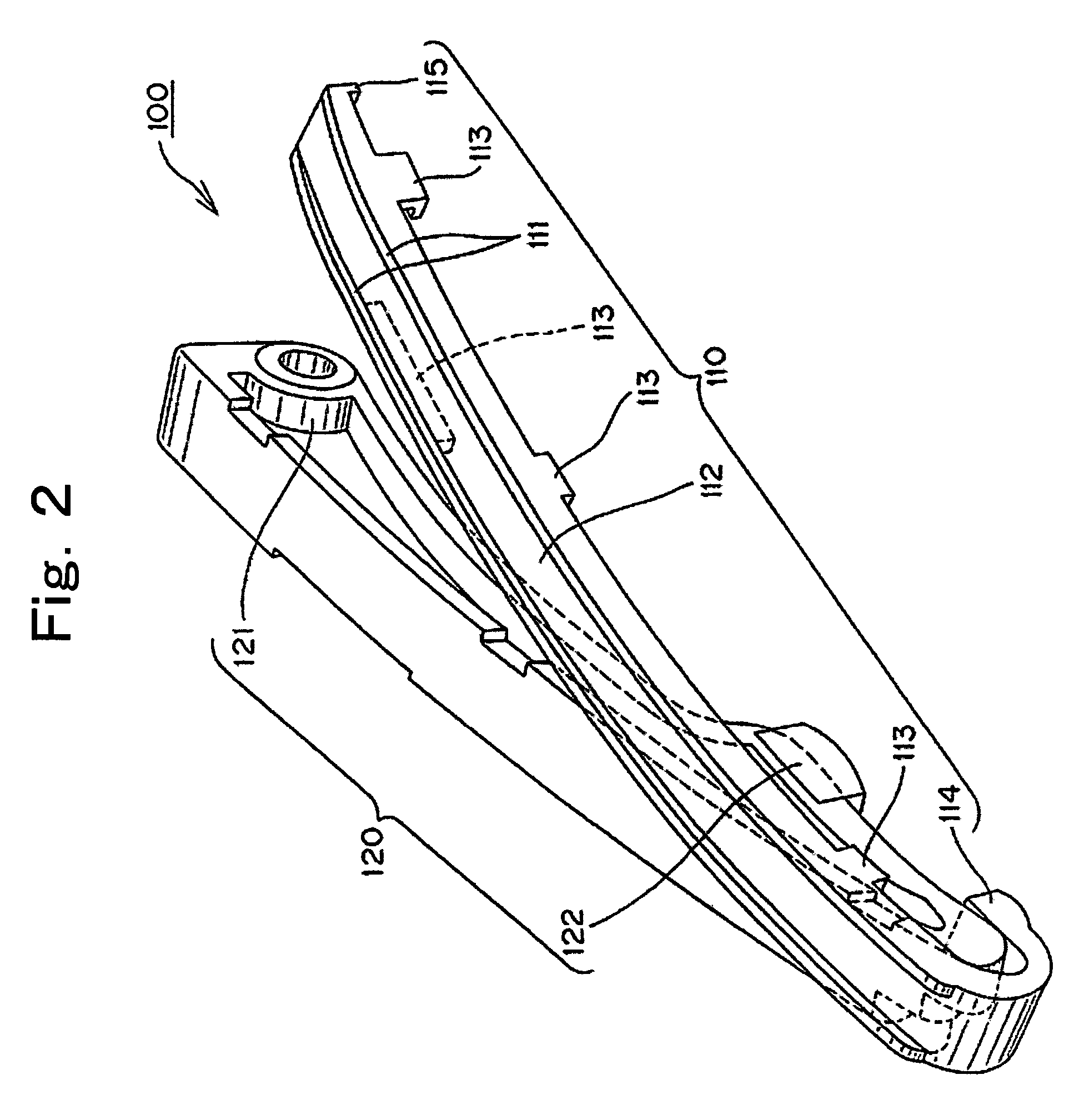
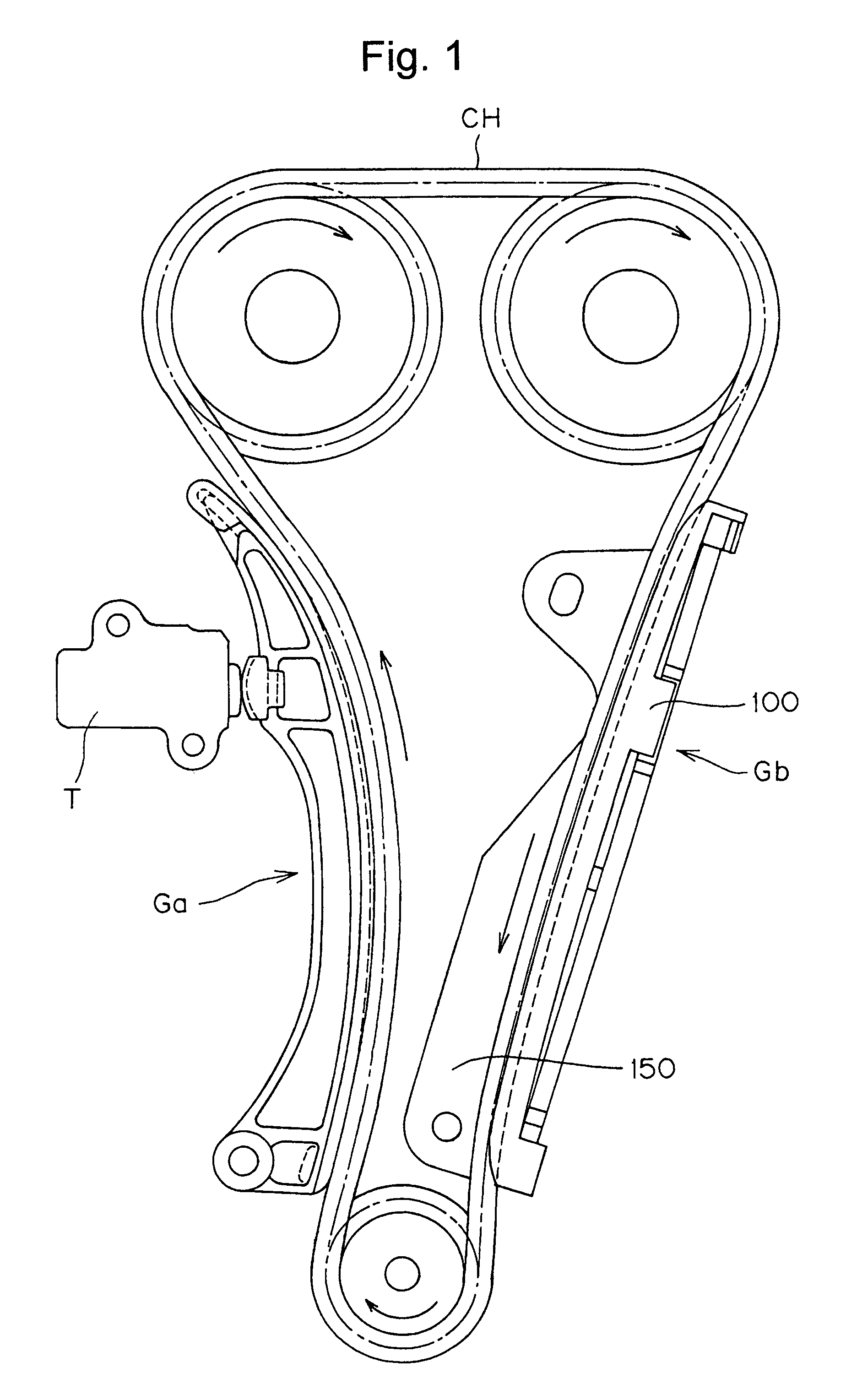
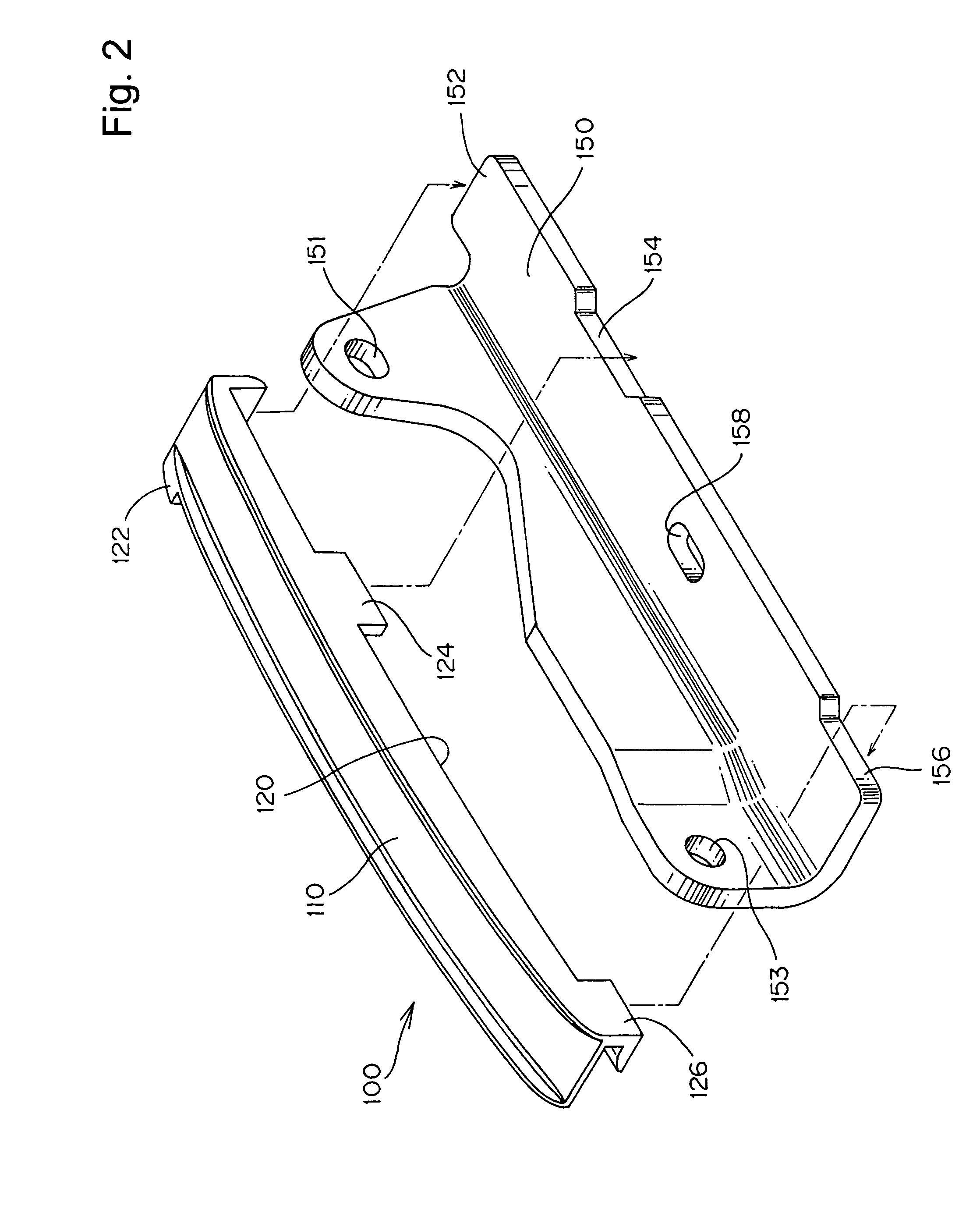
Sliding contact guide for transmission device
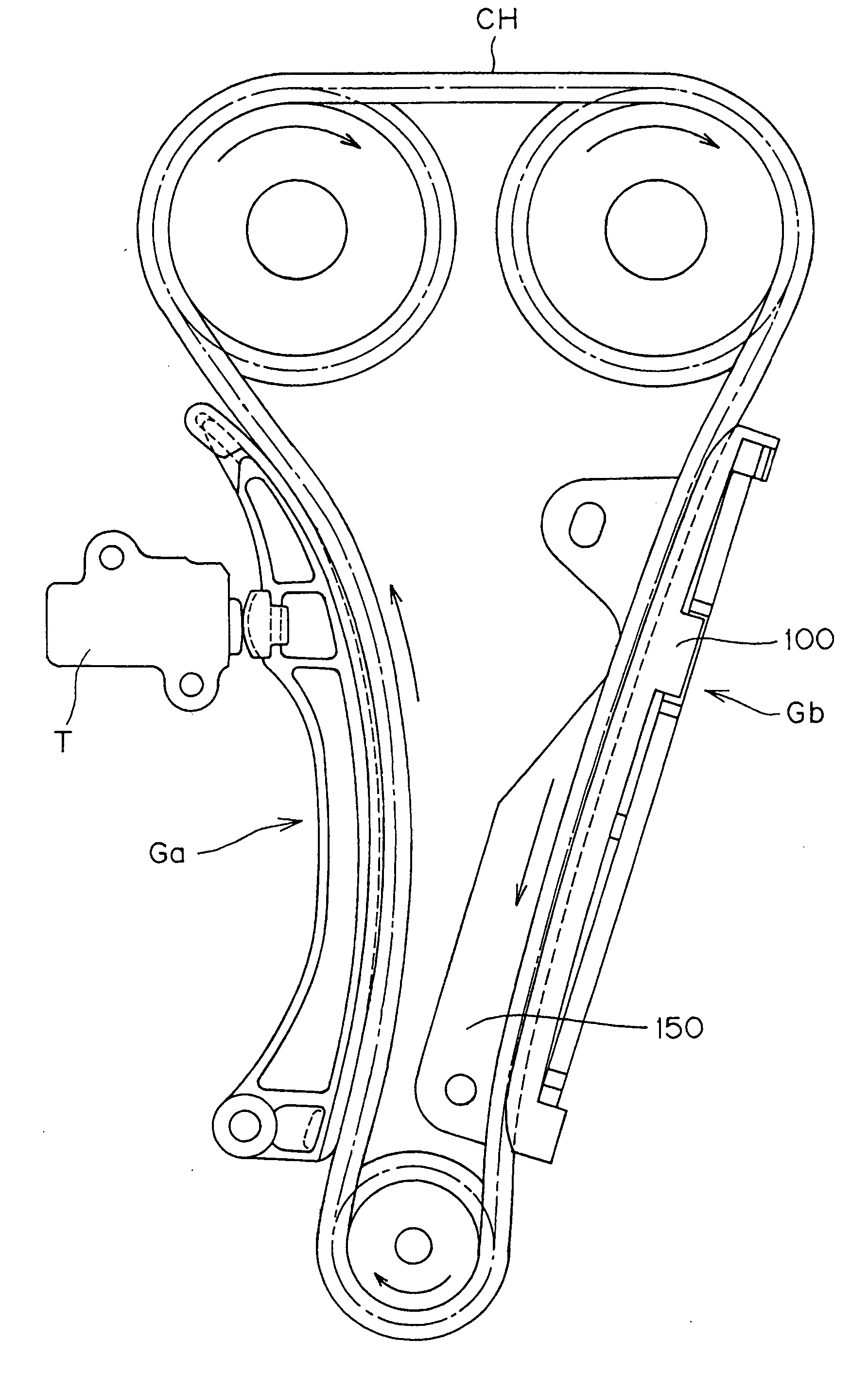
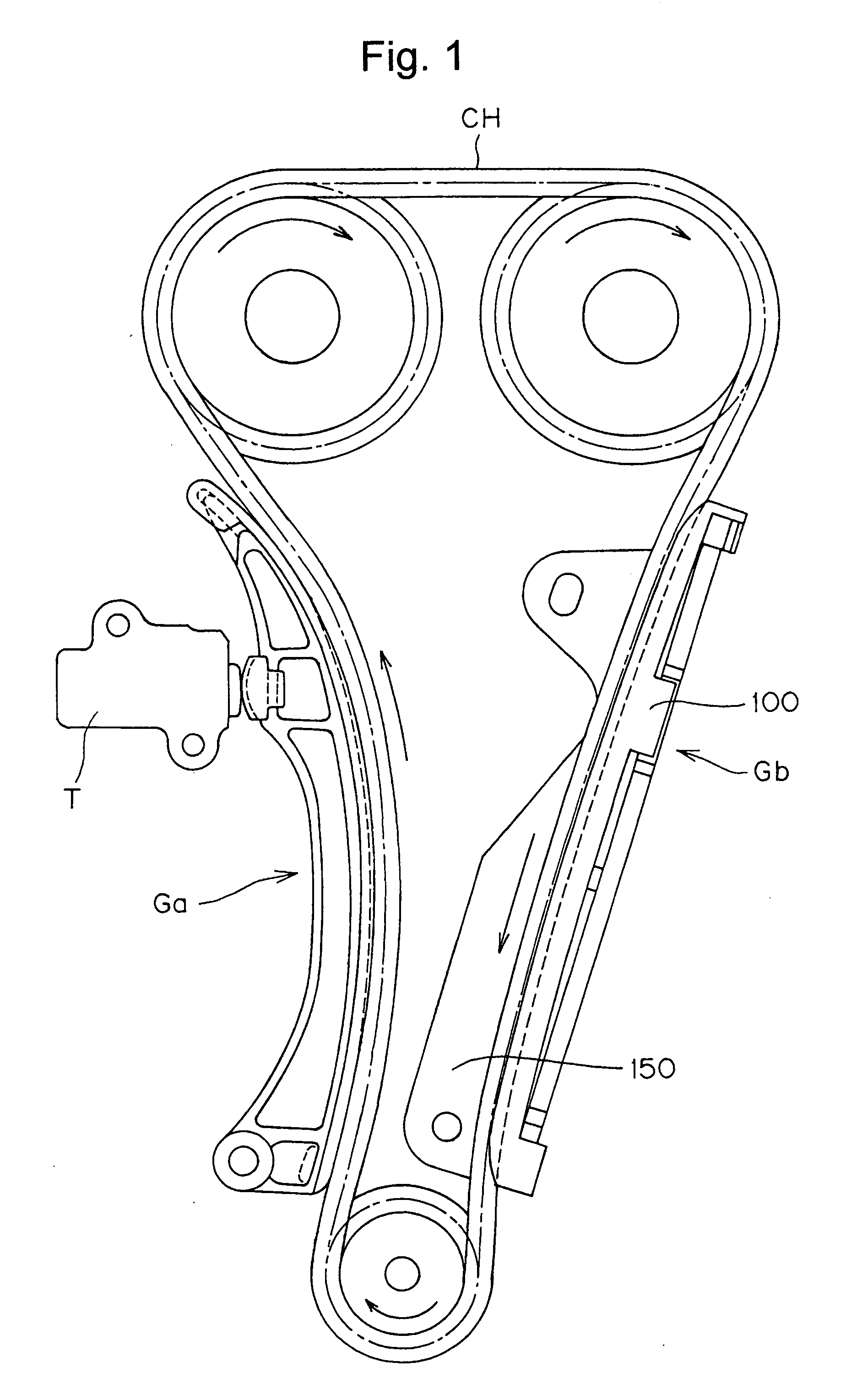
In a sliding contact chain guide of the kind used in the timing transmission of an internal combustion engine, the back of the guide shoe, which engages a metal guide base, is formed with two, spaced longitudinal ribs, having between them a set of ribs formed in a lattice. The longitudinal ribs are wider than the ribs of the lattice.
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO CHAIN CO
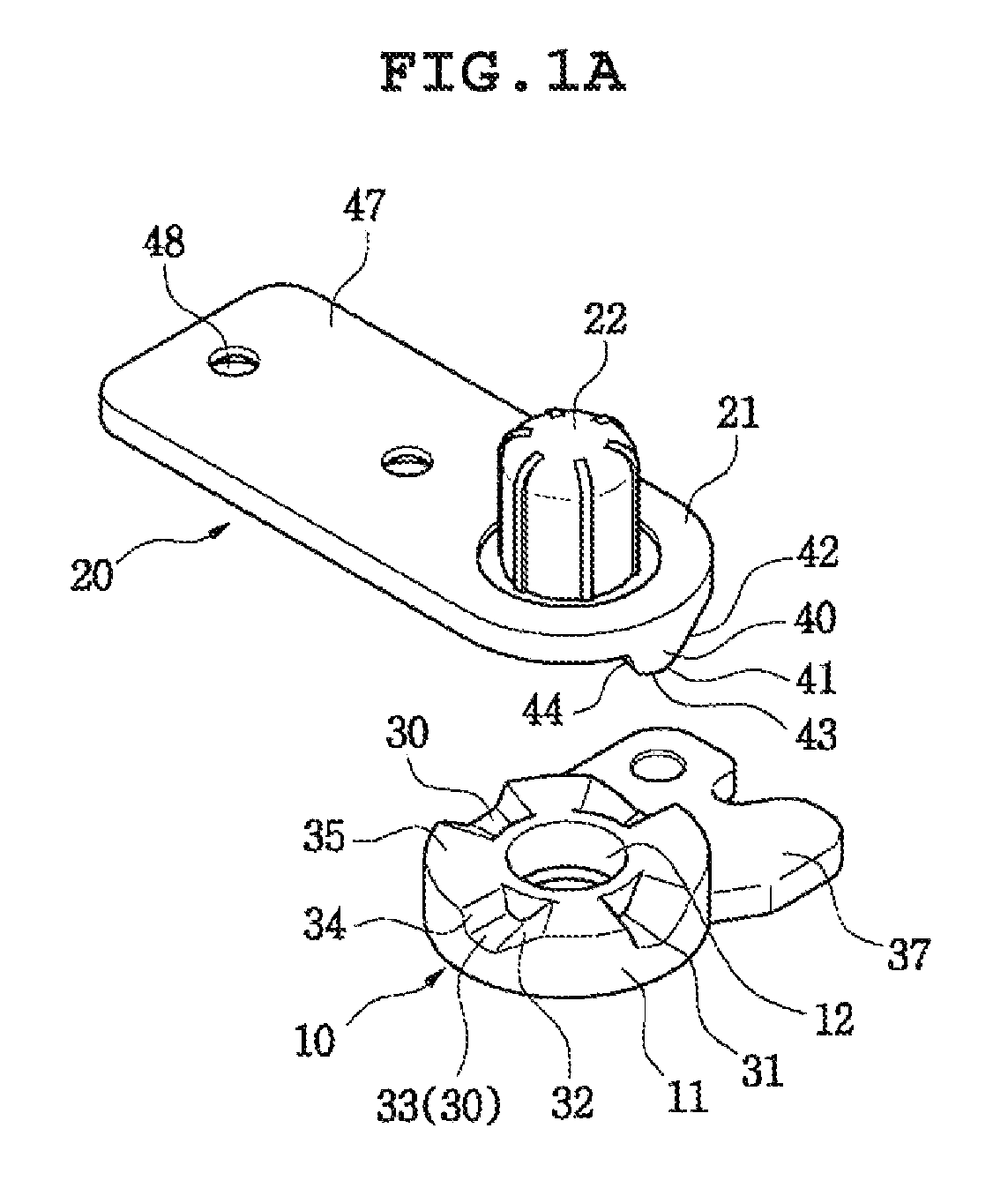
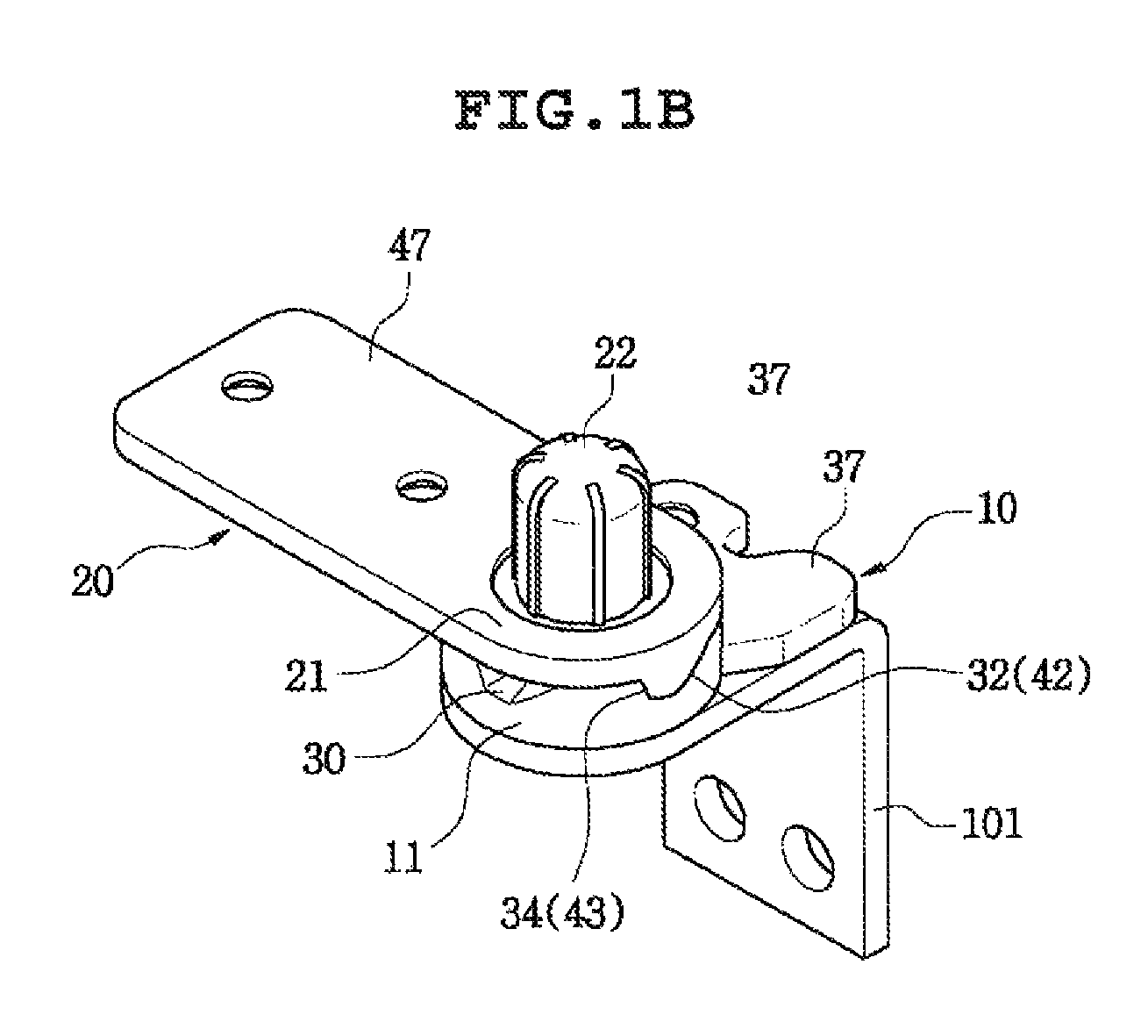
Door hinge for a refrigerator
ActiveUS8510913B2Simple configurationMinimal wearDomestic cooling apparatusLighting and heating apparatusIceboxStructural engineering
A door hinge unit in a refrigerator which pivots a door on a refrigerator body, and holds the door to maintain an opened state or a maximum opened state at a predetermined position for preventing the door from hitting an external object and a hinge shaft from breaking, and minimizes a friction surface between a male member and a female member of the hinge for making movement of the hinge smooth and preventing the hinge from causing noise.
Owner:BLUENIX CO LTD
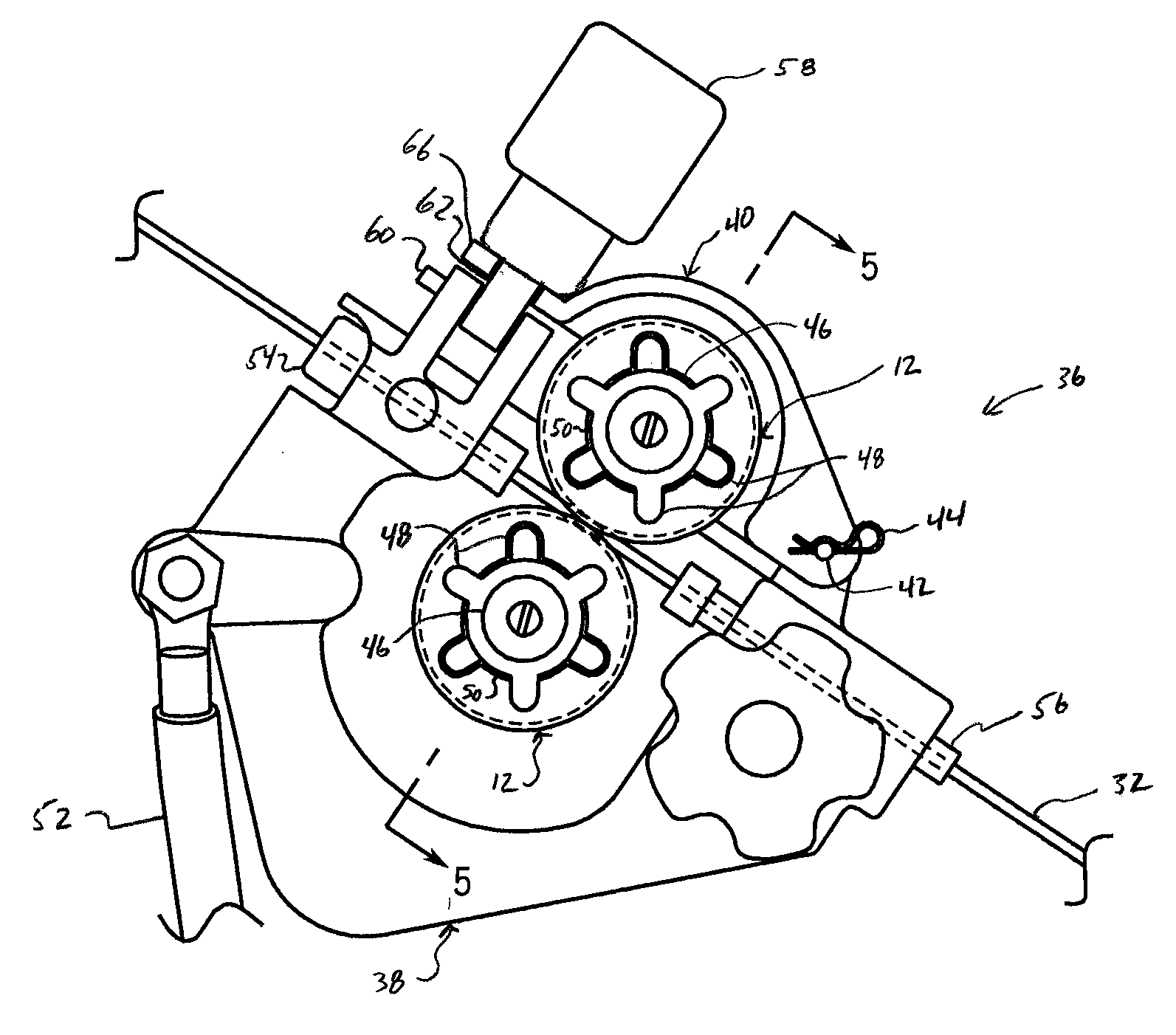
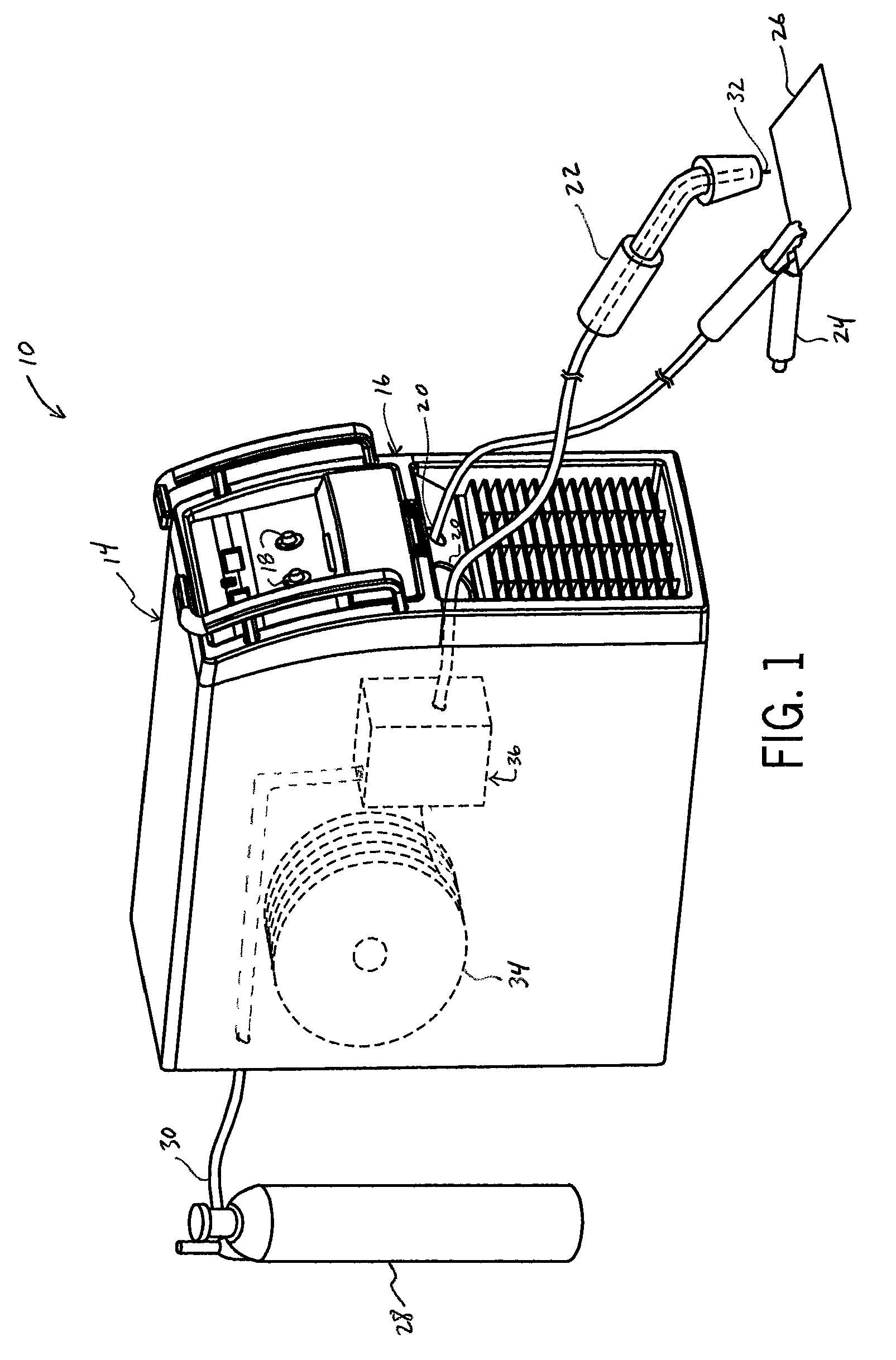
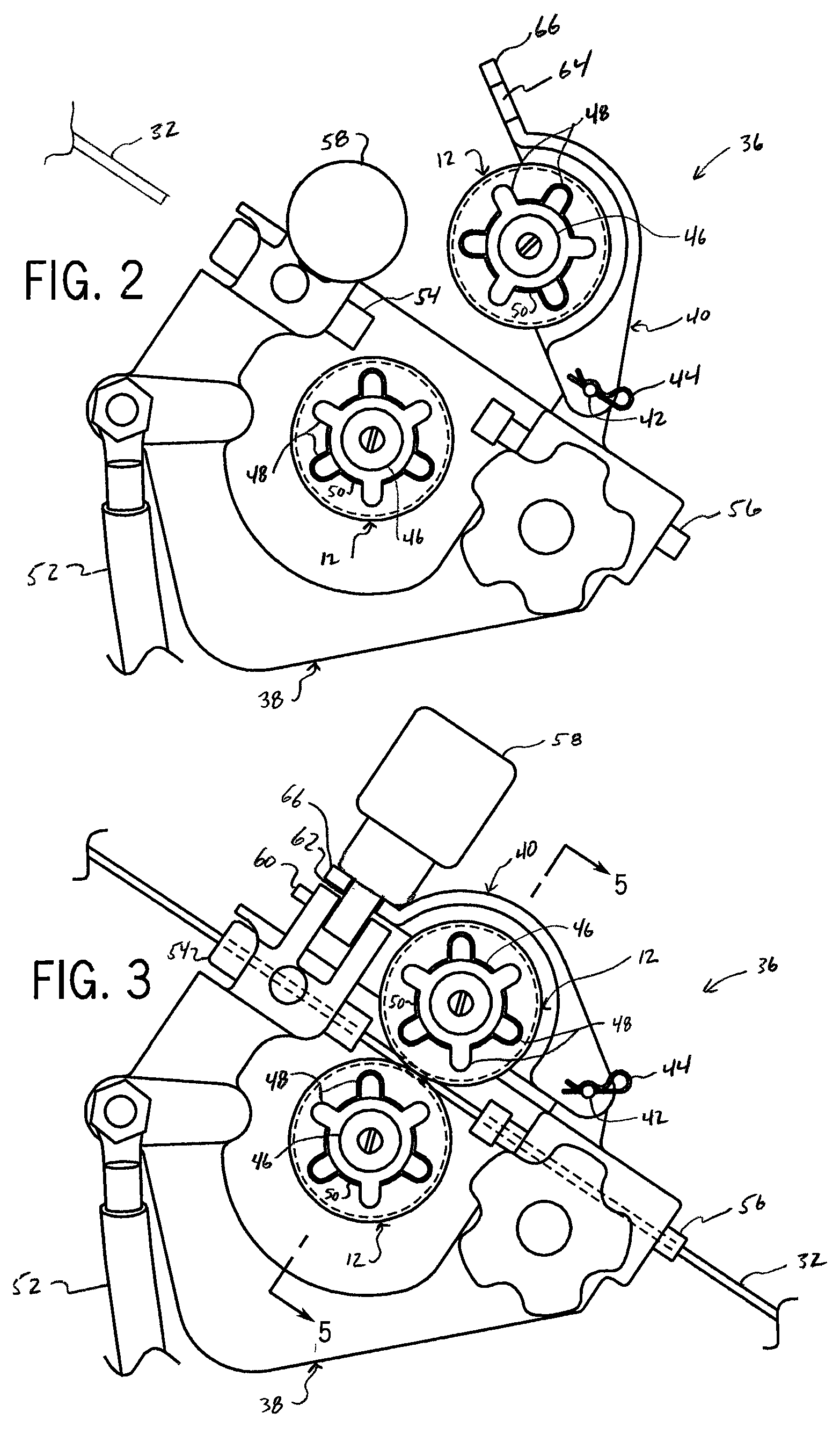
Drive roll for a wire feeder
ActiveUS20090277890A1Minimal wearAbsorb cyclical stressArc welding apparatusTurning toolsWire rodEngineering
A drive roll is disclosed that is useable in a wire feeder for advancing a wire. The drive roll includes a first side, a second side offset from the first side, and an annular surface between the first side and the second side. An annular groove is formed in the annular surface and defines an engagement surface. Pluralities of lands are spaced along the engagement surface and pluralities of notches are formed in the engagement surface for engaging and advancing the wire. An engagement ratio is defined between the total land area of the plurality of lands and the total notch area of the plurality of notches calculated at the engagement surface. The engagement ratio defines a drive roll that accurately engages and advances the wire over a longer period of use.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Horizontal drilling system with oscillation control
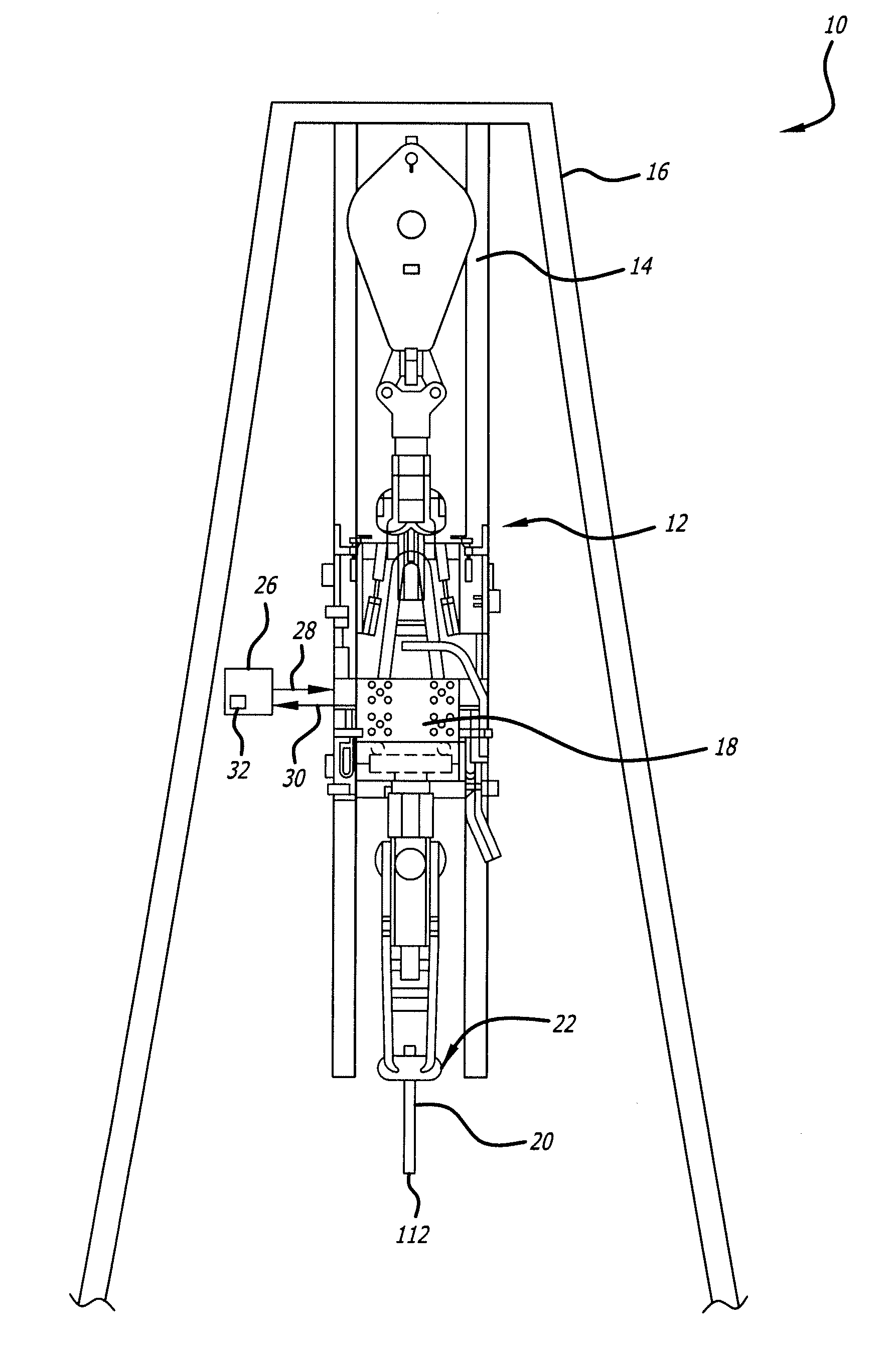
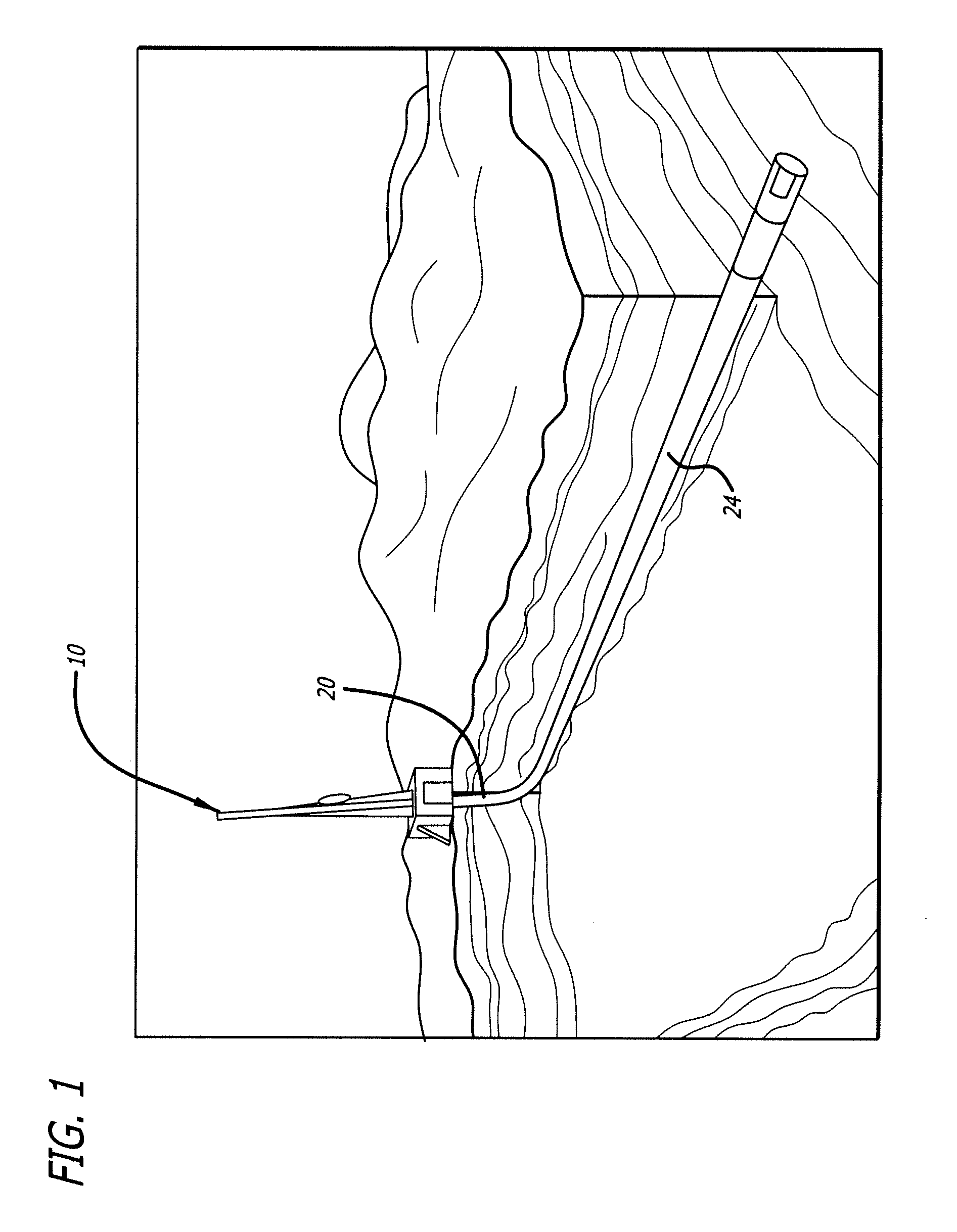
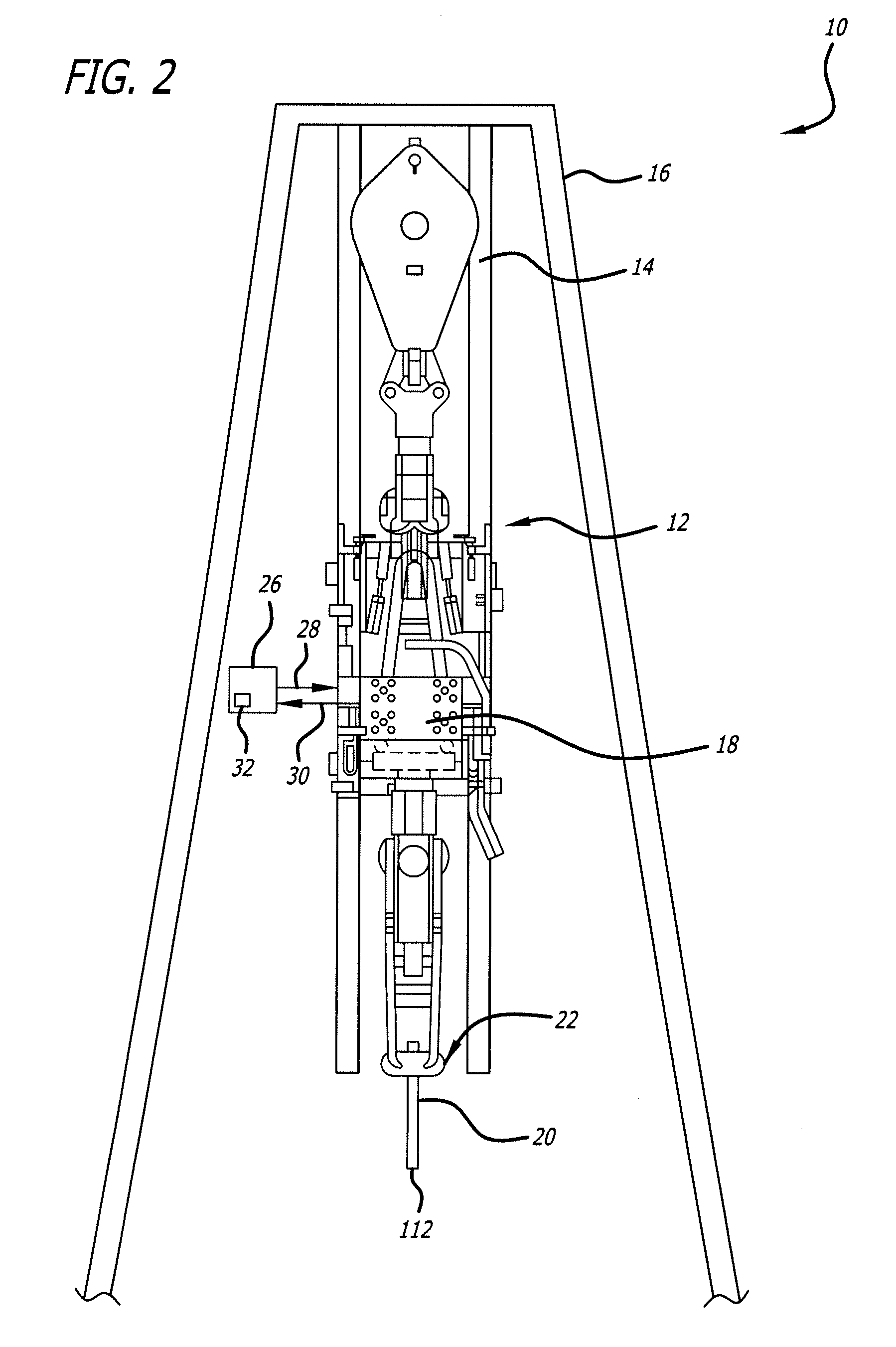
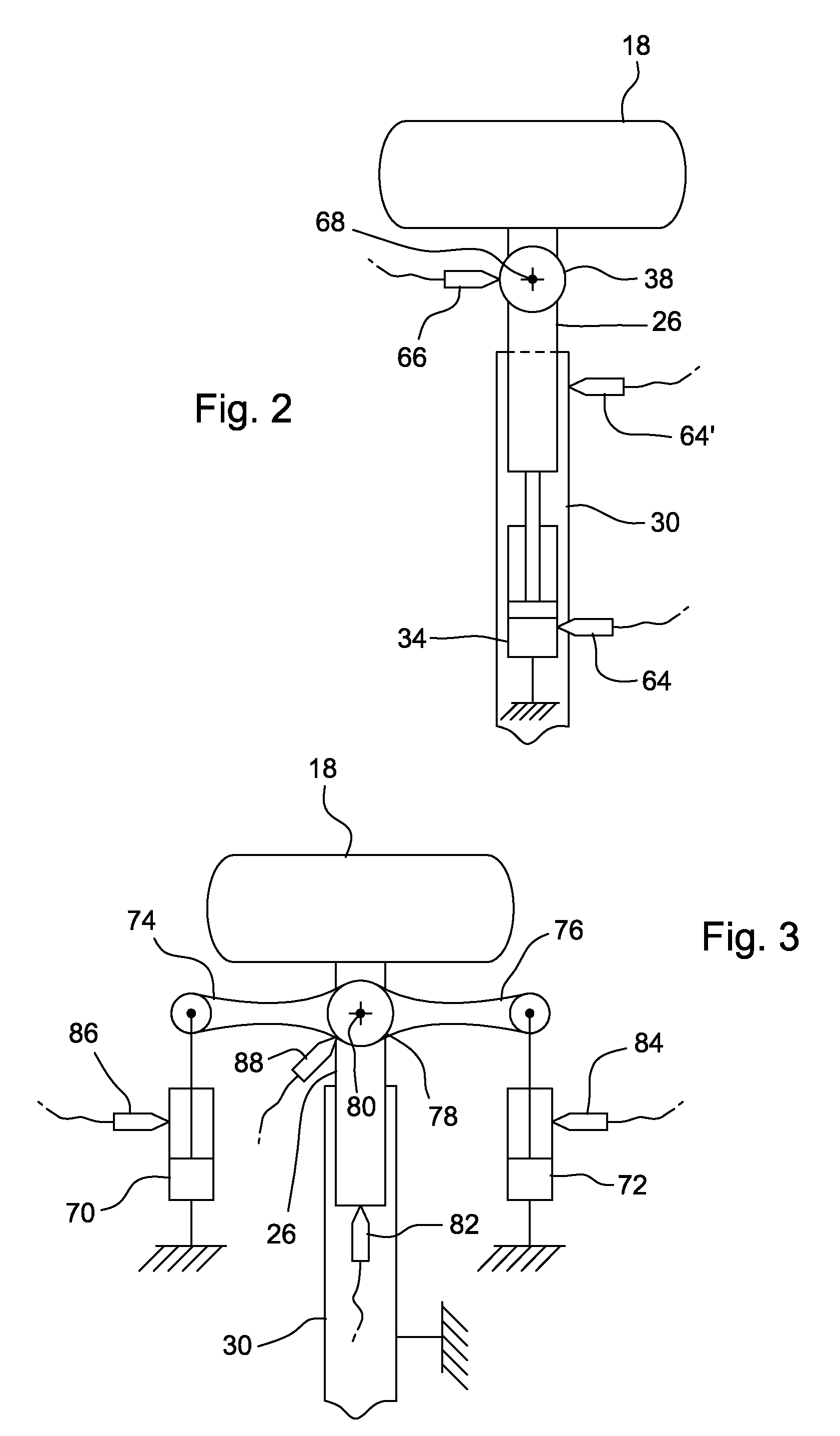
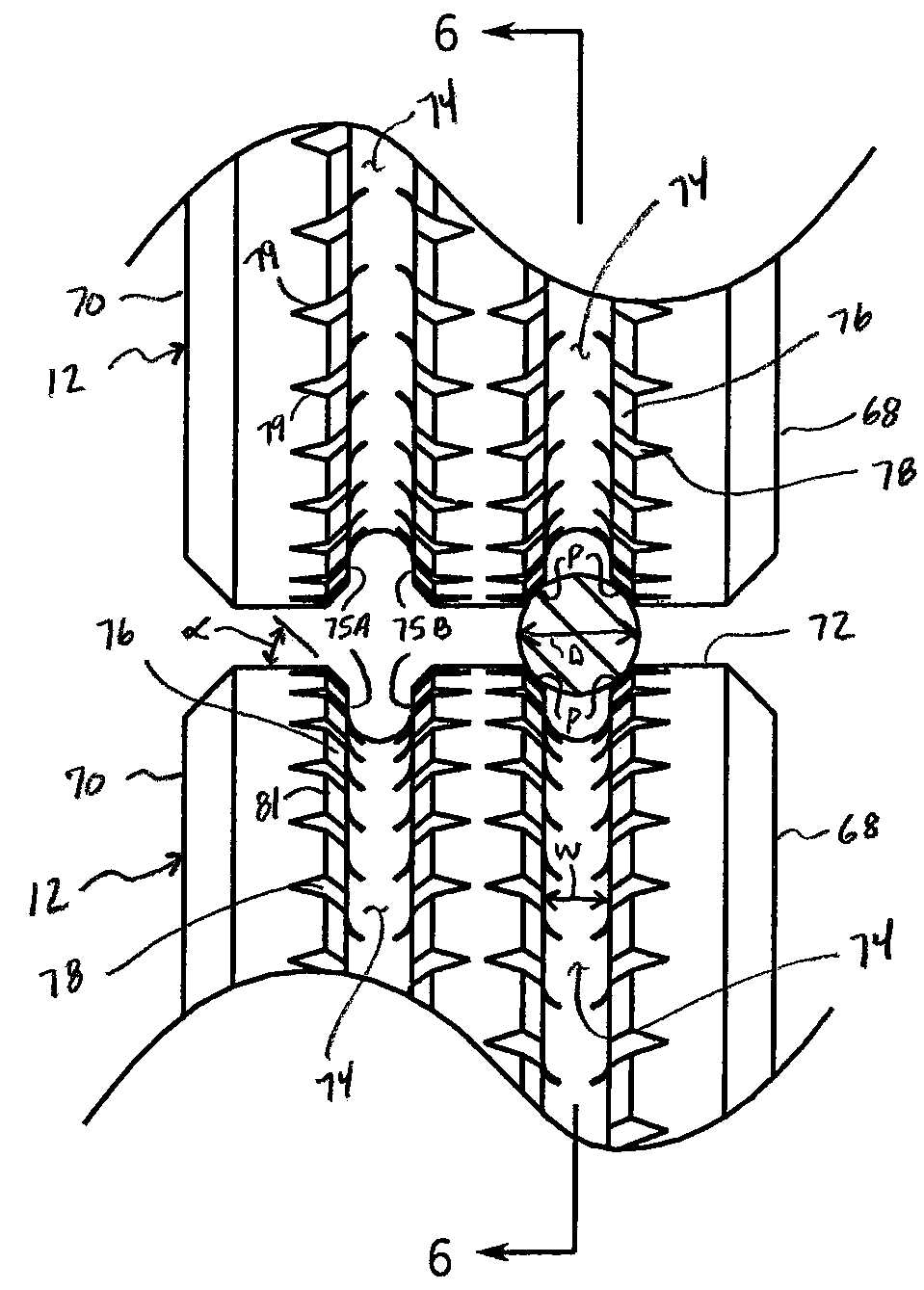
ActiveUS20070175662A1Precise and stable controlMinimal machine wearSurveyDrilling rodsTop driveEngineering
A system and method for controlling drill string frictional forces during horizontal drilling are provided. The system includes a top drive having a motor that transmits a torque to a drill string to rotate the drill string, and an automated controller operably connected to the top drive to send at least one command signal to the top drive to initiate the rotation of the drill string. The controller monitors torque feedback signals, indicating that a torque limit on the drill string is exceeded, and / or a turn feedback signals indicating that the drill string is stalled to control the direction of the torque applied to the drill string when either the torque limit is exceeded or the drill string stalls.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
Horizontal drilling system with oscillation control
A system and method for controlling drill string frictional forces during horizontal drilling are provided. The system includes a top drive having a motor that transmits a torque to a drill string to rotate the drill string, and an automated controller operably connected to the top drive to send at least one command signal to the top drive to initiate the rotation of the drill string. The controller monitors torque feedback signals, indicating that a torque limit on the drill string is exceeded, and / or a turn feedback signals indicating that the drill string is stalled to control the direction of the torque applied to the drill string when either the torque limit is exceeded or the drill string stalls.
Owner:VARCO I P INC
Guide for transmission device
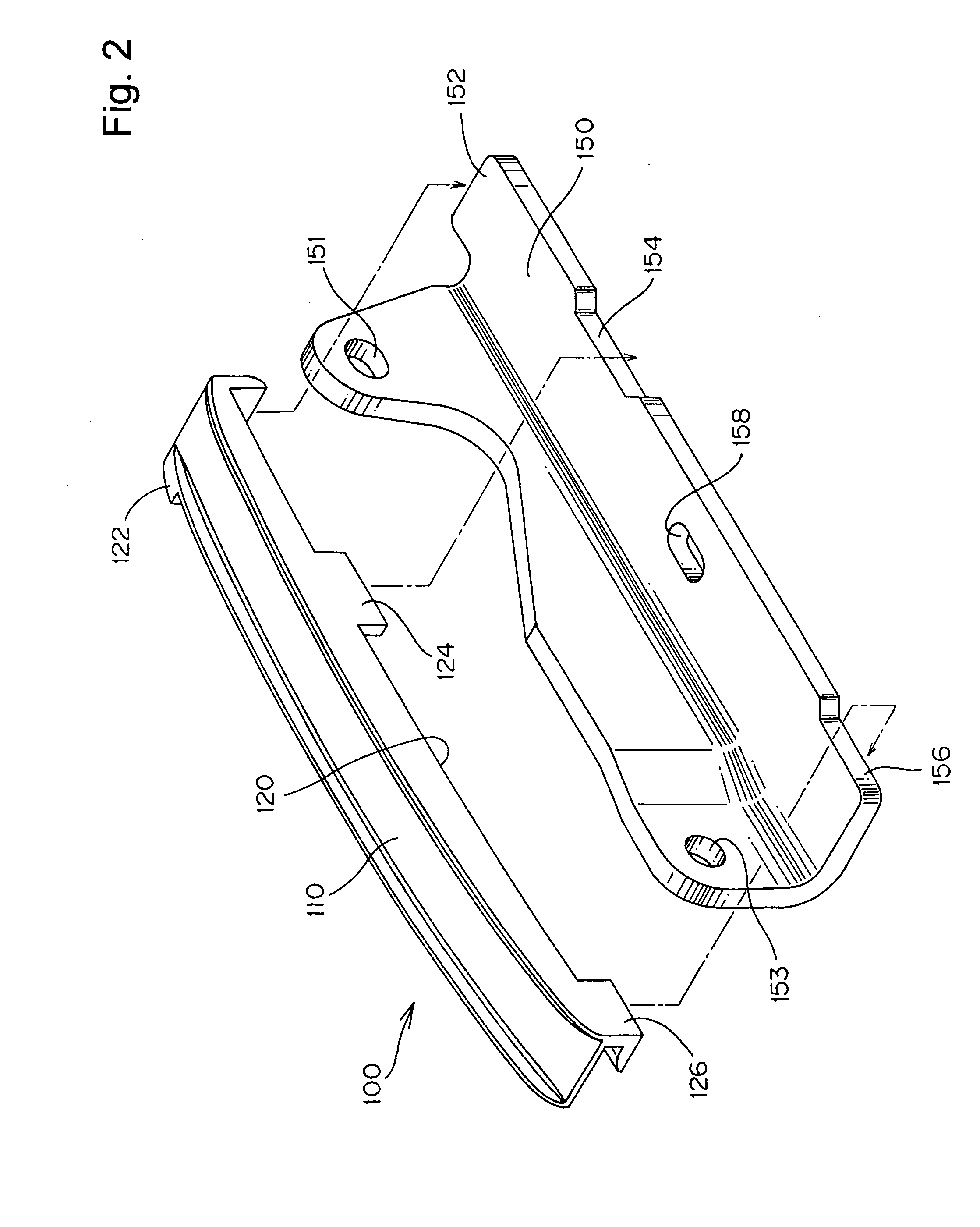
A guide for an engine timing chain comprises a metal supporting base and a resin shoe, the shoe having integrally formed hooks for attachment to the supporting base, and integrally formed side walls for limiting lateral movement of the chain on the sliding contact surface of the shoe. A central portion of the shoe has a sandwich injection molded structure and comprises a high strength core of glass fiber-reinforced polyamide resin, and a polyamide skin layer. The side walls and the hooks are formed entirely of the skin layer material.
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO CHAIN CO
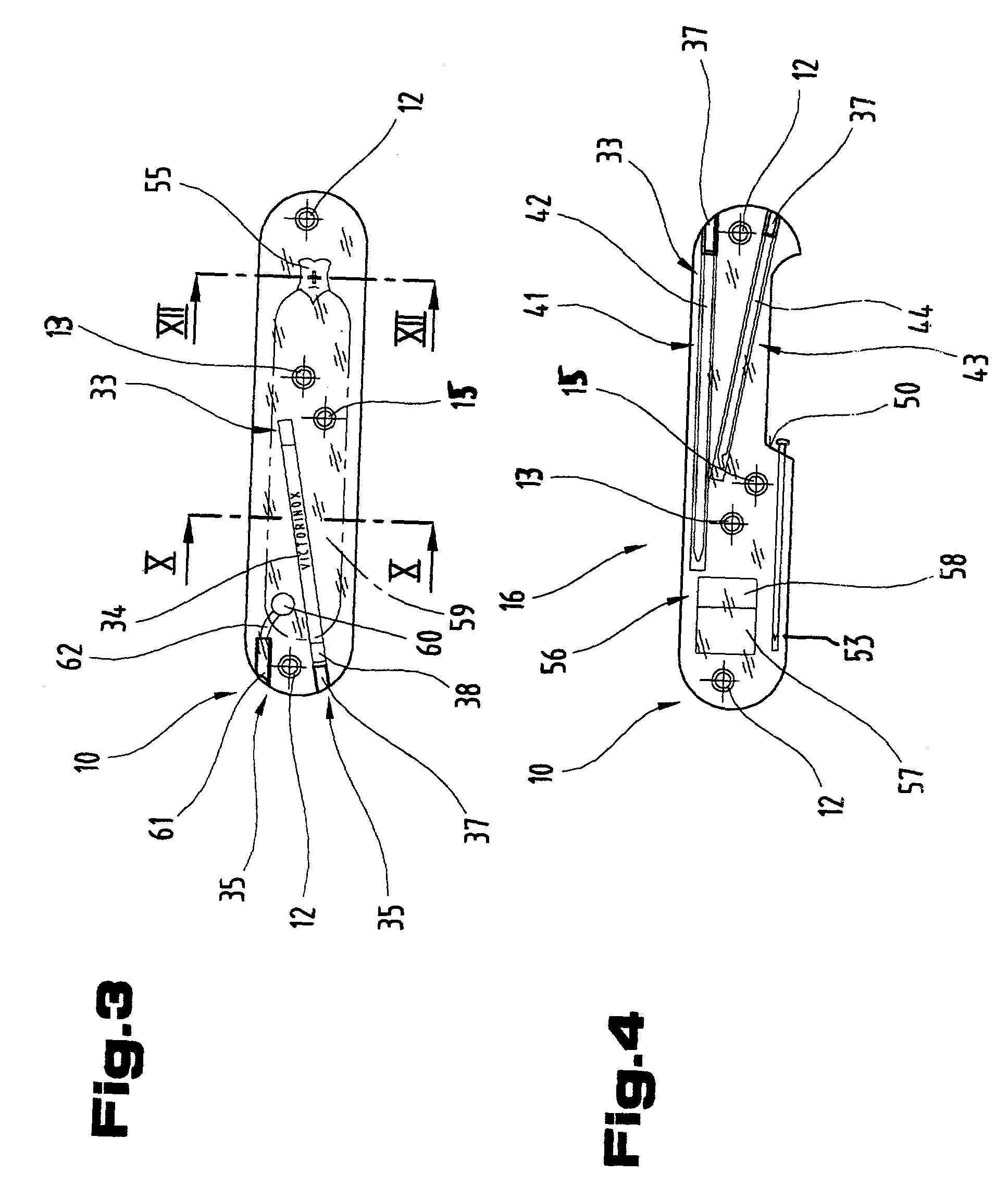
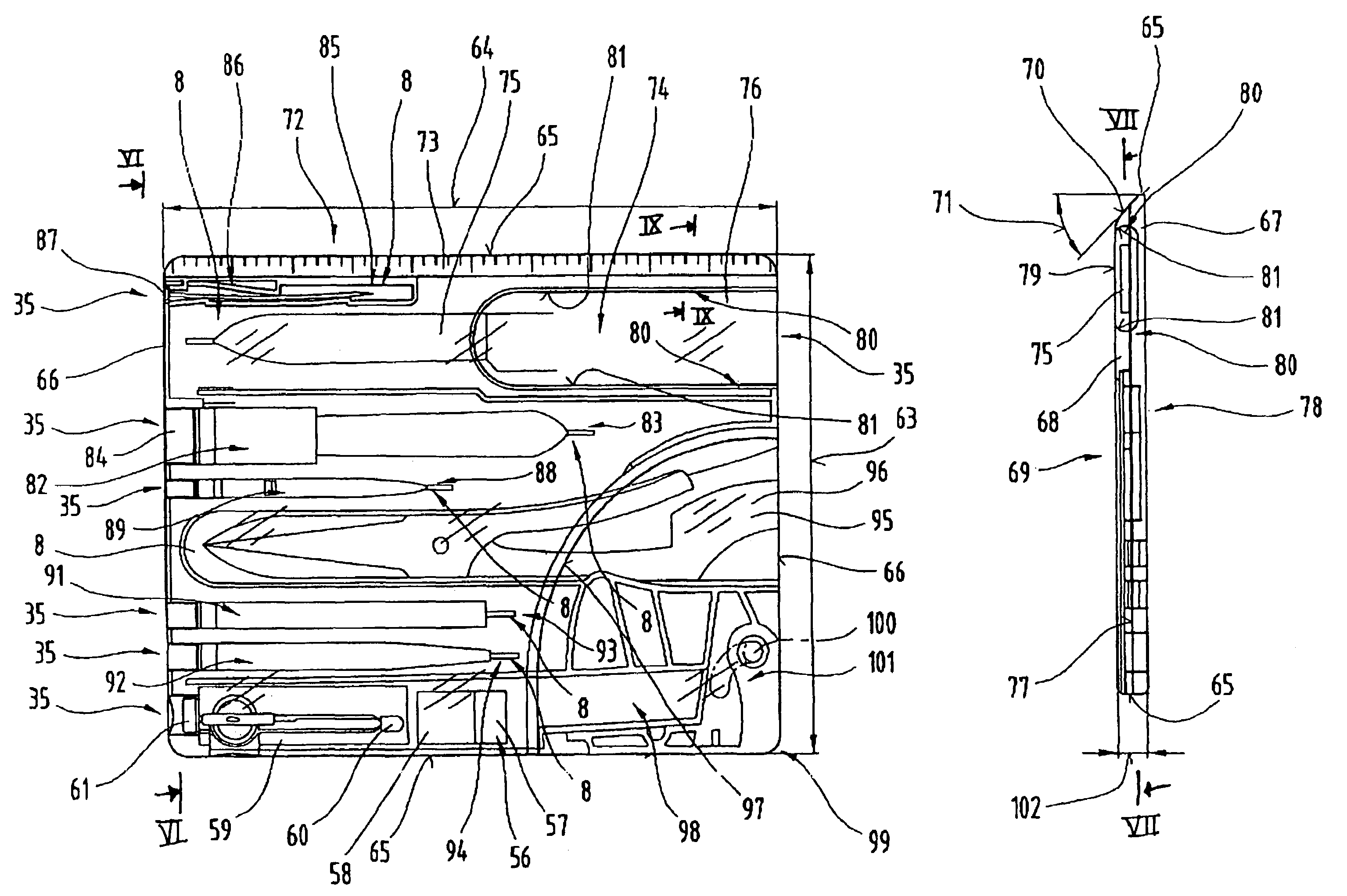
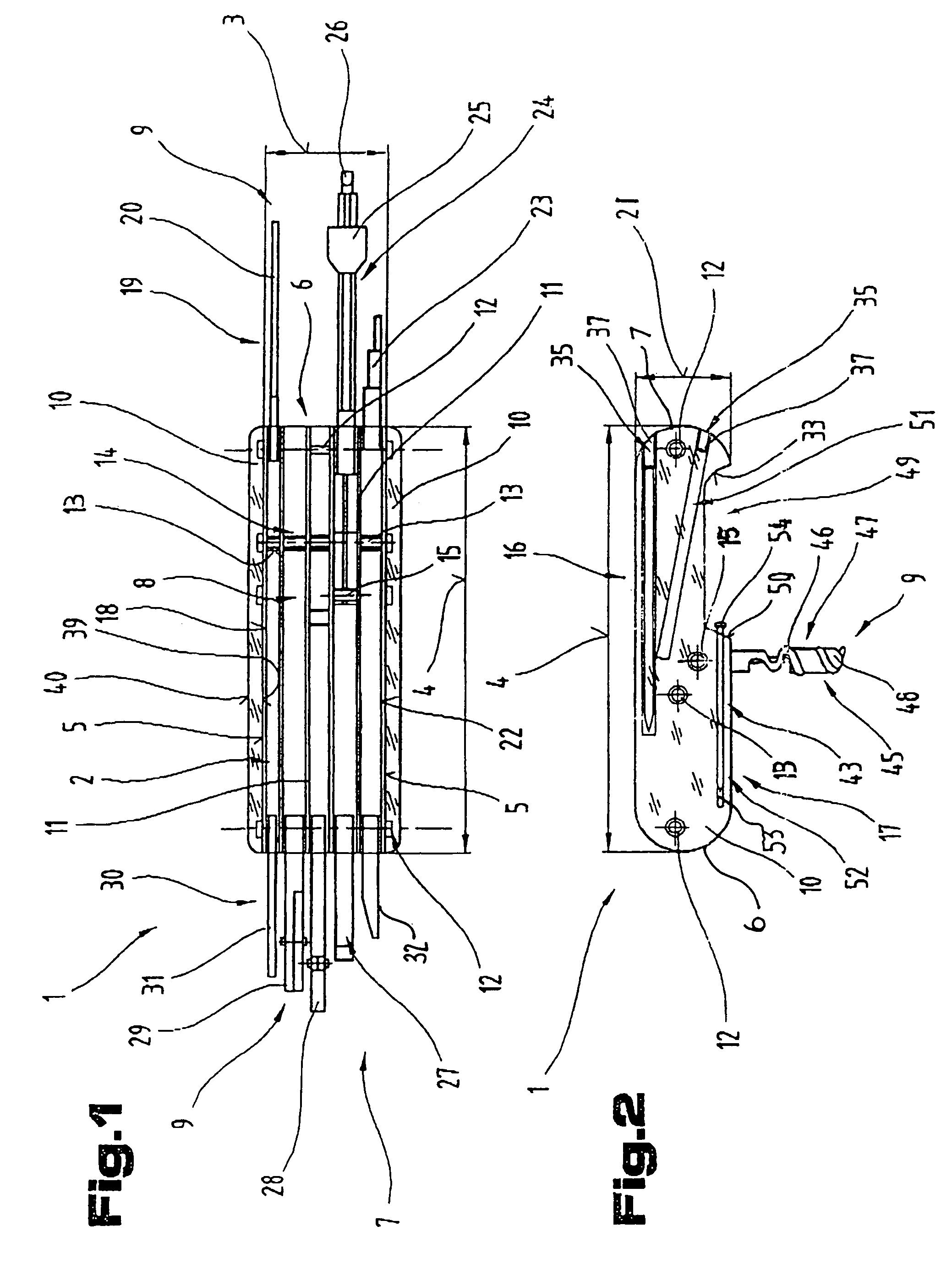
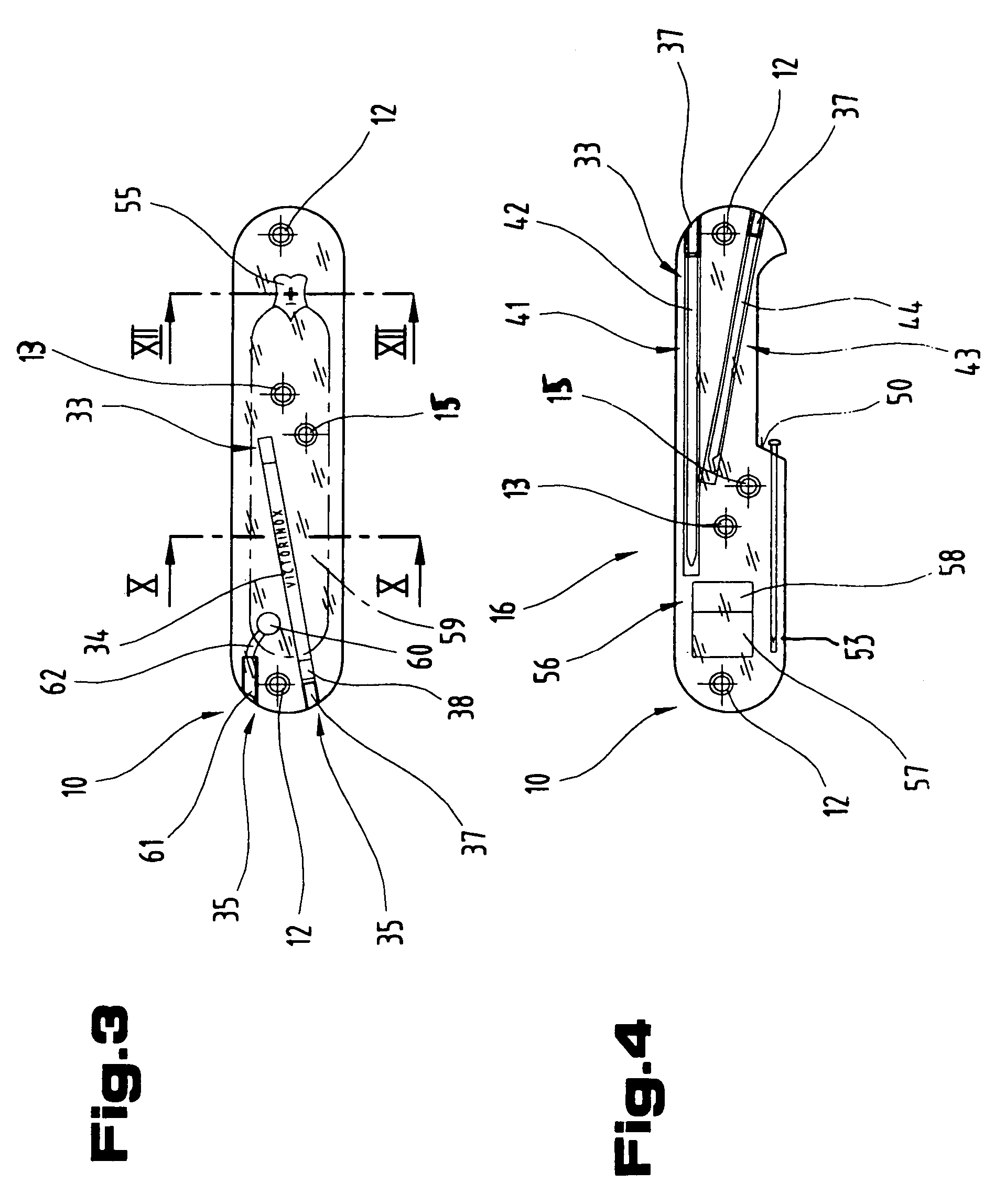
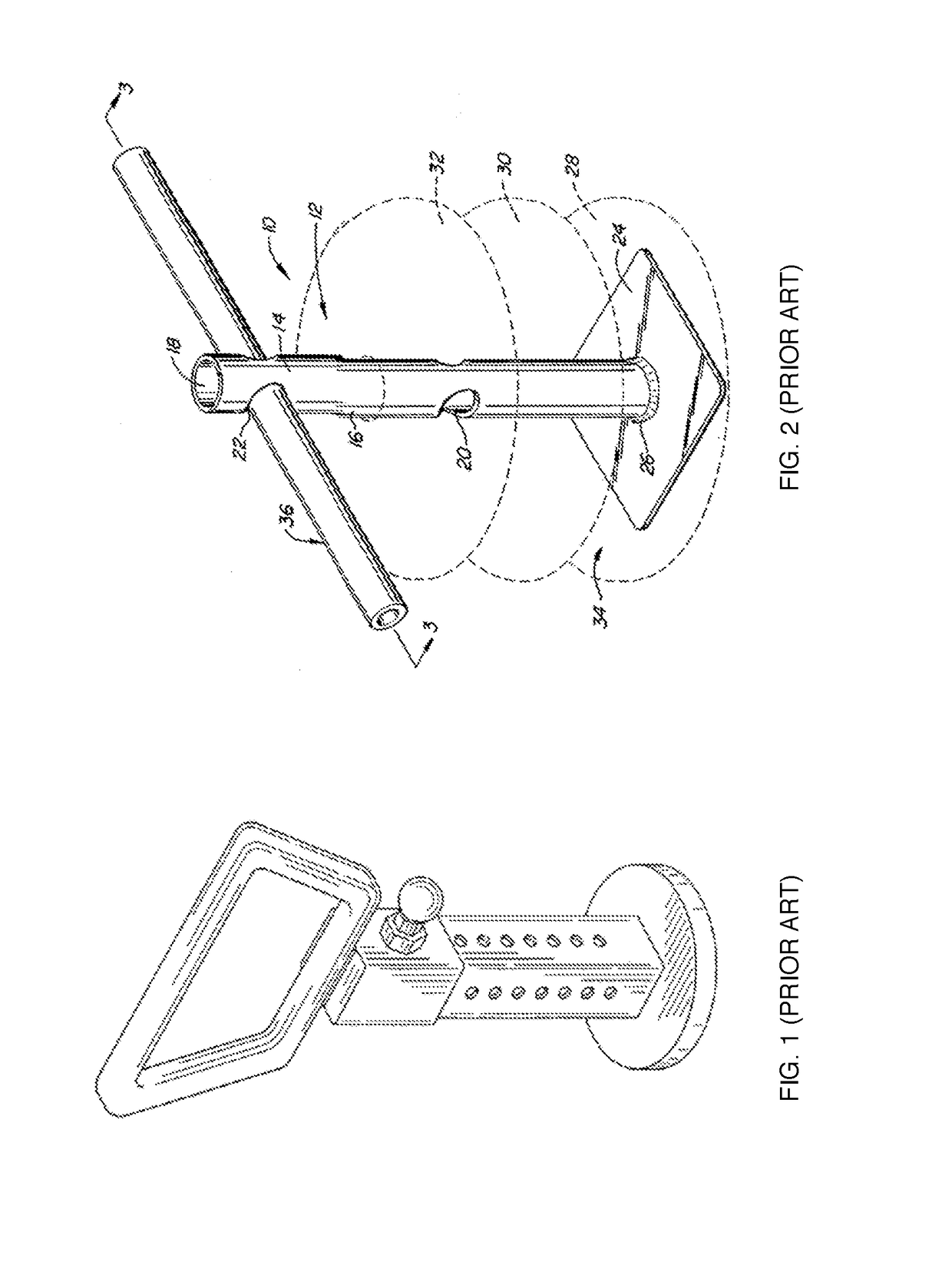
Operational tools carrier
InactiveUS7036174B2Avoid premature failureEasy to assembleLighting elementsThrusting weaponsEngineeringMechanical engineering
Owner:VICTORINOX
Excavation system employing a jet pump
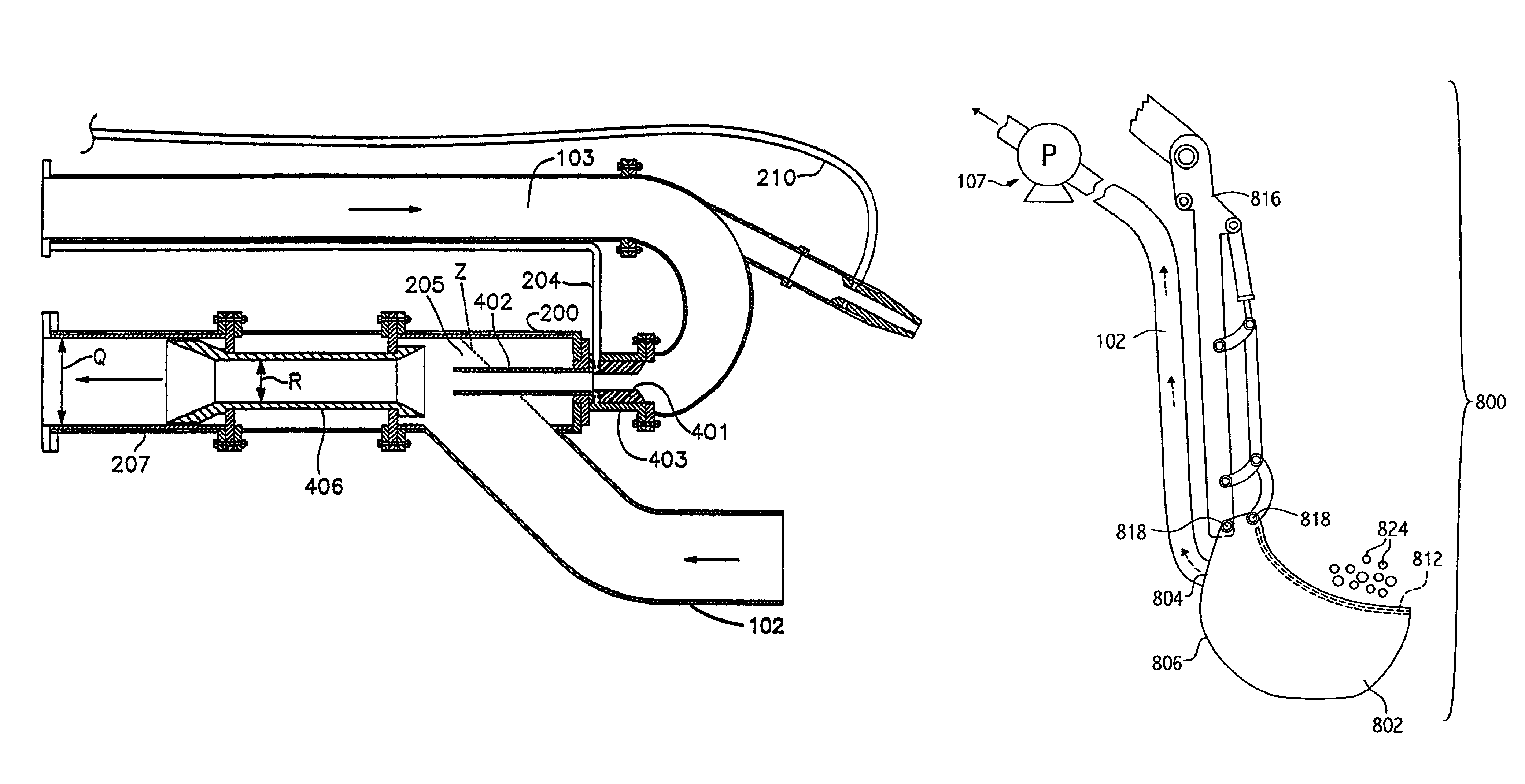
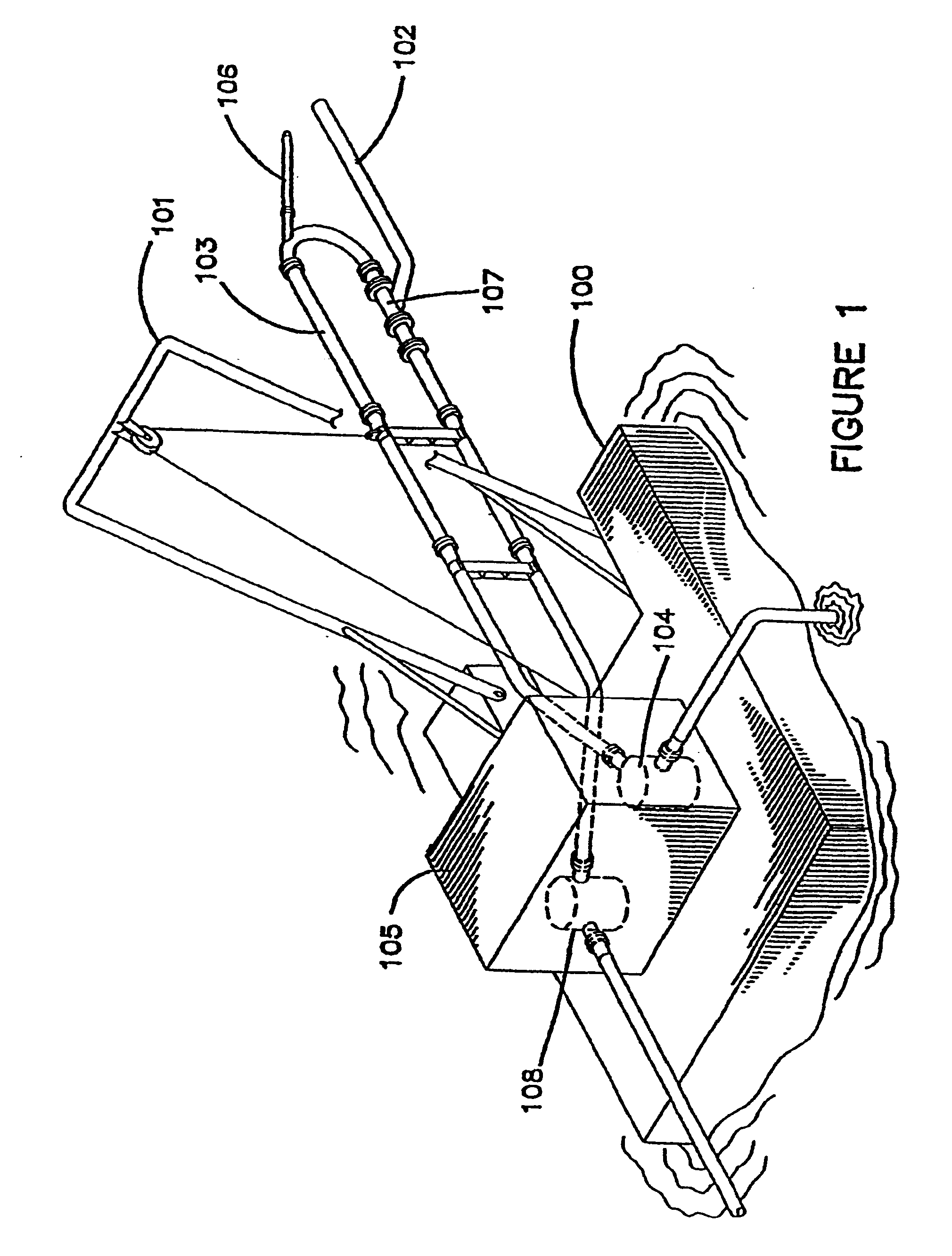
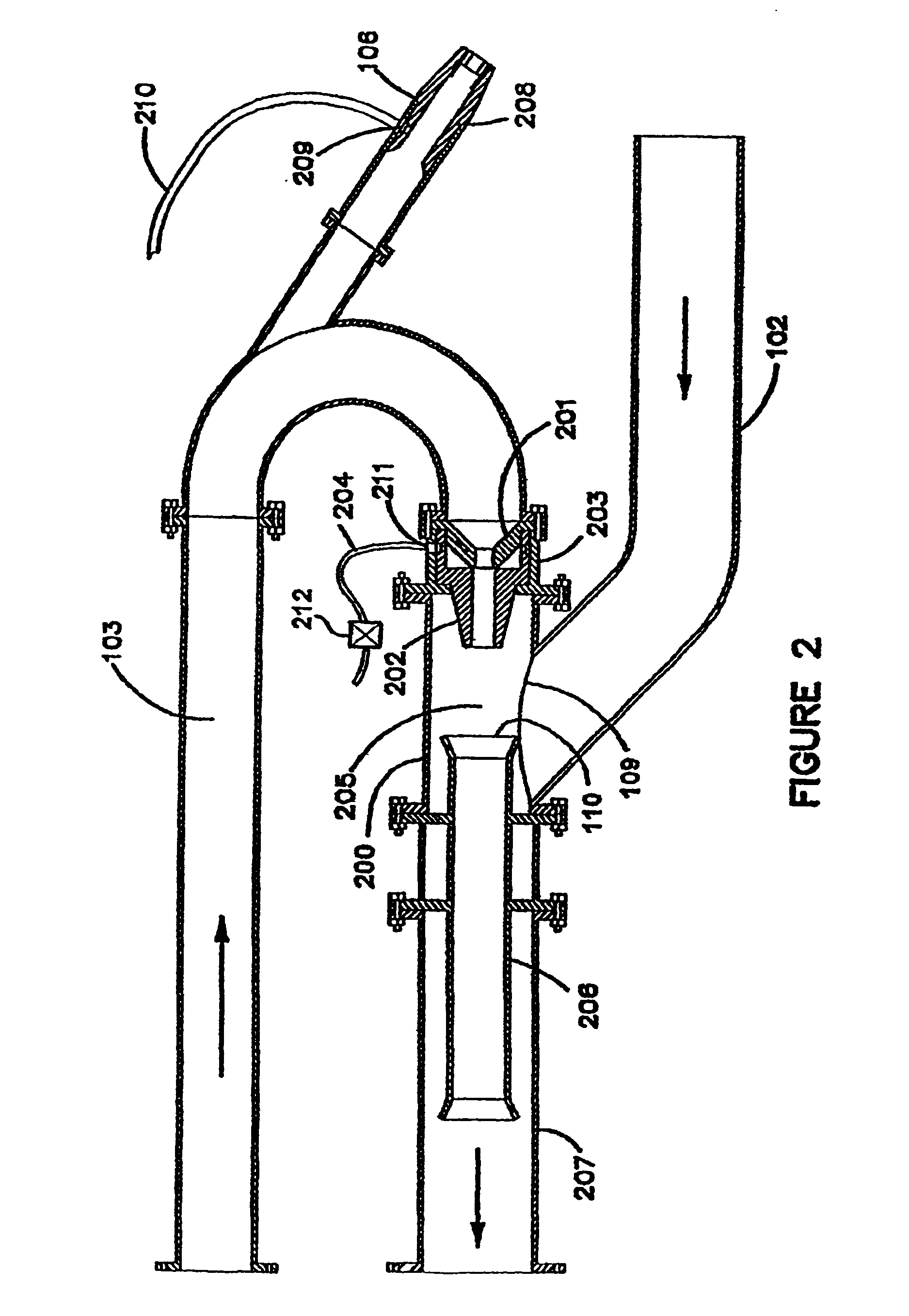
InactiveUS6860042B2Efficient transportIncrease the amount of materialMechanical machines/dredgersVessel salvagingInjection pumpWaste management
An excavation system comprises a bucket, defining an outlet at its base, in fluid communication with a suction tube in fluid communication with a jet pump, configured to create a suction in the suction tube. A related method of excavating comprises loading excavation material into a bucket which defines an outlet at its base, sizing the excavation material by sieving action of a guard substantially covering the bucket outlet, and suctioning the sized material though the bucket outlet using a vacuum created by a jet pump.
Owner:WALKER DAWSON INTERESTS
Transparent operational tools carrier
InactiveUS7344023B2Avoid premature failureEasy to assembleOther accessoriesContainer/bottle contructionMechanical engineeringEngineering
Owner:VICTORINOX
Deadlift bar apparatus and method
InactiveUS10188899B1Minimal wearLarge diameterDumb-bellsTeaching apparatusPhysical exerciseEngineering
A deadlift device includes a cylindrical shaft attached to a base, and one or more weights to be inserted onto the shaft. Horizontal channels in the shaft each have a main horizontal through hole with a downwardly extending keyhole slot extension with beveled edges, so that portions of one or more resistance bands may be routed through the keyhole slot extensions and used with minimal wear. A removable elongated lift bar which may be inserted into any of the channels. A removable handle with a grip may be secured to the top end of the shaft. A combination of the lift bar and the handle permit the deadlift device to be used effectively with a range of lift and walking exercises using the deadlift device with the one or more weights and / or the one or more resistance bands.
Owner:ACUNA JR ROBERTO
Modular printer having narrow print zone
ActiveUS9061531B2Width minimizedMaximize print qualityInking apparatusPower drive mechanismsModularityComputer module
Owner:MEMJET TECH LTD
Accessory adapter system for wearable computing device
ActiveUS20160255923A1Maximize interferenceMinimal wearBraceletsClockwork casesEmbedded systemPull force
Owner:WISECRACK LLC
Handling device for repositioning parts
InactiveUS20040197182A1High precisionMinimal wearLifting devicesSoil-shifting machines/dredgersEngineeringCam follower
A handling device for repositioning parts having a pivot arm able to be pivoted about a first pivot axis and a handling part adapted to bear a gripper and able to be pivoted with respect to a second pivot axis. The handling part is furthermore carried so that it may be radially moved in relation to the second pivot axis and cooperate by way of a cam follower with a path setting cam having two linear terminal sections. During operation of the device the handling part may move along a handling path, which has two linear terminal sections.
Owner:FESTO AG & CO KG
Sliding contact guide for transmission device
ActiveUS8007385B2High strengthCool evenlyGearingExternal combustion engineInternal combustion engine
In a sliding contact chain guide of the kind used in the timing transmission of an internal combustion engine, the back of the guide shoe, which engages a metal guide base, is formed with two, spaced longitudinal ribs, having between them a set of ribs formed in a lattice. The longitudinal ribs are wider than the ribs of the lattice.
Owner:TSUBAKIMOTO CHAIN CO
Agricultural harvester rear axle arrangement for narrow transport
ActiveUS7954583B2Easy to wearMinimizing componentWheel based transmissionFrictional rollers based transmissionElectronic controllerEngineering
An agricultural harvester rear axle arrangement for an agricultural harvester (10) having a body (12), the arrangement comprising left and right rear wheels (18, 20); means for supporting the wheels for rotation about a generally vertical steering axis (38, 40, 78, 94) and for supporting the wheels for extension and retraction from the body of the combine (26, 28, 30, 90); actuator means for steering the wheels (38, 40, 70, 72, 94) and for extending and retracting the wheels (34, 36, 70, 72); an electronic controller (50) coupled to the actuator means to steer, extend and retract the wheels.
Owner:DEERE & CO
Drive roll for a wire feeder
ActiveUS8450647B2Minimal wearAbsorb cyclical stressArc welding apparatusTurning toolsEngineeringMechanical engineering
A drive roll is disclosed that is useable in a wire feeder for advancing a wire. The drive roll includes a first side, a second side offset from the first side, and an annular surface between the first side and the second side. An annular groove is formed in the annular surface and defines an engagement surface. Pluralities of lands are spaced along the engagement surface and pluralities of notches are formed in the engagement surface for engaging and advancing the wire. An engagement ratio is defined between the total land area of the plurality of lands and the total notch area of the plurality of notches calculated at the engagement surface. The engagement ratio defines a drive roll that accurately engages and advances the wire over a longer period of use.
Owner:ILLINOIS TOOL WORKS INC
Mining utility transport vehicle
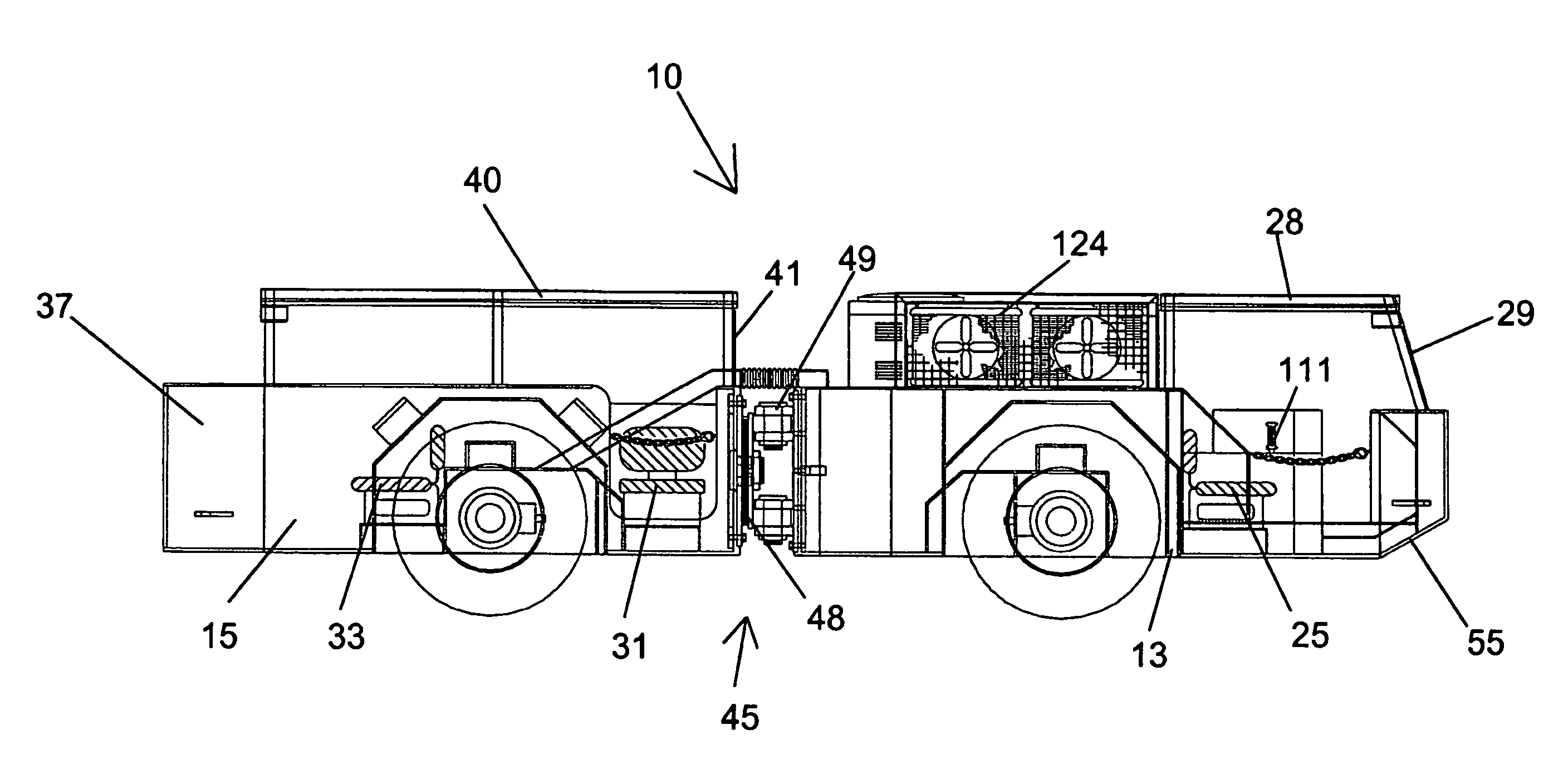
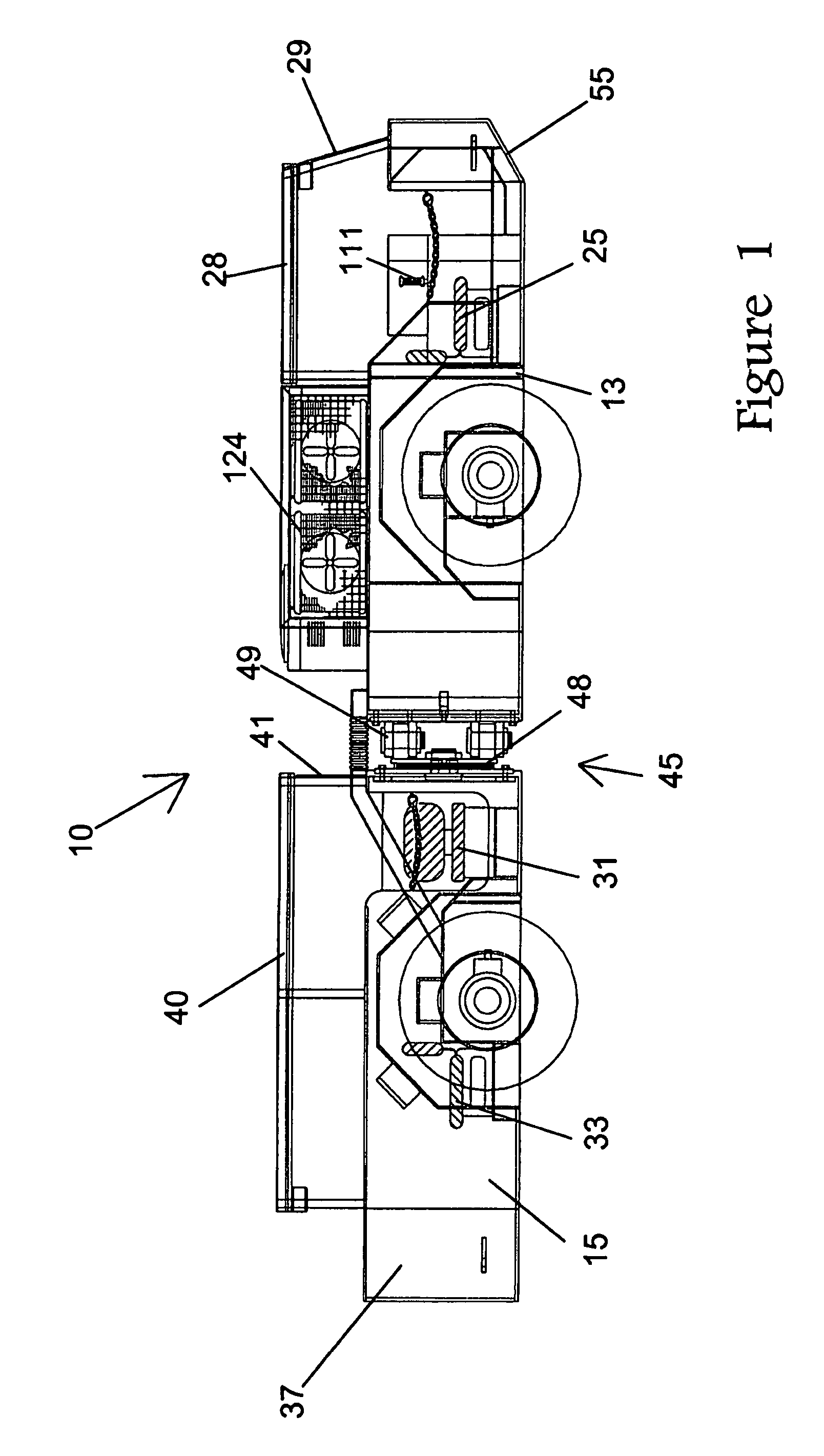
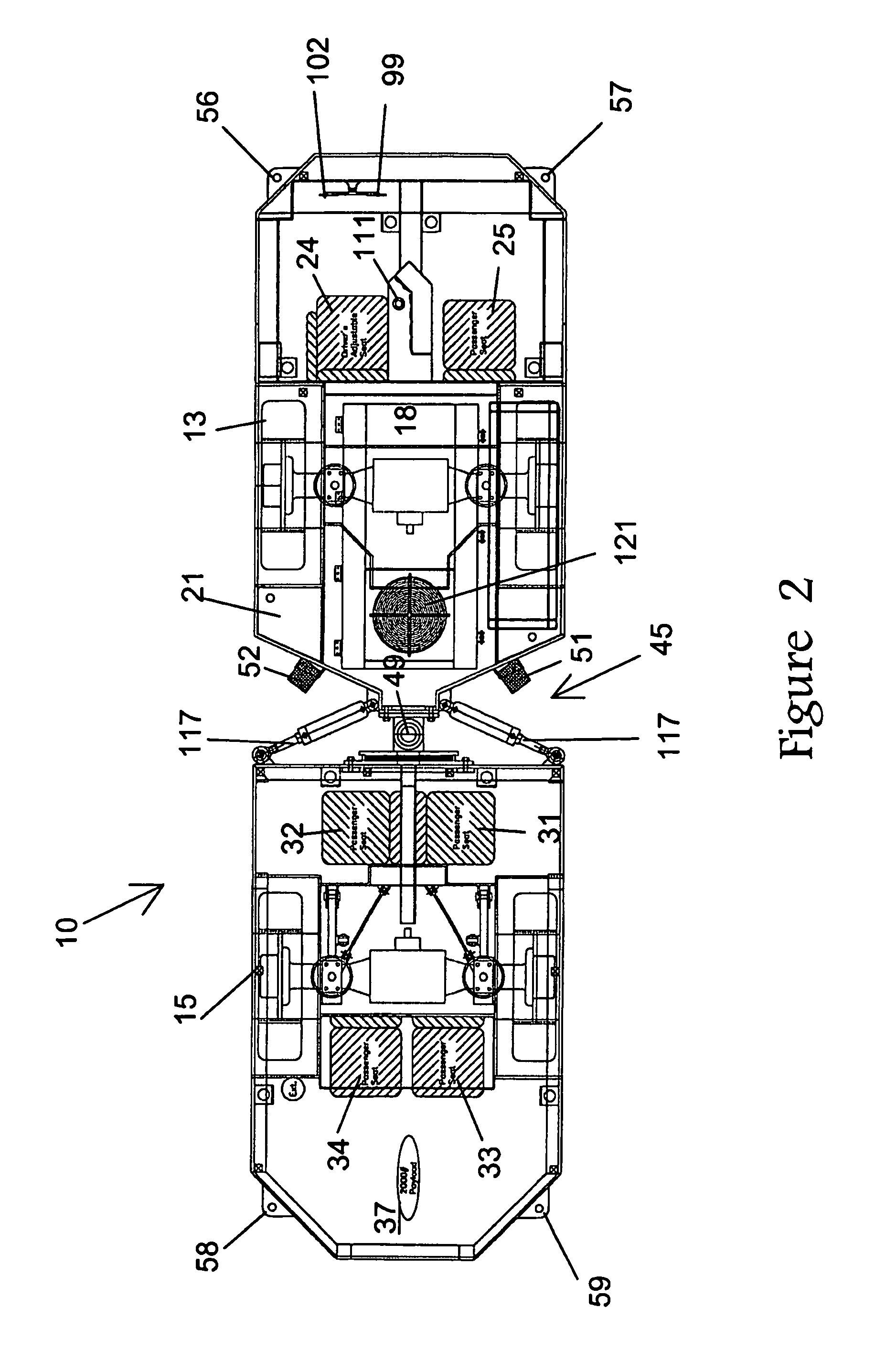
InactiveUS7743869B2Improve joint lifeLittle or no significant downtimeFluid steeringTractor-trailer combinationsLife timeWeight distribution
A mine transport vehicle is disclosed having two main bodies, one a power and control section and the other a payload section, the two sections being connected by an articulating joint. The power and control section has seating for an operator and a passenger. The payload section has seating for four passengers as well as capacity for at least approximately 2000 pounds of equipment. The weight distribution of each section is such that the stress on the frame and articulating joint is minimized thus providing improved life of the joint.
Owner:LISTERHILL TOTAL MAINTENANCE CENT
Brush holder for dynamoelectric machines
InactiveUS6838802B2Easy to replace the brushMinimal brush wearRotary current collectorSupports/enclosures/casingsEngineeringElectrical and Electronics engineering
A brush holder (100) for carrying a brush (102) and for providing adjustment of the brush relative to the commutator (104) of a dynamoelectric machine (105). The brush holder provides for adjustment of the gap (110) between the commutator and the brush, and for adjustment of the brush in the axial direction along the commutator. The brush holder also locks the brush at the desired position for operation in the dynamoelectric machine.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Deadlift bar apparatus and method
A deadlift device includes a cylindrical shaft attached to a base with a selectable weight. Horizontal channels in the shaft have a main horizontal through hole with a downwardly extending keyhole slot extension with beveled edges, so that portions of one or more resistance bands may be routed through the keyhole slots and used with minimal wear. A removable Y-lift bar with right and left hand vertical upper portion and diagonal lower portion which may be attached at any of the channels. An alternative removable short horizontal bar may be inserted at at any of the channels to permit kettlebell swing exercises. The device may be used effectively with a range of lift and walking exercises using the deadlift device with added weights and / or one or more resistance bands.
Owner:ACUNA JR ROBERTO
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com