Energy dissipation vibrator and standing wave area power protecting system and method
A vibrator and energy dissipation technology, used in protection devices, buildings, infrastructure engineering, etc., can solve problems such as large deformation of buffer layer materials, large deformation of rock and soil mass, and complicated construction, and achieve the effect of reducing peak stress and reducing energy.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
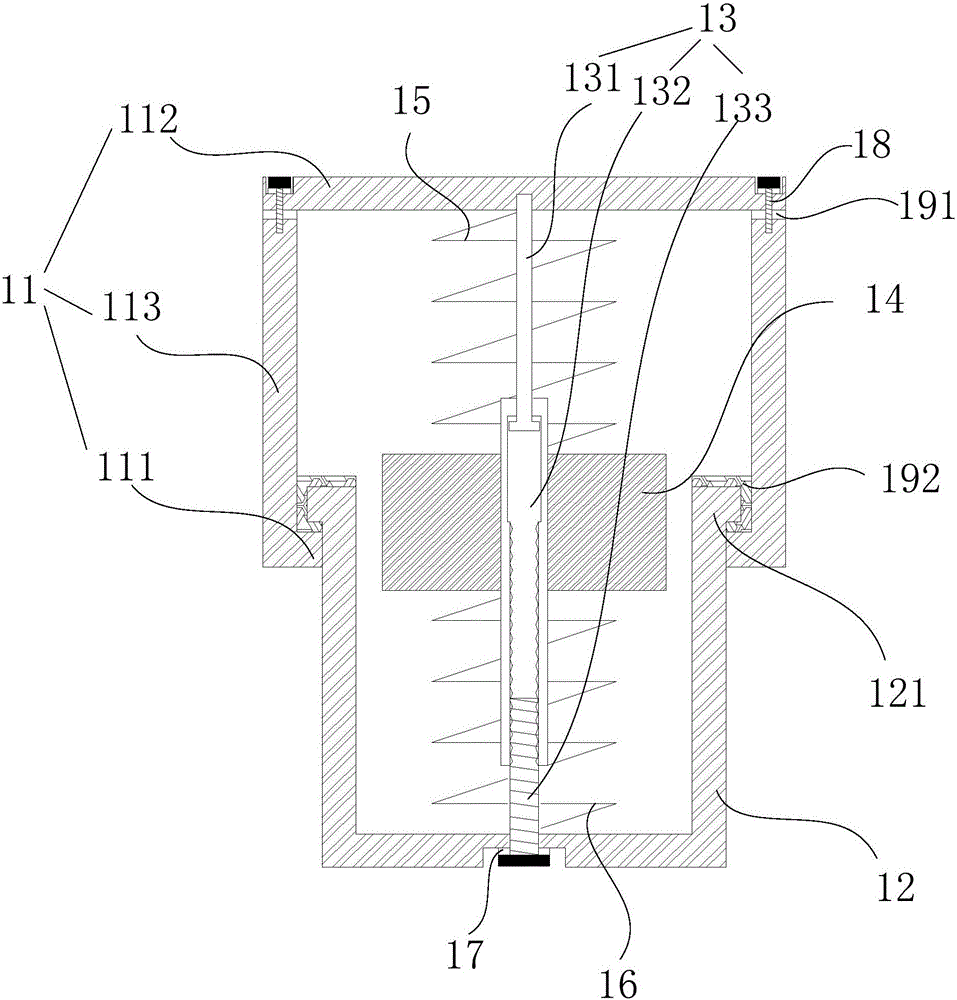
[0047] The embodiment of the present invention provides an energy dissipation vibrator 1, see figure 1 , the energy-dissipating vibrator 1 includes: an upper shell 11, a lower shell 12, a telescopic rod 13, a mass 14, a first spring 15 and a second spring 16;
[0048] The lower end of the upper case 11 is provided with a first blocking portion 111, and the upper end of the lower case 12 is provided with a second blocking portion 121, the second blocking portion 121 is located between the first blocking portion 111 and the upper case 11, and the first blocking portion 111 is The second blocking portion 121 limits the position;
[0049] One end of the telescopic rod 13 is connected to the upper case 11, and the other end is connected to the lower case 12. The mass block 14, the first spring 15 and the second spring 16 are all set on the telescopic rod 13; one end of the first spring 15 is connected to the upper case 11 , the other end is connected to the mass block 14; one end ...
Embodiment 2
[0081] see Figure 10 , the embodiment of the present invention also provides a dynamic protection system in the standing wave area, including a low wave impedance layer 2 and multiple energy-dissipating vibrators 1 described in Embodiment 1;
[0082] The low-wave impedance layer 2 is used to form on the protected underground structure 3, and each energy-dissipating vibrator 1 among the plurality of energy-dissipating vibrators 1 is used to arrange and arrange on the low-wave-impedance layer 2, and the energy-dissipating vibrator 1 is used to support the low-wave impedance layer 2. The rock mass 4 above the acoustic impedance layer 2;
[0083] The upper shell 11 of the energy-dissipating vibrator 1 is connected to the low wave impedance layer 2, and the lower shell 12 is used to connect to the rock mass 4, or
[0084] The lower shell 12 of the energy-dissipating vibrator 1 is connected with the low wave impedance layer 2 , and the upper shell 11 is used for connecting with th...
Embodiment 3
[0089] The embodiment of the present invention also provides a dynamic protection method in the standing wave area, see Figure 10 ,include:
[0090] A low-wave impedance layer 2 is formed on the protected underground structure 3, and a plurality of energy-dissipating vibrators 1 are arranged between the low-wave impedance layer 2 and the rock mass 4;
[0091] Wherein, the upper shell 11 of the energy-dissipating vibrator 1 is connected to the low wave impedance layer 2, and the lower shell 12 is used to connect with the rock mass 4, or
[0092] The lower shell 12 of the energy-dissipating vibrator 1 is connected to the low wave impedance layer 2, and the upper shell 11 is used to connect to the rock mass 4
[0093] The dynamic protection method for the standing wave area adopts the energy-dissipating vibrator 1 described in the first embodiment, so that the dynamic protection method for the standing wave area can better protect the overall stability of the underground struct...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com