A kind of Escherichia coli movement rate determination method in water and aqueous solution
A technology of Escherichia coli and aqueous solution, applied in the field of instrument analysis, to achieve the effect of no pollution risk and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
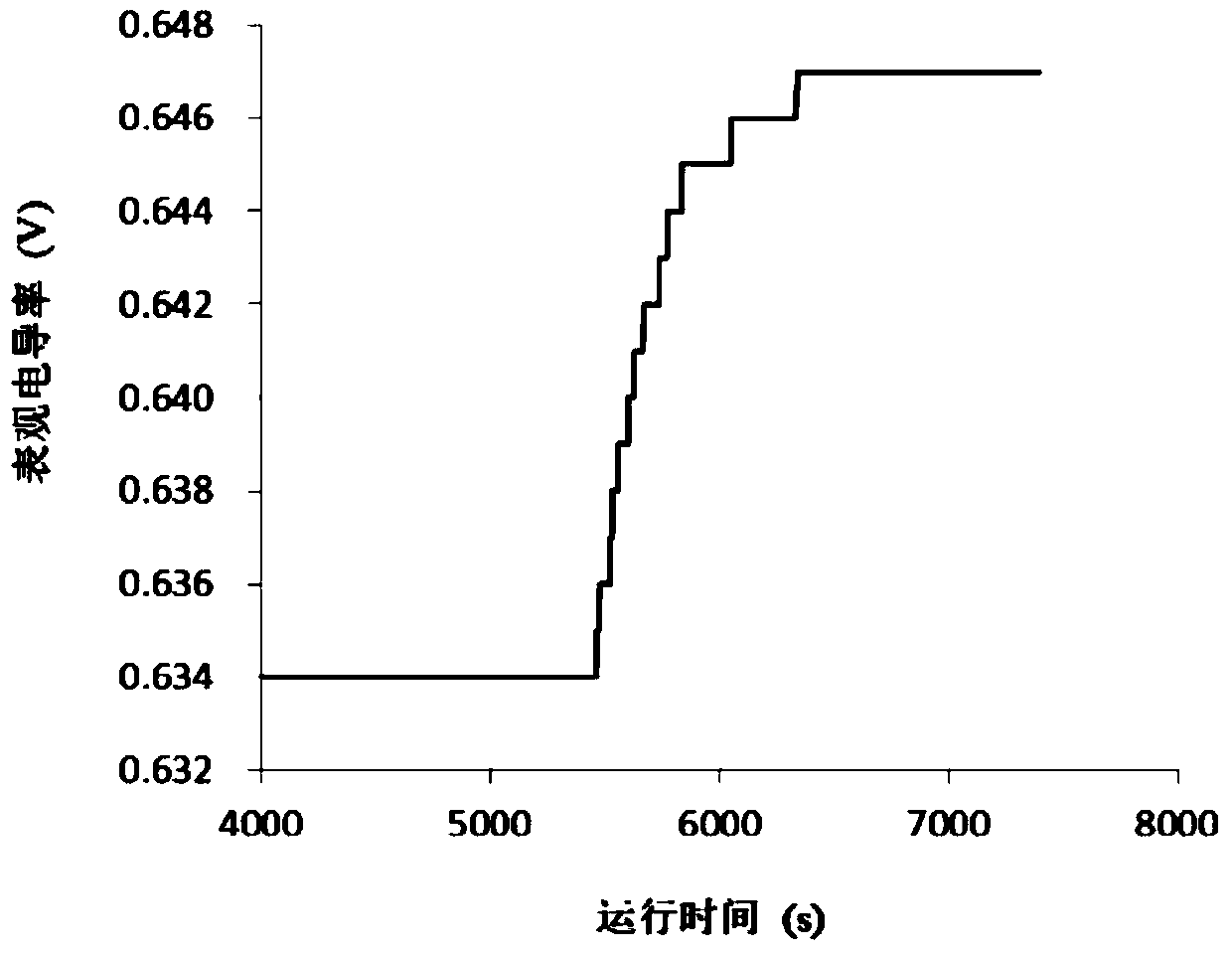
[0020] Example Determination of the maximum movement rate of Escherichia coli under the action of gravity in 0.9% NaCl solution at 25°C
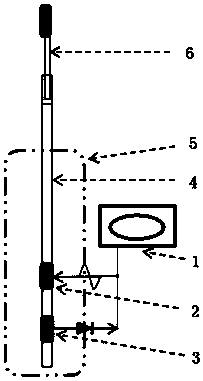
[0021] Step 1. Inject 116.56 microliters of 0.9% NaCl solution (5.8 cm in length of the liquid column) into the graduated glass detection tube (6.0 cm in length) with a micro-injector. At this time, the distance between the liquid level at the opening end of the graduated glass detection tube and the receiving electrode is 5.0 cm, that is, the effective motion length L is 5.0 cm.
[0022] Step 2. Insert the scaled glass detection tube into the capacitively coupled non-contact conductivity sensor probe, and adjust the probe bracket so that the detection tube is vertically downward.
[0023] Step 3. Adjust the laboratory temperature to a constant temperature of 25°C.
[0024] Step 4: Centrifuge and wash the Escherichia coli cultured according to conventional methods (4000r / min) for 5 times, and remove the residual culture medium therein. The...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com