Low-energy-consumption aporadic task scheduling method based on RM strategy
A scheduling method and low energy consumption technology, applied in energy-saving computing, resource allocation, program control design, etc., can solve problems such as ignoring processor static power consumption, processor speed switching overhead, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0059] The present invention will be further described in detail below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
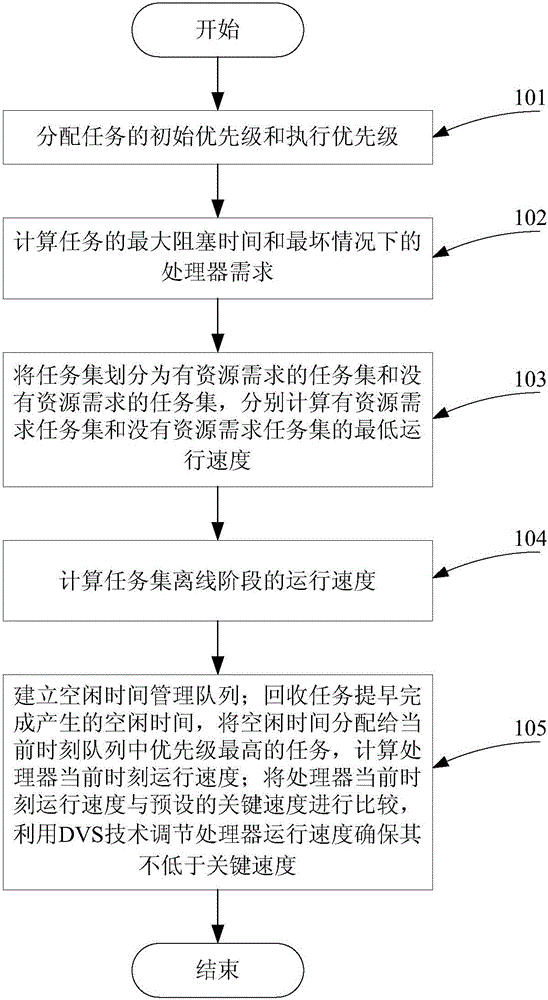
[0060] see figure 1 , a resource-constrained sporadic task low-energy scheduling method based on an RM scheduling policy provided by the present invention includes the following steps:
[0061] Step 101: Assign initial priority and execution priority of tasks;
[0062] Specifically, the initial priority is assigned according to the RM algorithm. The smaller the minimum release interval of the task, the higher its priority; the execution priority is assigned when the task obtains CPU and other resources and starts to execute, and its priority is executed after the task is completed. All remain the same; for tasks with no resource requirements, their initial priority is equal to their execution priority.
[0063] Further, task T i initial priority IP i Assigned according to the RM algorithm, its value is IP i =n-i+1, i represents task T i ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com