A kind of method that uses low-grade magnesite to prepare magnesium oxide raw material and low particle size magnesium hydroxide
A technology of magnesium hydroxide and magnesium oxide, applied in the production of magnesium hydroxide and lime, which can solve the problems of long washing cycle, numerous process steps, small magnesium hydroxide, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
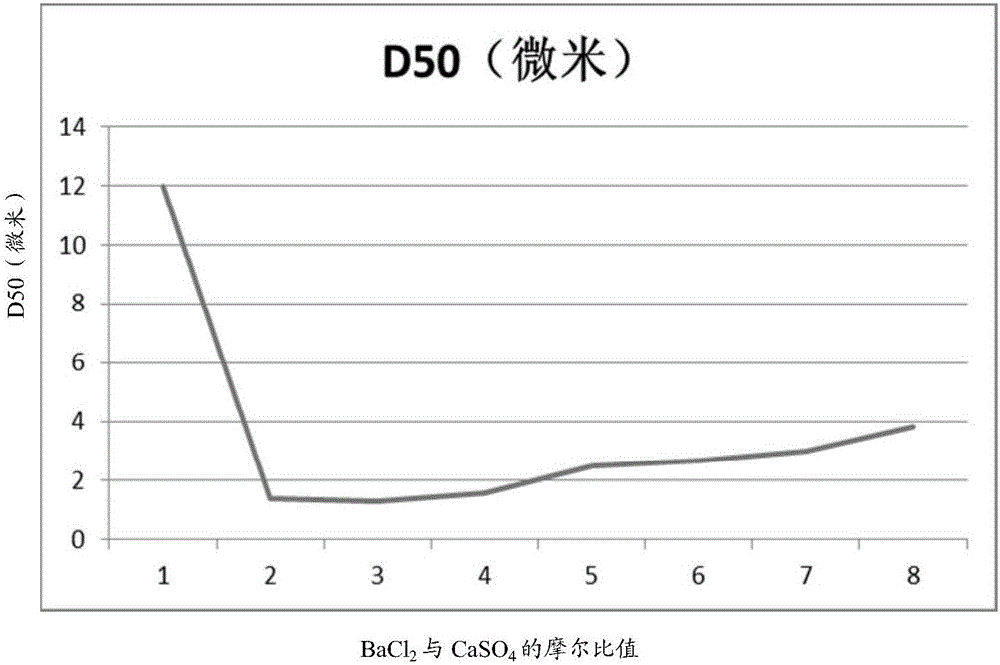
[0047] Magnesium oxide with a measured calcium sulfate content of 0.61% by mass, produced from bischofite, was used. According to the ratio shown in Table 1, magnesium oxide, distilled water and barium chloride (with no addition of barium chloride as a control) were added and placed in a reaction kettle in a water bath at 50°C, stirred at a speed of 400 rpm for 6 hours, passed The liquid was filtered off by suction to obtain crude magnesium hydroxide. Then dry to constant weight (moisture content is lower than 1% by weight) at 50 ℃, make dry magnesium hydroxide, use 100 micron mesh sieve to sieve off residue, obtain final magnesium hydroxide product, and according to HG / The method described in T 3607-2007 (issued on April 13, 2007, implemented on October 1, 2007) measures D50. The results are shown in Table 1 below as well as figure 1 middle.
[0048] Table 1
[0049] Barium Chloride: Calcium Sulfate Molar Ratio D50(micron) 1 12.0 2 1.4 3 1.3 ...
Embodiment 2
[0052] Example 2 was carried out in the same manner as in Example except for the contents shown in Table 2 below.
[0053] Table 2
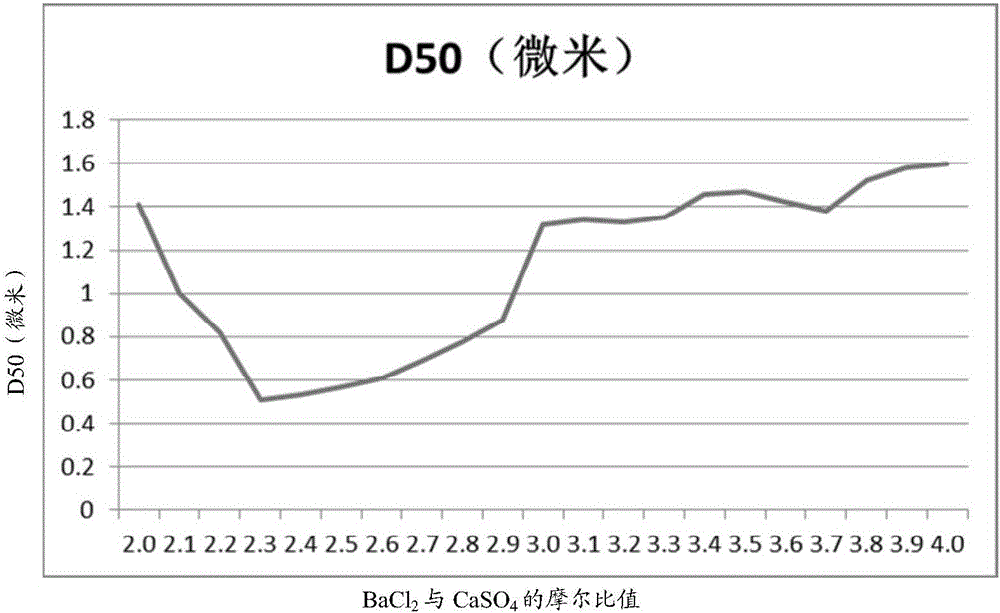
[0054] Barium Chloride: Calcium Sulfate Molar Ratio D50(micron) 2.0 1.41 2.1 1 2.2 0.82 2.3 0.51 2.4 0.53 2.5 0.57 2.6 0.61 2.7 0.69 2.8 0.78 2.9 0.88 3.0 1.32 3.1 1.34 3.2 1.33 3.3 1.35 3.4 1.46 3.5 1.47 3.6 1.42 3.7 1.38 3.8 1.52 3.9 1.58 4.0 1.6
[0055] From figure 2 combined with the results in Table 2 figure 1 It can be seen from the results that in figure 1 In the flat section where the molar ratio of barium chloride and calcium sulfate is 2:1 to 4:1, there is actually a "deep pit" between the molar ratio of 2.3:1 and 2.9:1. The D50 can be stably in the range of 0.5 to 1.0 micron, and a magnesium hydroxide product with a smaller particle size can be obtained by adopting the molar ratio in this range.
Embodiment 3
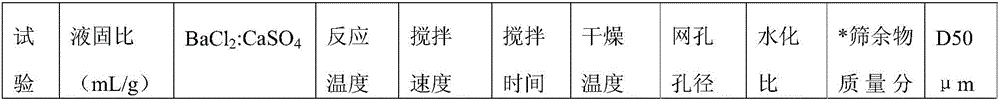
[0057] Example 3 was carried out in the same manner as in Example 1 except for the contents described in Table 3 below. See Table 3 below for the results.
[0058] table 3
[0059]
[0060]
[0061] Note:
[0062] (1)*The mass fraction of the sieve residue refers to the mass percentage of the material that does not pass through the 75-micron mesh when sieving with a 75-micron test sieve to the entire material.
[0063] (2) The mass fraction of sieve residue and D50 are carried out according to the method stipulated in the industry standard of HG / T 3607-2007 (issued on April 13, 2007, implemented on October 1, 2007), and the mass fraction of sieve residue is class II The standards for first-class products and qualified products are less than or equal to 0.02% and less than or equal to 0.05% respectively; the standards for Class III first-class products and qualified products are respectively less than or equal to 0.5 and less than or equal to 1.0. The D50 Class I stand...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| refractive index | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com