A division method of parallel gpdt algorithm on multi-core soc
A parallel computing and multi-core technology, applied in computing, computer components, CAD circuit design, etc., can solve problems such as large amount of calculation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0067] Below in conjunction with accompanying drawing, the present invention will be further described.
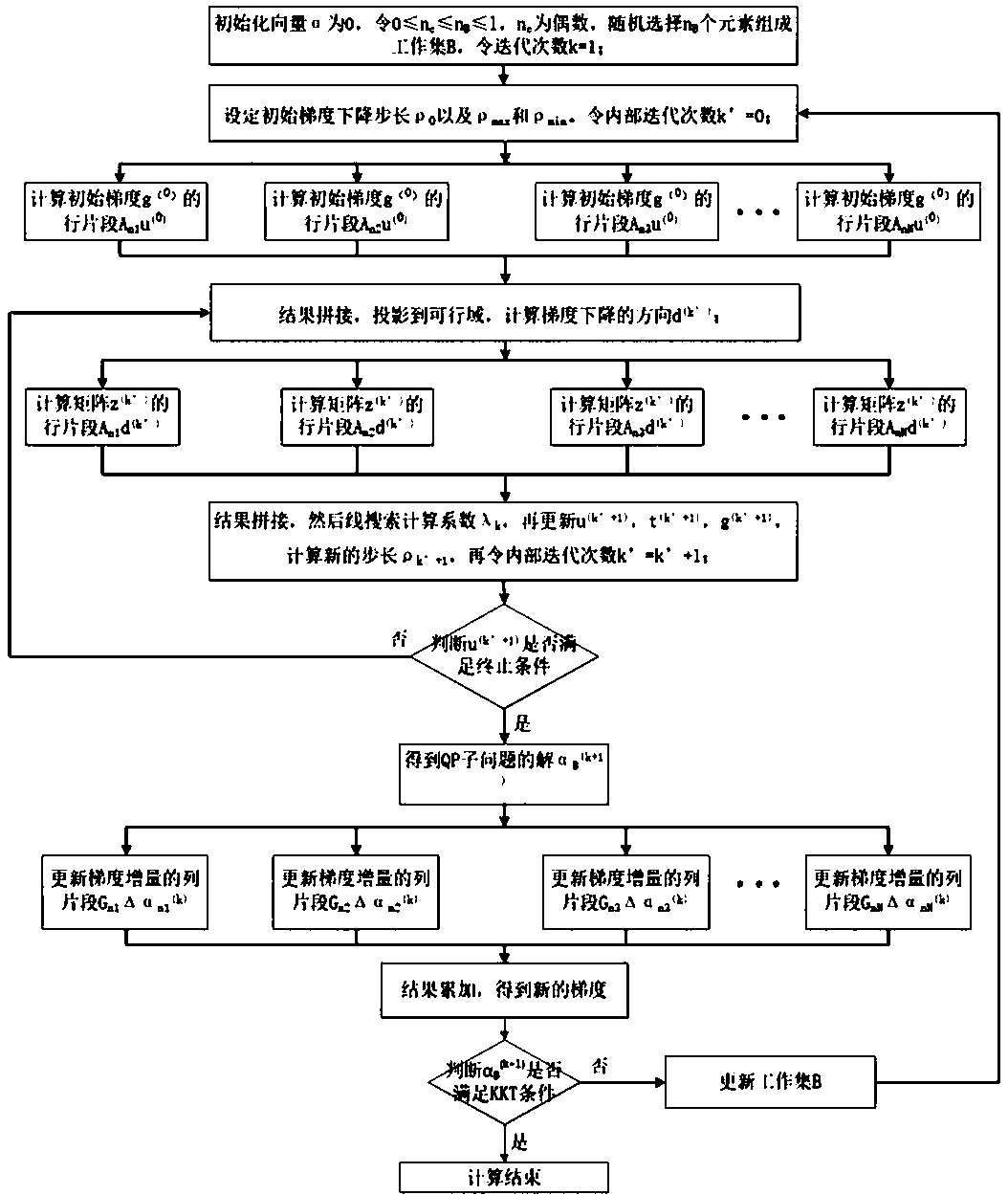
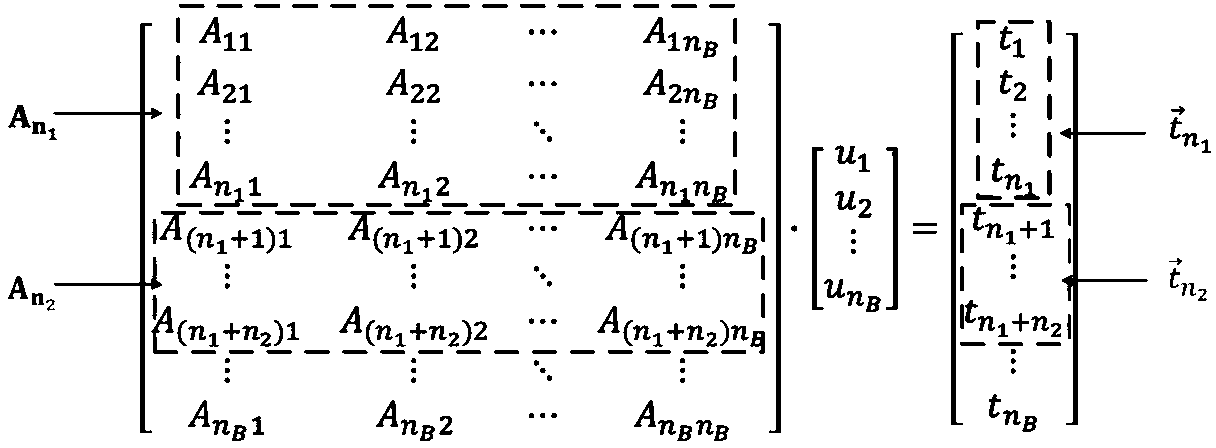
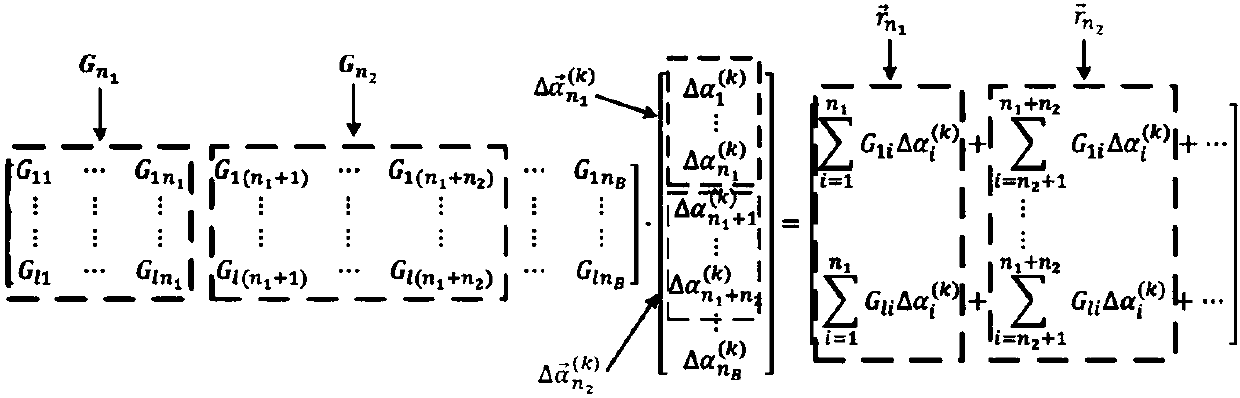
[0068] Such as figure 1 As shown, the present invention calculates the initial gradient in the algorithm middle The inner loop calculates the matrix z (k’) , the outer loop calculates the gradient increment The process is parallelized and distributed to multiple processors, which will greatly reduce the time of matrix operations in each iteration process. In addition, other parts of the algorithm are still serialized operations, including gradient projection and working set. update etc. According to Amdahl's law, the speedup ratio of the parallelized algorithm is not only related to the speedup ratio of the parallelizable part, but also related to the proportion of the parallelizable part. Therefore, as the training data increases, the proportion of computing time of the parallelizable part increases. , the overall speedup of the algorithm will gradually approach t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com