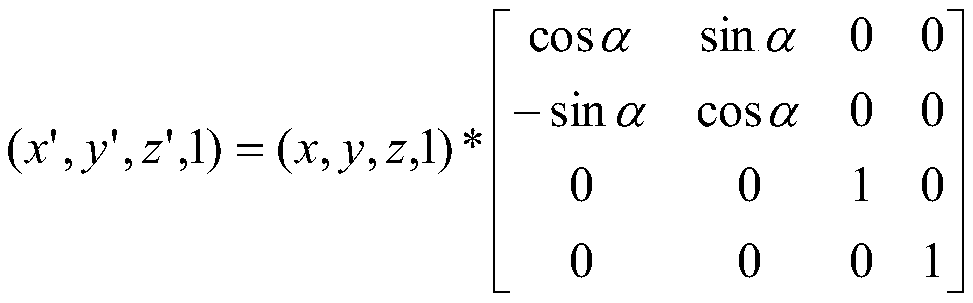Automatic tree classification method based on laser scanning 3D point cloud based on deep learning
A deep learning and laser scanning technology, applied in neural learning methods, 3D image processing, instruments, etc., can solve problems such as insufficient use of information, inability to measure, single projection angle, etc., to reduce training time and overcome the number of samples. The effect of less and better training
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
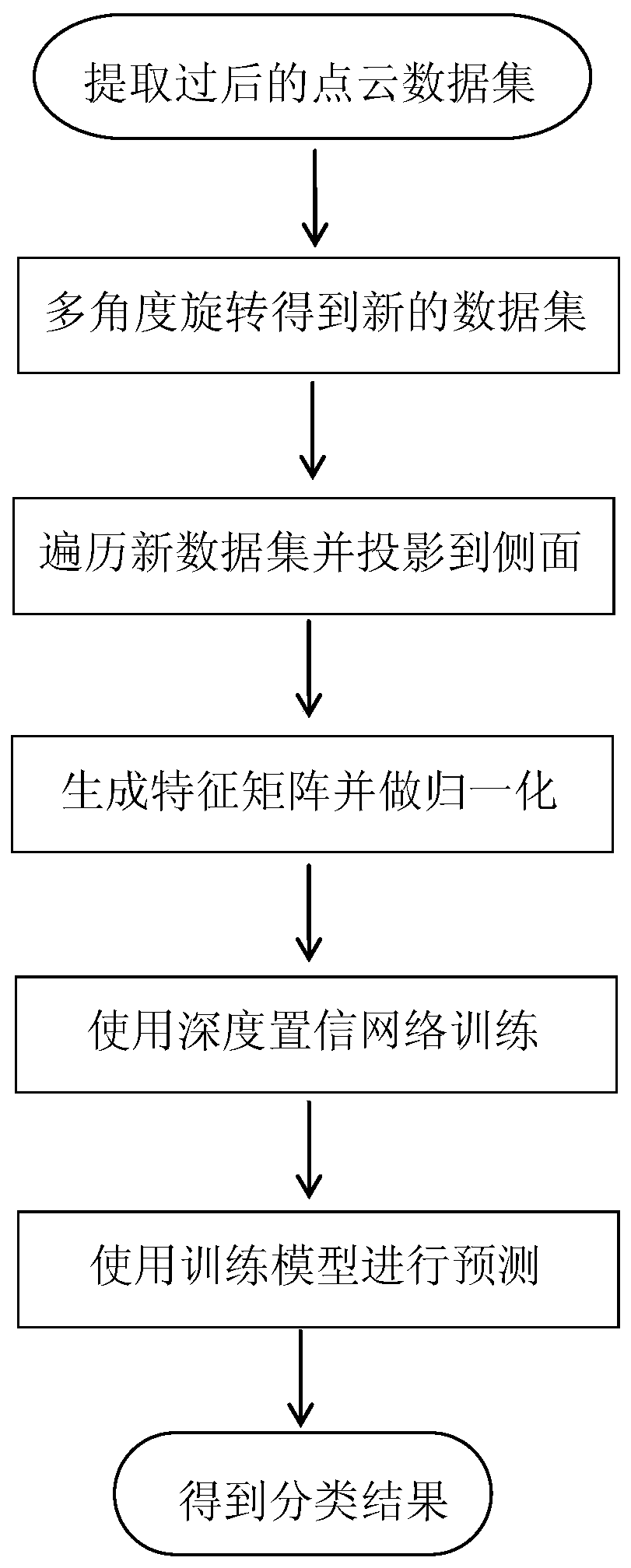
[0047] Such as figure 1 Shown is a schematic flow sheet of the present invention, and the present invention comprises the following steps:
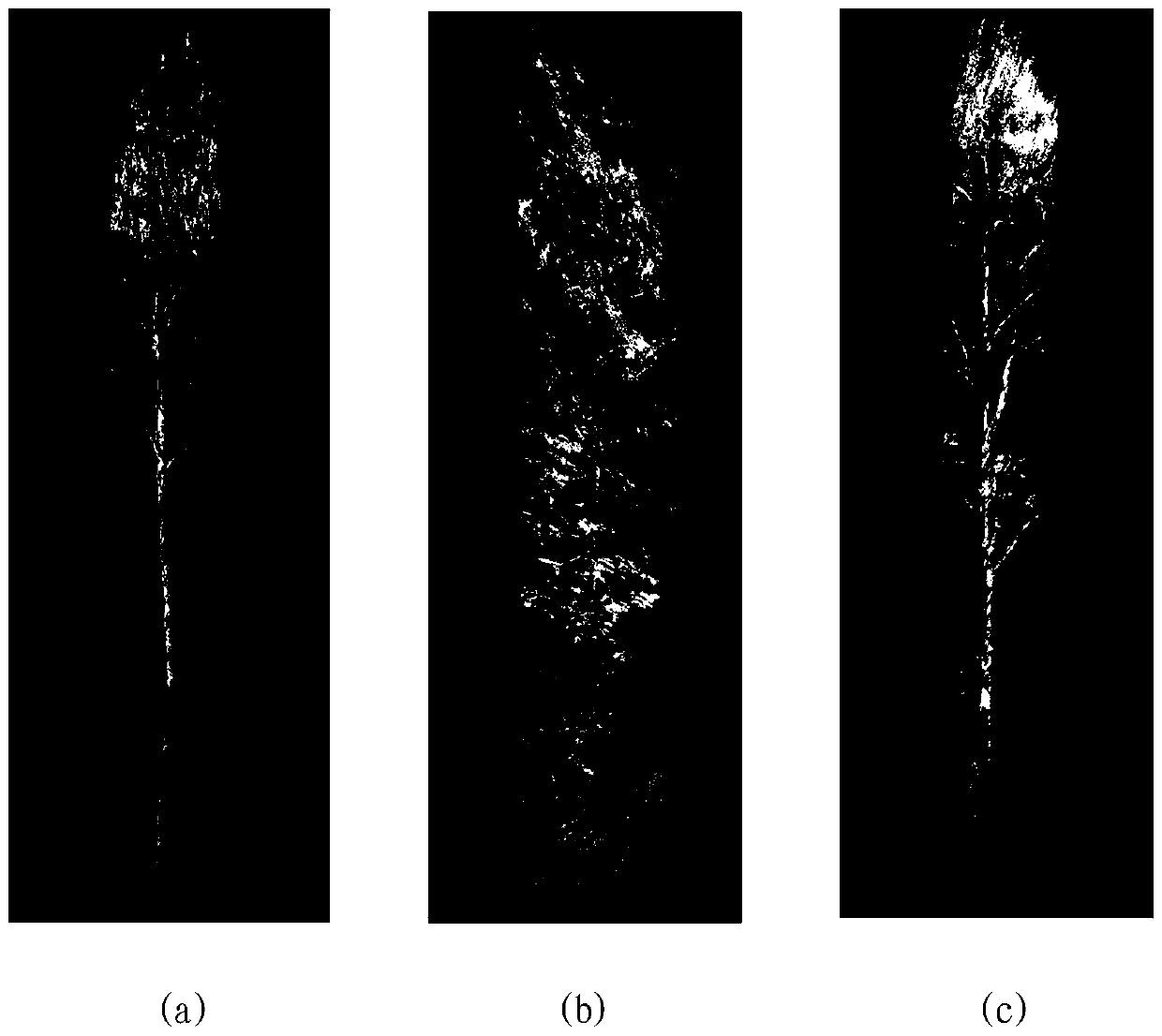
[0048] S1. In the XYZ three-dimensional coordinate system, rotate each sample in the original single tree point cloud set P around the Z axis at a certain angle, and keep the result after each rotation as a new single tree point cloud sample. After the data set is rotated, a new single tree point cloud set P' is obtained;
[0049] Input the original single tree point cloud set P, set the point of each sample as p i =[x i ,y i ,z i ], keeping the coordinates in the Z direction unchanged, multiplying the coordinates in the X and Y directions by the rotation matrix to get the rotated coordinates p' i =[x' i ,y' i ,z' i ], the rotation matrix is,
[0050]
[0051] Where α is the angle of rotation, then the change of coordinates of each point is x' i =x i *cosα-y i *sinα,y' i =y i *cosα+x i *sinα, z' i =z i , rotate each sa...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com