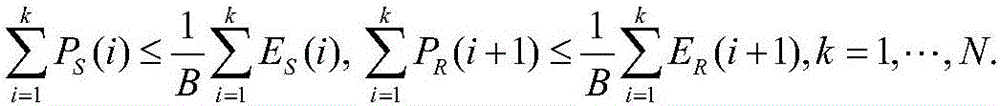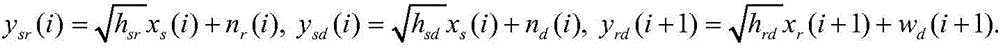Resource distribution method in energy acquisition small cellular network
A technology of energy collection and resource allocation, applied in the field of wireless communication
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0082] A resource allocation method in an energy harvesting small cell network, characterized in that it comprises:
[0083] Step 1: system scene analysis, problem analysis;
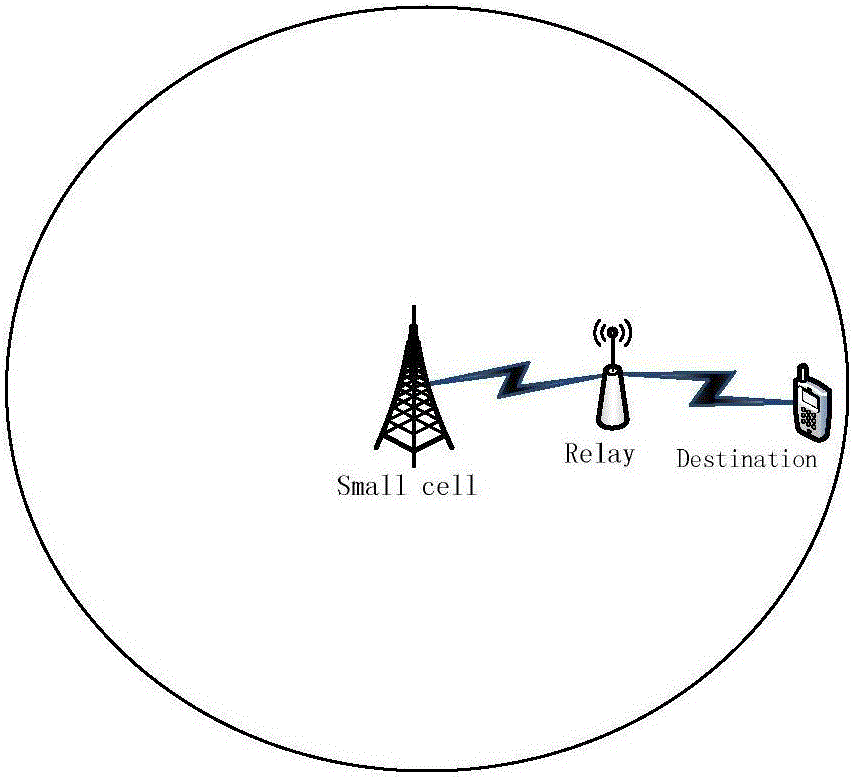
[0084] The present invention considers a classic three-node scenario in an energy-harvesting small-cell network, and aims at a special application scenario, sourced from practical applications, and the scenario setting is meticulous and reasonable, and has practical guiding significance. In the scene, there is an energy harvesting small cell Small Cell (abbreviated as S), an energy harvesting relay station Relay (abbreviated as R) and a target communication cellular user Destination (abbreviated as D). The invention fully considers the environmental protection scheme of renewable energy, combines the cooperative forwarding function of the relay station, adopts the cooperative forwarding data of the energy collection relay station, and maximizes the performance of the user network. Considering that there...
Embodiment 2
[0141] On the basis of Embodiment 1 of the present invention, we further improve, for solving the optimization problem, adopt convex optimization processing, transform the objective function of the optimization problem, without approximate calculation, do not affect the accuracy of the problem, and greatly reduce the Computational complexity, reducing the delay caused by system overhead.
[0142] Specifically, the step 2 may also include: convex optimization processing, using the Lagrangian theorem and KKT conditions in the convex optimization theory, the optimization problem can be subjected to convex optimization processing, and the optimization problem can be transformed into:
[0143] P2:
[0144] s . t . Σ i = 1 k P S ( i ) ≤ 1 ...
Embodiment 3
[0152] The solution of the second embodiment can adopt the classic interior point method, but the calculation complexity is high and the calculation time is long. On the basis of the second embodiment, the present invention is further improved, and the optimization adopts the Lagrange multiplier method, so the optimization speed is fast and the algorithm complexity is low.
[0153] Specifically, we can write the Lagrangian form of problem P2,
[0154] L ( P S ( i ) , P R ( i + 1 ) , ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com