Small-current grounding fault positioning method employing transient zero sequence current
A technology of small current grounding and zero-sequence current, which is applied in the direction of fault location and fault detection according to conductor type, can solve problems such as power system hazards, phase-to-phase short-circuit faults, and inability to operate for a long time. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0042] The present invention will be further described below in conjunction with the accompanying drawings and embodiments.
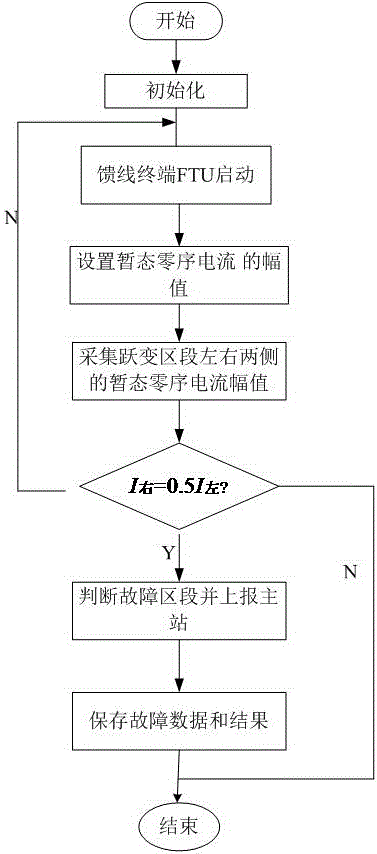
[0043] This embodiment provides a method for locating ground faults using transient zero-sequence currents and small currents, such as figure 1 shown, including the following steps:
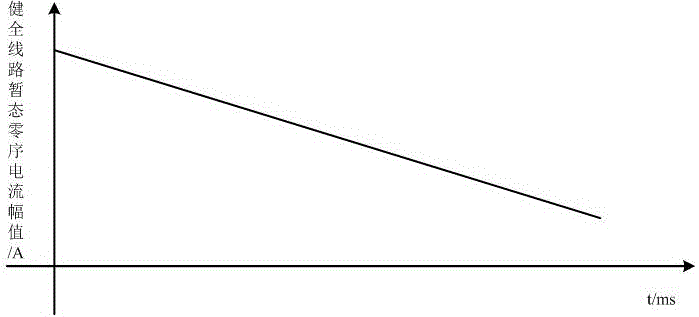
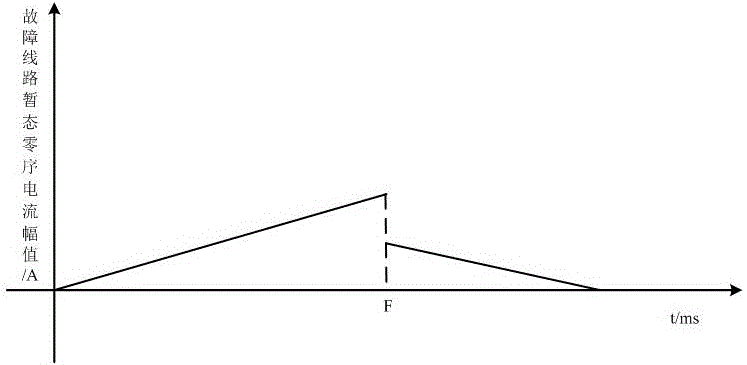
[0044]Step S1: Collect the transient zero-sequence current of each detection point on each line at the exit of the busbar. When the line fails, the transient zero-sequence current changes suddenly;
[0045] Step S2: Calculate the amplitude of the transient zero-sequence current at each detection point on each line, and select at least three lines with the largest amplitude of the transient zero-sequence current;
[0046] Step S3: Locate the small current grounding fault according to the variation of the transient zero-sequence current amplitude of each detection point on the line selected in the step S2.
[0047] In this embodiment, the step S1 specifically includes the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com