Few-mode fiber device
A few-mode optical fiber and device technology, applied in the field of optical fiber communication, can solve problems such as poor output spectrum uniformity, difficulty in multiplexing and decomposition, and narrow operating bandwidth, and achieve good output energy uniformity, wide operating wavelength range, and polarization-independent Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
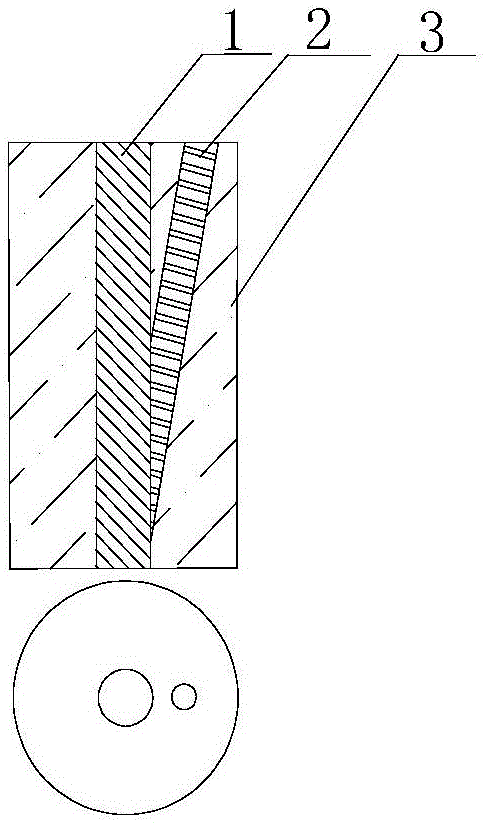
[0032] figure 1 It is a schematic diagram of the structure of the optical fiber embodiment 1 of the present invention. The number of auxiliary cores is M=1, and it satisfies: n i-1 >n f >n i (I≥i>1) or n f >n i (i=1); where, n i The effective refractive index of the i-th mode of the main core, I is the total number of modes of the main core, and there are n i-1 >n i (I≥i>1), n f is the effective refractive index of the fundamental mode of the auxiliary core. Both the main fiber core and the auxiliary fiber core have one number. There are main fiber core and auxiliary fiber core at the multi-core end face, while only the main fiber core exists at the single core end face.
[0033] At the working wavelength, the main fiber core 1 is a few-mode fiber core, that is, it can transmit high-order modes. The present invention implements operations such as introducing, extracting, and converting modes in the main fiber core 1 by introducing an auxiliary fiber core 2 .
[0034...
Embodiment 2
[0058] The invention can realize multiplexing and demultiplexing of optical fiber modes. The relationship between the quantity M of the auxiliary fiber core and the number of main fiber core modes I and the number of degenerate modules N of the main fiber core is: M=I+N; the central axes of I auxiliary fiber cores are in the same plane, and the auxiliary fiber core is defined as The first type of auxiliary fiber core is used to input the I modes of the main fiber core respectively; the central axis of the other N auxiliary fiber cores is not in this plane, which is defined as the second type of auxiliary fiber core, which is used to input the main fiber core respectively. Another of the N quadruple degenerate patterns.
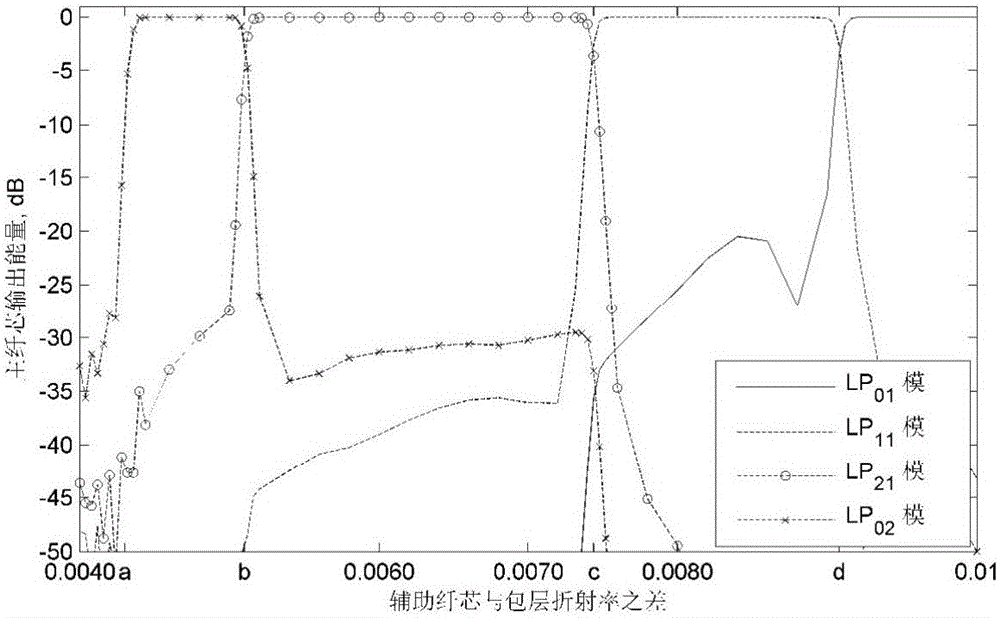
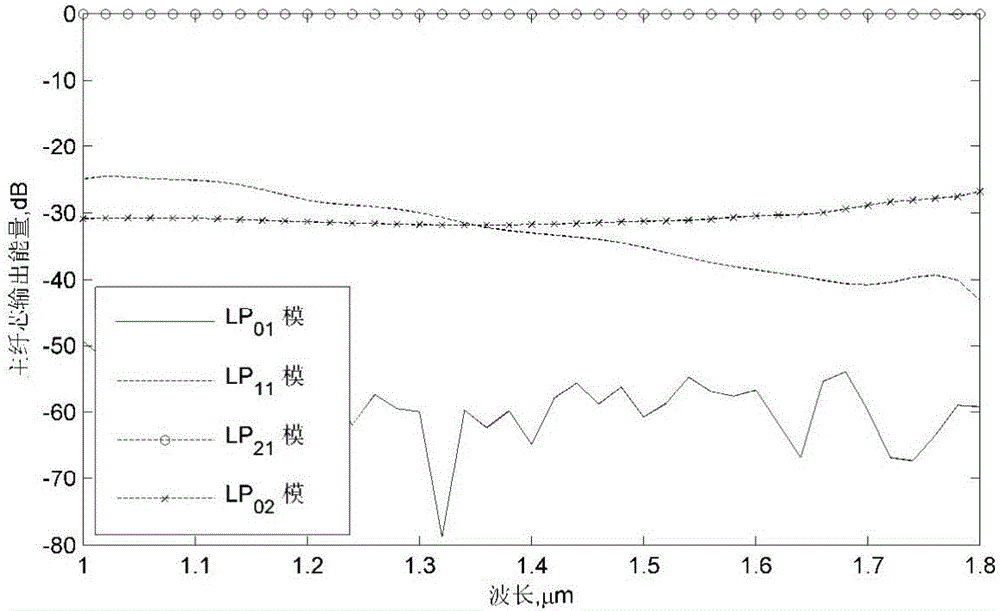
[0059] Image 6 Given one of the schemes, there are 6 auxiliary fiber cores, of which 4 are first-type auxiliary fiber cores, and the central axes of the four first-type auxiliary fiber cores 21, 22, 23, 24 are connected to the center of the main fiber core. ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com