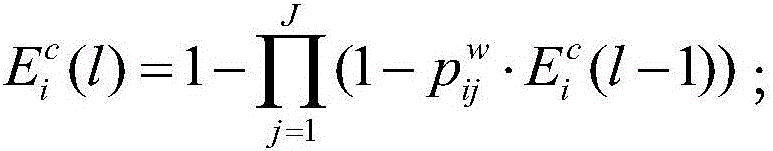Minimum-cost-path-based mobile random D2D network data query method
A network data and query method technology, applied in the field of computer networks, can solve the problems of low path overhead, unawareness, high retrieval cost of data and data providers, and achieve the effect of the lowest path overhead and the least path overhead
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
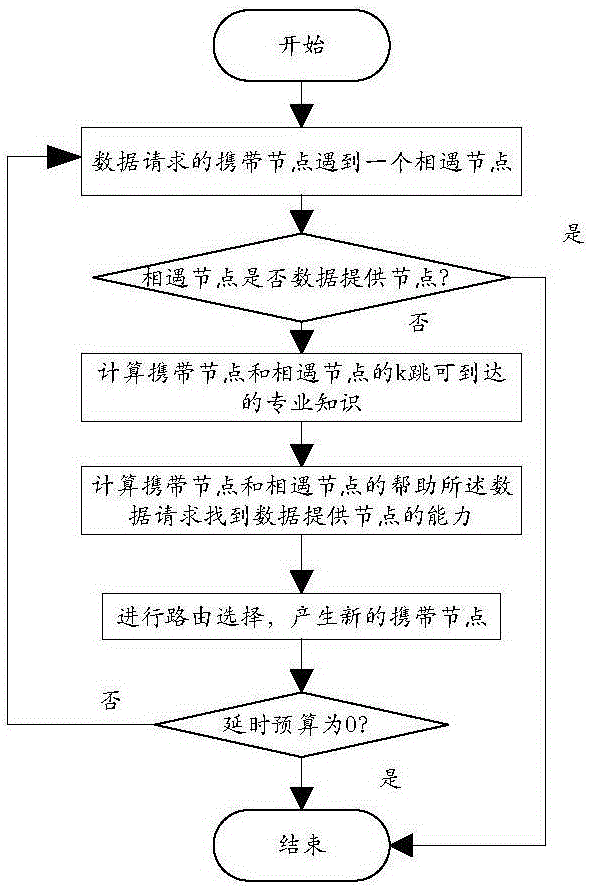
[0028] Embodiment 1. A mobile random D2D network data query method based on a minimum overhead path. The method performs routing according to the following steps for a newly generated data request in a D2D network:
[0029] Step 1. The carrier node carrying the data request encounters an encounter node, and judges whether the encounter node is a data provider. If so, the routing ends. Otherwise, calculate the k-hop reachable expertise of the carrier node and the encounter node. Among them, only when the encountering node has the professional knowledge of the professional field to which the data request belongs, can it become a data provider, and the professional knowledge of the meeting node can be judged here.
[0030] Step 2. According to the k-hop reachable professional knowledge of the carrying node and the encountering node calculated in step 1, on this basis, calculate the ability of the carrying node and the encountering node's help data request to find the data providin...
Embodiment 2
[0043] The basic idea of the data query method of Embodiment 2 and Embodiment 1 is as follows: use the historical information of node encounters in the network to calculate the reachable expertise of k hops between every two nodes, and assume node v in the routing process i There is a data request Mq and at some point it encounters node v j And the node does not carry Mq. first node v i and node v j They will exchange each other's contact rate table, and then calculate their own k-hop reachable professional knowledge, and on this basis, calculate the ability of the two to help the data request to find the data provider node, and select the ability after comparison The larger node, thus determining the node v i Whether to forward the data request Mq to node v j .
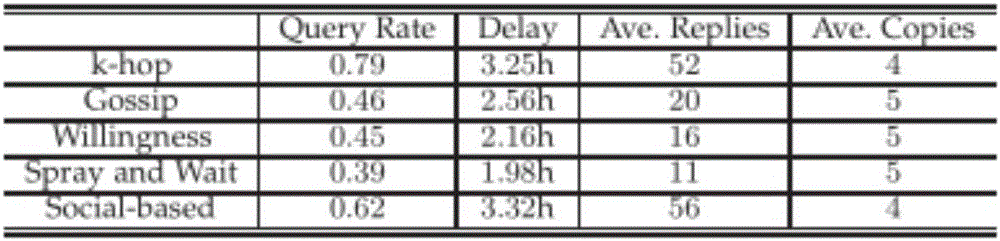
[0044] In order to verify that the data request forwarding strategy proposed by the present invention can achieve a higher success rate of data request reply in the mobile random D2D network, the following con...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com