Coral larva oriented bottom sowing method
A polyp and coral technology, applied in the field of stony coral breeding, can solve the problems of low attachment rate of coral larvae, speed up the restoration progress of degraded coral reefs, etc., and achieve the effects of improving attachment efficiency, improving survival rate, and speeding up restoration.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
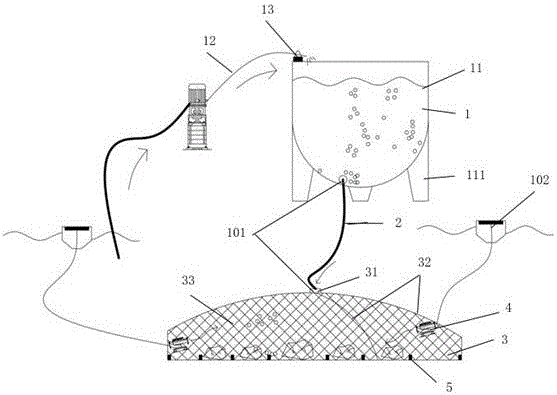
[0031] Embodiment 1 first fully introduces the structure of the coral larva directional bottom sowing device used in the present invention, as figure 1 As shown, the directional bottom sowing device for coral larvae includes an upper container 1, a draft tube 2 and a bottom cover net 3, wherein the upper container 1 is arranged above the bottom cover net 3, and the upper container 1 passes through the draft tube 2 and the bottom cover net 3 connect.
[0032] Its specific usage principle is as follows:
[0033] Before sowing the coral larvae at the bottom, first make the bottom cover net 3 tightly cover the attached reef to isolate the interference of external organisms, then use a scoop to carefully scoop the coral larvae close to the upper container 1, and slowly put the coral larvae into the upper container 1. At this time, coral larvae rely on water pressure or self-weight to flow into the bottom cover net 3 through the upper container 1 and the diversion tube 2, and dispe...
Embodiment 2
[0041] The present embodiment adopts the device described in embodiment 1 to carry out a coral larva directional bottom sowing, and its specific process is as follows:
[0042] 1. The source of coral larvae
[0043] Coral fertilized eggs are hatched indoors, and after cultivation, floating larvae are formed. During the planktonic stage, the larvae are quickly transported to the bottom sowing site for bottom sowing.
[0044] 2. Bottom broadcast time selection
[0045] The suitable time for directional bottom sowing of coral larvae is from April to June, because most of the corals spawn during this period, and the water temperature is suitable to increase the survival rate of larvae.
[0046] 3. Bottom broadcast site selection
[0047] Choose a sea area with gentle terrain, less suspended matter, high transparency of seawater, abundant light, no industrial discharge pollution and rich bait for bottom sowing. The bottom sowing site is preferably located near similar coral reefs...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com